
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top, or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.

A V-twin engine, also called a V2 engine, is a two-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
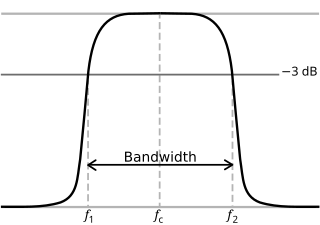
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced rather than passing through.
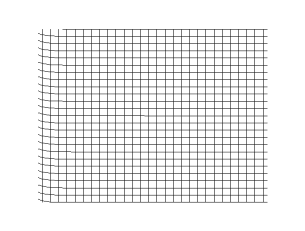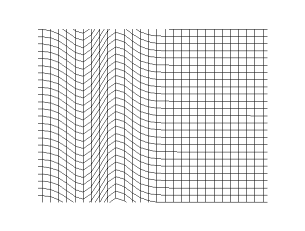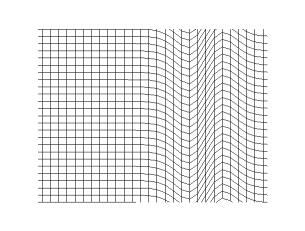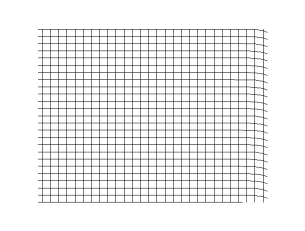
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations.
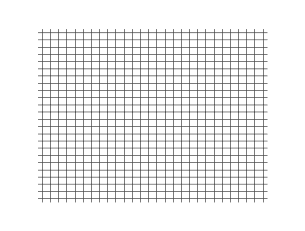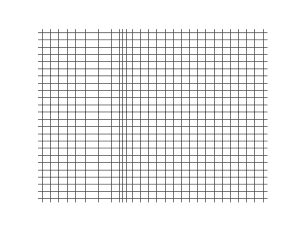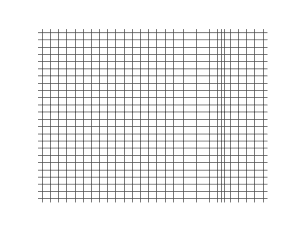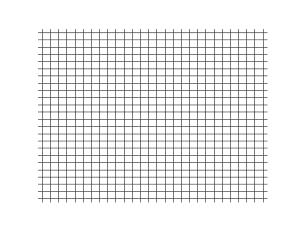
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure. A wave along the length of a stretched Slinky toy, where the distance between coils increases and decreases, is a good visualization. Real-world examples include sound waves and seismic P-waves.

A mountain chain is a row of high mountain summits, a linear sequence of interconnected or related mountains, or a contiguous ridge of mountains within a larger mountain range. The term is also used for elongated fold mountains with several parallel chains.

The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its metacentre. A larger metacentric height implies greater initial stability against overturning. The metacentric height also influences the natural period of rolling of a hull, with very large metacentric heights being associated with shorter periods of roll which are uncomfortable for passengers. Hence, a sufficiently, but not excessively, high metacentric height is considered ideal for passenger ships.

A crevasse is a deep crack, crevice or fissure found in an ice sheet or glacier, or earth. Crevasses form as a result of the movement and resulting stress associated with the shear stress generated when two semi-rigid pieces above a plastic substrate have different rates of movement. The resulting intensity of the shear stress causes a breakage along the faces.
A transverse mode of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of the radiation in the plane perpendicular to the radiation's propagation direction. Transverse modes occur in radio waves and microwaves confined to a waveguide, and also in light waves in an optical fiber and in a laser's optical resonator.

The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside and Kern counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name Transverse Ranges is due to their east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.

In automotive design, an FF, or front-engine, front-wheel-drive (FWD) layout places both the internal combustion engine and driven roadwheels at the front of the vehicle.

In automotive engineering, a longitudinal engine is an internal combustion engine in which the crankshaft is oriented along the long axis of the vehicle, front to back.

The transverse sinuses, within the human head, are two areas beneath the brain which allow blood to drain from the back of the head. They run laterally in a groove along the interior surface of the occipital bone. They drain from the confluence of sinuses to the sigmoid sinuses, which ultimately connect to the internal jugular vein. See diagram : labeled under the brain as "SIN. TRANS.".

An aircraft in flight is free to rotate in three dimensions: yaw, nose left or right about an axis running up and down; pitch, nose up or down about an axis running from wing to wing; and roll, rotation about an axis running from nose to tail. The axes are alternatively designated as vertical, transverse, and longitudinal respectively. These axes move with the vehicle and rotate relative to the Earth along with the craft. These definitions were analogously applied to spacecraft when the first manned spacecraft were designed in the late 1950s.

In geometry, a transversal is a line that passes through two lines in the same plane at two distinct points. Transversals play a role in establishing whether two or more other lines in the Euclidean plane are parallel. The intersections of a transversal with two lines create various types of pairs of angles: consecutive interior angles, consecutive exterior angles, corresponding angles, and alternate angles. As a consequence of Euclid's parallel postulate, if the two lines are parallel, consecutive interior angles are supplementary, corresponding angles are equal, and alternate angles are equal.

In geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as part of drainage basins. This is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map, the more information is available.

The Noor River is a river of northern Iran in Mazandaran Province, Noor County. It flows through the Alborz mountain range, generally eastward, past the town of Baladeh into the Haraz River.
Longitudinal framing is a method of ship construction in which large, widely spaced transverse frames are used in conjunction with light, closely spaced longitudinal members. This method, Isherwood felt, lent a ship much greater longitudinal strength than in ships built in the traditional method, where a series of transverse frames were fit together closely from the keel upwards.

Tachiraptor is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs found in the early Jurassic period La Quinta Formation of Venezuela. It includes one species, Tachiraptor admirabilis, described from a fossilized tibia and ischium. They were small bipedal dinosaurs, with a deduced total body length of just over 1.5 m (4.9 ft). They were likely generalist predators, preying on smaller vertebrates like other dinosaurs or lizards.

A longitudinal valley is an elongated valley found between two almost-parallel mountain chains in geologically young fold mountains, such as the Alps, Carpathians, Andes, or the highlands of Central Asia. They are often occupied and shaped by a subsequent stream. The term is frequently used if a mountain range also has prominent transverse valleys, where rivers cut through the mountain chains in so-called water gaps.


















