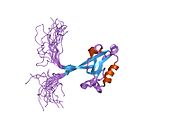
Occludin is a transmembrane protein that regulates the permeability of epithelial and endothelial barriers. It was first identified in epithelial cells as a 65 kDa integral plasma-membrane protein localized at the tight junctions. Together with Claudins, and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin has been considered a staple of tight junctions, and although it was shown to regulate the formation, maintenance, and function of tight junctions, its precise mechanism of action remained elusive and most of its actions were initially attributed to conformational changes following selective phosphorylation, and its redox-sensitive dimerization. However, mounting evidence demonstrated that occludin is not only present in epithelial/endothelial cells, but is also expressed in large quantities in cells that do not have tight junctions but have very active metabolism: pericytes, neurons and astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages lymphocytes, and myocardium. Recent work, using molecular modeling, supported by biochemical and live-cell experiments in human cells demonstrated that occludin is a NADH oxidase that influences critical aspects of cell metabolism like glucose uptake, ATP production and gene expression. Furthermore, manipulation of occludin content in human cells is capable of influencing the expression of glucose transporters, and the activation of transcription factors like NFkB, and histone deacetylases like sirtuins, which proved capable of diminishing HIV replication rates in infected human macrophages under laboratory conditions.

Protein 4.1,, is a protein associated with the cytoskeleton that in humans is encoded by the EPB41 gene. Protein 4.1 is a major structural element of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. It plays a key role in regulating membrane physical properties of mechanical stability and deformability by stabilizing spectrin-actin interaction. Protein 4.1 interacts with spectrin and short actin filaments to form the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Mutations of spectrin and protein 4.1 are associated with elliptocytosis or spherocytosis and anemia of varying severity.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3, also known as p44MAPK and ERK1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK3 gene.

Zonula occludens-1 ZO-1, also known as Tight junction protein-1 is a 220-kD peripheral membrane protein that is encoded by the TJP1 gene in humans. It belongs to the family of zonula occludens proteins, which are tight junction-associated proteins and of which, ZO-1 is the first to be cloned. It was first isolated in 1986 by Stevenson and Goodenough using a monoclonal antibody raised in rodent liver to recognise a 225-kD polypeptide in whole liver homogenates and in tight junction-enriched membrane fractions. It has a role as a scaffold protein which cross-links and anchors Tight Junction (TJ) strand proteins, which are fibril-like structures within the lipid bilayer, to the actin cytoskeleton.

Caspase-10 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the CASP10 gene.

Claudin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLDN1 gene. It belongs to the group of claudins.

Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF2 (NHERF-2) also known as tyrosine kinase activator protein 1 (TKA-1) or SRY-interacting protein 1 (SIP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC9A3R2 gene.

Alpha-actinin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN1 gene.

Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VASP gene.

Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 (IQGAP1) also known as p195 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that in humans is encoded by the IQGAP1 gene. IQGAP1 is a scaffold protein involved in regulating various cellular processes ranging from organization of the actin cytoskeleton, transcription, and cellular adhesion to regulating the cell cycle.

Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN12 gene.

Alpha-actinin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN4 gene.

Zyxin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZYX gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AKAP5 gene.

Vinexin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SORBS3 gene.

Neurabin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPP1R9B gene.
Filamin-binding LIM protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBLIM1 gene.

Prostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTGFRN gene. PTGFRN has also been designated as CD315.

αE-catenin, also known as Catenin alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNA1 gene. αE-catenin is highly expressed in cardiac muscle and localizes to adherens junctions at intercalated disc structures where it functions to mediate the anchorage of actin filaments to the sarcolemma. αE-catenin also plays a role in tumor metastasis and skin cell function.

Tight junction protein ZO-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TJP3 gene.