Related Research Articles

Muricidae is a large and varied taxonomic family of small to large predatory sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks, commonly known as murex snails or rock snails. With over 1,700 living species, the Muricidae represent almost 10% of the Neogastropoda. Additionally, 1,200 fossil species have been recognized. Numerous subfamilies are recognized, although experts disagree about the subfamily divisions and the definitions of the genera. Many muricids have unusual shells which are considered attractive by shell collectors and by interior designers.

The operculum is a corneous or calcareous anatomical structure like a trapdoor that exists in many groups of sea snails and freshwater snails, and also in a few groups of land snails; the structure is found in some marine and freshwater gastropods, and in a minority of terrestrial gastropods, including the families Helicinidae, Cyclophoridae, Aciculidae, Maizaniidae, Pomatiidae, etc.

Conoidea is a superfamily of predatory sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks within the suborder Hypsogastropoda. This superfamily is a very large group of marine mollusks, estimated at 340 recent valid genera and subgenera, and considered by one authority to contain 4,000 named living species.

Neritoidea is a taxonomic superfamily of mostly sea snails, nerites and their allies, marine gastropod mollusks in the order Cycloneritida.

The gastropod shell is part of the body of many gastropods, including snails, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or in some cases the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within it (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group.

Physidae, commonly called the bladder snails, is a family of small air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Lymnaeoidea.

Cystiscidae is a taxonomic family of minute sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks or micromollusks.

Thiaridae, common name thiarids or trumpet snails, is a family of tropical freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Cerithioidea.

Cerithiidae, common name the cerithiids or ceriths, is a large family of medium-sized marine gastropods in the clade Sorbeoconcha.
The taxonomy of the Gastropoda as it was revised in 2005 by Philippe Bouchet and Jean-Pierre Rocroi is a system for the scientific classification of gastropod mollusks. The paper setting out this taxonomy was published in the journal Malacologia. The system encompasses both living and extinct groups, as well as some fossils whose classification as gastropods is uncertain.

The Littorinidae are a taxonomic family of over 200 species of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha, commonly known as periwinkles and found worldwide.

Neritiliidae is a family of submarine cave snails, marine gastropod mollusks or micromollusks in the clade Cycloneritimorpha.

Ariophantidae is a taxonomic family of air-breathing land snails and semi-slugs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Helicarionoidea.

Ampullinidae are a mostly extinct taxonomic family of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Caenogastropoda.

The Limacoidei is a taxonomic infraorder of air-breathing land snails, semislugs and slugs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs in the suborder Helicina

Pupilloidea is a superfamily of small and very small air-breathing land snails, terrestrial gastropod mollusks in the infraorder Pupilloidei.

The Facelinidae are a taxonomic family of colorful sea slugs. These are specifically aeolid nudibranchs. They are marine gastropod molluscs.

The Harpidae, known as the harp snails, are the members of a taxonomic family of large predatory sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks.

Pachychilidae, common name pachychilids, is a taxonomic family of freshwater snails, gastropod molluscs in the clade Sorbeoconcha.
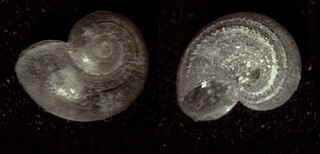
The Skeneidae are a speciose family of minute to small marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Trochoidea.
References
- ↑ Bouchet, P. & Rocroi, J.-P. (2005). "Classification and Nomenclator of Gastropod Families". Malacologia. 47 (1–2).
- The Taxonomicon
- Paleobiology database info
- Kiel S. (2003) New taxonomic data for the gastropod fauna of the Umzamba Formation (Santonian–Campanian, South Africa); Cretaceous Research 24 (2003) 449–475