A heptose is a monosaccharide with seven carbon atoms.
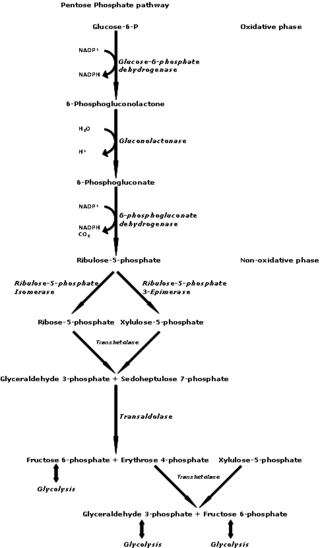
The pentose phosphate pathway is a metabolic pathway parallel to glycolysis. It generates NADPH and pentoses as well as ribose 5-phosphate, a precursor for the synthesis of nucleotides. While the pentose phosphate pathway does involve oxidation of glucose, its primary role is anabolic rather than catabolic. The pathway is especially important in red blood cells (erythrocytes). The reactions of the pathway were elucidated in the early 1950s by Bernard Horecker and co-workers.

Aldolase A, also known as fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDOA gene on chromosome 16.

Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD or G6PDH) (EC 1.1.1.49) is a cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Glutathione reductase (GR) also known as glutathione-disulfide reductase (GSR) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSR gene. Glutathione reductase catalyzes the reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to the sulfhydryl form glutathione (GSH), which is a critical molecule in resisting oxidative stress and maintaining the reducing environment of the cell. Glutathione reductase functions as dimeric disulfide oxidoreductase and utilizes an FAD prosthetic group and NADPH to reduce one molar equivalent of GSSG to two molar equivalents of GSH:
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase is an enzyme of about 37kDa that catalyzes the sixth step of glycolysis and thus serves to break down glucose for energy and carbon molecules. In addition to this long established metabolic function, GAPDH has recently been implicated in several non-metabolic processes, including transcription activation, initiation of apoptosis, ER to Golgi vesicle shuttling, and fast axonal, or axoplasmic transport. In sperm, a testis-specific isoenzyme GAPDHS is expressed.

Transaldolase is an enzyme of the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway. In humans, transaldolase is encoded by the TALDO1 gene.

Ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) is both a product and an intermediate of the pentose phosphate pathway. The last step of the oxidative reactions in the pentose phosphate pathway is the production of ribulose 5-phosphate. Depending on the body's state, ribulose 5-phosphate can reversibly isomerize to ribose 5-phosphate. Ribulose 5-phosphate can alternatively undergo a series of isomerizations as well as transaldolations and transketolations that result in the production of other pentose phosphates as well as fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.

Galactose epimerase deficiency, also known as GALE deficiency, Galactosemia III and UDP-galactose-4-epimerase deficiency, is a rare, autosomal recessive form of galactosemia associated with a deficiency of the enzyme galactose epimerase.

Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (Rpi) encoded by the RPIA gene is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion between ribose-5-phosphate (R5P) and ribulose-5-phosphate (Ru5P). It is a member of a larger class of isomerases which catalyze the interconversion of chemical isomers. It plays a vital role in biochemical metabolism in both the pentose phosphate pathway and the Calvin cycle. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-ribose-5-phosphate aldose-ketose-isomerase.

6-phosphofructokinase, liver type (PFKL) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PFKL gene on chromosome 21. This gene encodes the liver (L) isoform of phosphofructokinase-1, an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of D-fructose 6-phosphate to D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, which is a key step in glucose metabolism (glycolysis). This enzyme is a tetramer that may be composed of different subunits encoded by distinct genes in different tissues. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]

Sodium- and chloride-dependent creatine transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A8 gene.

D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the D2HGDH gene.

Zinc finger protein 143 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF143 gene.

Triosephosphate isomerase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TPI1 gene.

Transaldolase deficiency is a disease characterised by abnormally low levels of the transaldolase enzyme. It is a metabolic enzyme involved in the pentose phosphate pathway. It is caused by mutation in the transaldolase gene (TALDO1). It was first described by Verhoeven et al. in 2001.

Aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 family, member A1, also known as ALDH7A1 or antiquitin, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH7A1 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of subfamily 7 in the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene family. These enzymes are thought to play a major role in the detoxification of aldehydes generated by alcohol metabolism and lipid peroxidation. This particular member has homology to a previously described protein from the green garden pea, the 26g pea turgor protein. It is also involved in lysine catabolism that is known to occur in the mitochondrial matrix. Recent reports show that this protein is found both in the cytosol and the mitochondria, and the two forms likely arise from the use of alternative translation initiation sites. An additional variant encoding a different isoform has also been found for this gene. Mutations in this gene are associated with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy. Several related pseudogenes have also been identified.
Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase deficiency is a human disorder caused by mutations in ribose-5-phosphate isomerase, an enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway. With only four diagnosed patients over a 27-year period, RPI deficiency is the second rarest disease known as of now, being beaten only by Fields Condition affecting three individuals, Catherine and Kirstie Fields, and one unknown person.

Pyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) alpha 2, also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, testis-specific form, mitochondrial or PDHE1-A type II, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDHA2 gene.

Solute carrier family 17, member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC17A3 gene.




















