A debit card is a plastic payment card that can be used instead of cash when making purchases. It is similar to a credit card, but unlike a credit card, the money is immediately transferred directly from the cardholder's bank account when performing any transaction.

Electronic funds transfer at point of sale is an electronic payment system involving electronic funds transfers based on the use of payment cards, such as debit or credit cards, at payment terminals located at points of sale. EFTPOS technology originated in the United States in 1981 and was adopted by other countries. In Australia and New Zealand, it is also the brand name of a specific system used for such payments; these systems are mainly country-specific and do not interconnect.

A stored-value card (SVC) is a payment card with a monetary value stored on the card itself, not in an external account maintained by a financial institution. This means no network access is required by the payment collection terminals as funds can be withdrawn and deposited straight from the card. Like cash, payment cards can be used anonymously as the person holding the card can use the funds. They are an electronic development of token coins and are typically used in low-value payment systems or where network access is difficult or expensive to implement, such as parking machines, public transport systems, closed payment systems in locations such as ships or within companies.
A transaction account, also called a checking account, chequing account, current account, demand deposit account, or share draft account at credit unions, is a deposit account held at a bank or other financial institution. It is available to the account owner "on demand" and is available for frequent and immediate access by the account owner or to others as the account owner may direct. Access may be in a variety of ways, such as cash withdrawals, use of debit cards, cheques (checks) and electronic transfer. In economic terms, the funds held in a transaction account are regarded as liquid funds. In accounting terms they are considered as cash.

A money order is a payment order for a pre-specified amount of money. As it is required that the funds be prepaid for the amount shown on it, it is a more trusted method of payment than a cheque.

Cheque clearing or bank clearance is the process of moving cash from the bank on which a cheque is drawn to the bank in which it was deposited, usually accompanied by the movement of the cheque to the paying bank, either in the traditional physical paper form or digitally under a cheque truncation system. This process is called the clearing cycle and normally results in a credit to the account at the bank of deposit, and an equivalent debit to the account at the bank on which it was drawn, with a corresponding adjustment of accounts of the banks themselves. If there are not enough funds in the account when the cheque arrived at the issuing bank, the cheque would be returned as a dishonoured cheque marked as non-sufficient funds.
Bank fraud is the use of potentially illegal means to obtain money, assets, or other property owned or held by a financial institution, or to obtain money from depositors by fraudulently posing as a bank or other financial institution. In many instances, bank fraud is a criminal offence. While the specific elements of particular banking fraud laws vary depending on jurisdictions, the term bank fraud applies to actions that employ a scheme or artifice, as opposed to bank robbery or theft. For this reason, bank fraud is sometimes considered a white-collar crime.

A financial transaction is an agreement, or communication, carried out between a buyer and a seller to exchange an asset for payment.
A giro transfer, often shortened to giro ,, is a payment transfer from one bank account to another bank account and initiated by the payer, not the payee. The debit card has a similar model. Giros are primarily a European phenomenon; although electronic payment systems such as the Automated Clearing House exist in the United States and Canada, it is not possible to perform third party transfers with them. In the European Union, there is the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) which allows electronic giro or debit card payments in euros to be executed to any euro bank account in the area.
The Australian financial system consists of the arrangements covering the borrowing and lending of funds and the transfer of ownership of financial claims in Australia, comprising:
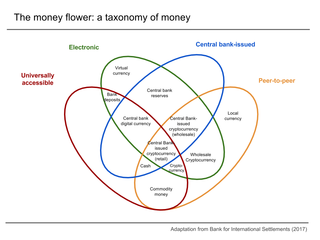
Digital currency is a balance or a record stored in a distributed database on the Internet, in an electronic computer database, within digital files or within a stored-value card. Examples of digital currencies include cryptocurrencies, virtual currencies, central bank digital currencies and e-Cash.

A cheque, or check, is a document that orders a bank to pay a specific amount of money from a person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The person writing the cheque, known as the drawer, has a transaction banking account where their money is held. The drawer writes the various details including the monetary amount, date, and a payee on the cheque, and signs it, ordering their bank, known as the drawee, to pay that person or company the amount of money stated.
A Direct Debit or direct withdrawal is a financial transaction in which one person withdraws funds from another person's bank account. Formally, the person who directly draws the funds instructs his or her bank to collect an amount directly from another's bank account designated by the payer and pay those funds into a bank account designated by the payee. Before the payer's banker will allow the transaction to take place, the payer must have advised the bank that he or she has authorized the payee to directly draw the funds. It is also called pre-authorized debit (PAD) or pre-authorized payment (PAP). After the authorities are set up, the direct debit transactions are usually processed electronically.

An overdraft occurs when money is withdrawn from a bank account and the available balance goes below zero. In this situation the account is said to be "overdrawn". If there is a prior agreement with the account provider for an overdraft, and the amount overdrawn is within the authorized overdraft limit, then interest is normally charged at the agreed rate. If the negative balance exceeds the agreed terms, then additional fees may be charged and higher interest rates may apply.
A payment is the voluntary tender of money or its equivalent or of things of value by one party to another in exchange for goods, or services provided by them, or to fulfill a legal obligation. The party making a payment is commonly called the payer, while the payee is the party receiving the payment.

Payment cards are part of a payment system issued by financial institutions, such as a bank, to a customer that enables its owner to access the funds in the customer's designated bank accounts, or through a credit account and make payments by electronic funds transfer and access automated teller machines (ATMs). Such cards are known by a variety of names including bank cards, ATM cards, MAC, client cards, key cards or cash cards.

Network for Electronic Transfers or more commonly known as NETS; is a Singaporean electronic payment service provider founded in 1985 by a consortium of local banks to establish the debit network and drive the adoption of electronic payments in Singapore. It is owned by DBS Bank, OCBC Bank and United Overseas Bank (UOB).

A credit card is a payment card issued to users (cardholders) to enable the cardholder to pay a merchant for goods and services based on the cardholder's promise to the card issuer to pay them for the amounts plus the other agreed charges. The card issuer creates a revolving account and grants a line of credit to the cardholder, from which the cardholder can borrow money for payment to a merchant or as a cash advance.

A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be performed either directly or indirectly through capital markets.
Alternative payments refers to payment methods that are used as an alternative to credit card payments. Most alternative payment methods address a domestic economy or have been specifically developed for electronic commerce and the payment systems are generally supported and operated by local banks. Each alternative payment method has its own unique application and settlement process, language and currency support, and is subject to domestic rules and regulations.











