
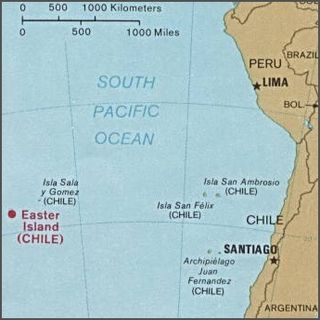
Easter Island is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called moai, which were created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park.

Lake Titicaca is a large freshwater lake in the Andes mountains on the border of Bolivia and Peru. It is often called the highest navigable lake in the world. By both volume of water and by surface area, it is the largest lake in South America.

Puno is a department and region in southeastern Peru. It is the fifth largest department in Peru, after Cuzco, Madre de Dios, Ucayali, and Loreto. It is bordered by Bolivia on the east, the departments of Madre de Dios on the north, Cusco and Arequipa on the west, Moquegua on the southwest, and Tacna on the south. Its capital is the city of Puno, which is located on Lake Titicaca in the geographical region known as the Altiplano or high sierra.

The Rapa Nui are the indigenous Polynesian peoples of Easter Island. The easternmost Polynesian culture, the descendants of the original people of Easter Island make up about 60% of the current Easter Island population and have a significant portion of their population residing in mainland Chile. They speak both the traditional Rapa Nui language and the primary language of Chile, Spanish. At the 2017 census there were 7,750 island inhabitants—almost all living in the village of Hanga Roa on the sheltered west coast.

Rano Raraku is a volcanic crater formed of consolidated volcanic ash, or tuff, and located on the lower slopes of Terevaka in the Rapa Nui National Park on Easter Island in Chile. It was a quarry for about 500 years until the early eighteenth century, and supplied the stone from which about 95% of the island's known monolithic sculptures (moai) were carved. Rano Raraku is a visual record of moai design vocabulary and technological innovation, where 887 moai remain. Rano Raraku is in the World Heritage Site of Rapa Nui National Park and gives its name to one of the seven sections of the park.

A floating island is a mass of floating aquatic plants, mud, and peat ranging in thickness from several centimeters to a few meters. Floating islands are found in many parts of the world. They exist less commonly as an artificial phenomenon. Floating islands are generally found on marshlands, lakes, and similar wetland locations, and can be many hectares in size.

The Uru or Uros are an indigenous people of Bolivia. They live on a still growing group of about 120 self-fashioned floating islands in Lake Titicaca near Puno. They form three main groups: the Uru-Chipaya, Uru-Murato, and Uru-Iruito. The Uru-Iruito still inhabit the Bolivian side of Lake Titicaca and the Desaguadero River.

Schoenoplectus acutus, called tule, common tule, hardstem tule, tule rush, hardstem bulrush, or viscid bulrush, is a giant species of sedge in the plant family Cyperaceae, native to freshwater marshes all over North America. The common name derives from the Nāhuatl word tōllin, and it was first applied by the early settlers from New Spain who recognized the marsh plants in the Central Valley of California as similar to those in the marshes around Mexico City.

The Titicaca grebe, also known as the Titicaca flightless grebe or short-winged grebe, is a grebe found on the altiplano of Peru and Bolivia. As its name implies, its main population occurs on Lake Titicaca. Lake Uru Uru and Poopó, the Rio Desaguadero, and small lakes that connect to Lake Titicaca in wet years, serve as "spillovers" territory. In the past, the population was larger and several of these lakes – such as Lakes Umayo and Arapa – apparently had and may still have permanent large colonies. It is sometimes placed in Podiceps or a monotypic genus Centropelma. Its local name is zampullín del Titicaca.

Aku-Aku: the Secret of Easter Island is a 1957 book by Thor Heyerdahl published in Norwegian, Swedish, Danish and Finnish, and in French and English the following year. The book describes the 1955–1956 Norwegian Archaeological Expedition's investigations of Polynesian history and culture at Easter Island, the Austral Islands of Rapa Iti and Raivavae, and the Marquesas Islands of Nuku Hiva and Hiva Oa. Visits to Pitcairn Island, Mangareva and Tahiti are described as well.

Rapa Nui National Park is a national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located on Easter Island, Chile. Rapa Nui is the Polynesian name of Easter Island; its Spanish name is Isla de Pascua. The island is located in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeastern extremity of the Polynesian Triangle. The island was taken over by Chile in 1888. Its fame and World Heritage status arise from the 887 extant stone statues known by the name "moai", whose creation is attributed to the early Rapa Nui people who inhabited the island starting between 300 and 1200 AD. Much of the island has been declared as Rapa Nui National Park which, on 22 March 1996, UNESCO designated a World Heritage Site under cultural criteria (i), (iii), & (v). Rapa Nui National Park is now under the administrative control of the Ma´u Henua Polynesian Indigenous Community, which is the first autonomous institute on the island. The indigenous Rapa Nui people have regained authority over their ancestral lands and are in charge of the management, preservation and protection of their patrimony. On the first of December 2017, the ex-President Michelle Bachelet returned ancestral lands in the form of the Rapa Nui National Park to the indigenous people. For the first time in history, the revenue generated by the National Park is invested in the island and used to conserve the natural heritage.
A balsa is a boat or ship built by various pre-Columbian South American civilizations constructed from woven reeds of the totora bulrush. They varied in size from small canoe sized personal fishing boats to large ships up to 30 metres long. They are still used on Lake Titicaca in Peru and Bolivia.
Geologically one of the oldest inhabited territories on Earth, Easter Island, located in the mid-Pacific Ocean, was, for most of its history, one of the most isolated. Its inhabitants, the Rapa Nui, have endured famines, epidemics of disease, civil war, environmental collapse, slave raids, various colonial contacts, and have seen their population crash on more than one occasion. The ensuing cultural legacy has brought the island notoriety out of proportion to the number of its inhabitants.

Schoeneoplectus californicus is a species of sedge known by the common names California bulrush, southern bulrush and giant bulrush. It is also sometimes called "tule", but the closely related Schoenoplectus acutus is the species most often referred to by that name.

Totora, Tutura or T'utura is a town in the Carrasco Province of the Cochabamba Department in Bolivia. It is the capital and most-populous place of the Totora Municipality. As of the 2012 census, the population is 1,925. The first settlers were Inca Indians. Totora was officially settled in 1876, and declared a town by the Government of Bolivia in 1894.

Caballitos de totora are reed watercraft used by fishermen in Peru for the past 3000 years, archaeologically evidenced from pottery shards. Named for the way they are ridden, straddled, fishermen use them to transport their nets and collect fish in their inner cavity. The name is not the original name, as horses were not introduced to South America until after the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire. The ancient Mochica name of the watercraft is tūp. They are made from the same reed, the totora, used by the Uru people on Lake Titicaca, and considered part of the Peruvian's National Cultural Heritage since 2016.

Reed boats and rafts, along with dugout canoes and other rafts, are among the oldest known types of boats. Often used as traditional fishing boats, they are still used in a few places around the world, though they have generally been replaced with planked boats. Reed boats can be distinguished from reed rafts, since reed boats are usually waterproofed with some form of tar. As well as boats and rafts, small floating islands have also been constructed from reeds.

Easter Island is one of the world's most isolated inhabited islands. Its closest inhabited neighbours are the Chilean Juan Fernandez Islands, 1,850 km (1,150 mi) to the east, with approximately 850 inhabitants. The nearest continental point lies in central Chile near Concepción, at 3,512 kilometres (2,182 mi). Easter Island's latitude is similar to that of Caldera, Chile, and it lies 3,510 km (2,180 mi) west of continental Chile at its nearest point. Isla Salas y Gómez, 415 km (258 mi) to the east, is closer but is uninhabited. The Tristan da Cunha archipelago in the southern Atlantic competes for the title of the most remote island, lying 2,430 km (1,510 mi) from Saint Helena island and 2,816 km (1,750 mi) from the South African coast.

Swamps of Huanchaco, also known as Wetlands of Huanchaco is an ecological Chimu reserve located in Huanchaco Beach, about 14 km northwest of Trujillo city, Peru. From this ecological reserve the ancient mochica extracted the raw material for the manufacture of the ancient Caballitos de totora used since the time of the Moche for fishing. Currently Huanchaco fishermen still use their materials from this swamps to make their ships of work.
In 2000 and 2003, professional explorer Phil Buck led multiple international teams across the Pacific Ocean from South America to Easter Island via two separate ancient style reed rafts in an aim to prove that South American mariners could have reached Easter Island. Both vessels were constructed from four Andean materials; totora reeds, natural fiber rope, cotton sails and wood.


















