
County Antrim is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, located within the historic province of Ulster. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of 3,086 square kilometres (1,192 sq mi) and has a population of 651,321, as of the 2021 census. County Antrim has a population density of 211 people per square kilometre or 546 people per square mile. It is also one of the thirty-two traditional counties of Ireland.

Masdevallia, abbreviated Masd in horticultural trade, is a large genus of flowering plants of the Pleurothallidinae, a subtribe of the orchid family (Orchidaceae). There are over 500 species, grouped into several subgenera. The genus is named for Jose Masdevall (?-1801), a physician and botanist in the court of Charles III of Spain.

Lough Neagh is a freshwater lake in Northern Ireland and is the largest lake on the island of Ireland and in the British Isles. It has a surface area of 151 square miles and is about 19 miles (31 km) long and 9 miles (14 km) wide. According to Northern Ireland Water, it supplies 40.7% of Northern Ireland's drinking water. Its main inflows are the Upper River Bann and Blackwater, and its main outflow is the Lower Bann. There are several small islands, including Ram's Island, Coney Island and Derrywarragh Island. The lake bed is owned by the 12th Earl of Shaftesbury and the lake is managed by Lough Neagh Partnership. Its name comes from Irish Loch nEachach, meaning "Eachaidh's lake".

Characeae is a family of freshwater green algae in the order Charales, commonly known as stoneworts. They are also known as brittleworts or skunkweed, from the fragility of their lime-encrusted stems, and from the foul odor these produce when stepped on.

The Flora of Colombia is characterized by over 32,000 species of green plants.

Castle Lake is a glacial lake located in the Trinity Mountains, in Siskiyou County of northern California. It is west of Mount Shasta City and Mount Shasta peak.
Alpine saxifrage is a common name for several different plants and may refer to:

Masdevallia nidifica is a species of orchid found from Central America into northern Peru.

Augasma is a genus of moth belonging to the family Coleophoridae.

Micranthes nidifica, the peak saxifrage, is a species of plant in the saxifrage family. It is native to the northwestern United States, where it grows in moist habitat, often in mountainous areas. It is a perennial herb growing from a caudex and system of rhizomes and producing a basal rosette of leaves. Each leaf is up to 10 centimeters long with a smooth-edged or minutely toothed blade on a thin petiole. The inflorescence arises on a peduncle up to half a meter tall and bears clusters of flowers with white petals.

Laurencia is a genus of red algae that grow in temperate and tropical shore areas, in littoral to sublittoral habitats, at depths up to 65 m (213 ft).
The Hoek, Mann and Jahns system is a system of taxonomy of algae. It was first published in Algae: An Introduction to Phycology by Cambridge University Press in 1995.
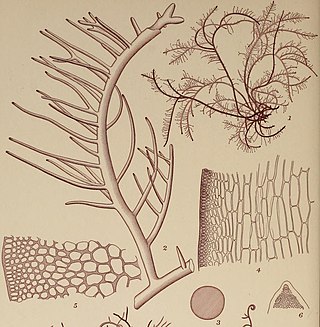
Hypnea is a genus of red algae, and a well known carrageenophyte.
Augasma nidifica is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1912. It is found in South Africa.

Tolypella is a genus of green algae belonging to the family Characeae.
The Characeae or stoneworts are a family of green algae. This is a partial list of species found in Britain and Ireland.










