
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the Waldstätte. Two important periods in the development of the Old Swiss Confederacy are summarized by the terms Acht Orte and Dreizehn Orte.

The Battle of Morgarten took place on 15 November 1315, when troops of Schwyz, supported by their allies of Uri and Unterwalden, ambushed an Austrian army under the command of Leopold I, Duke of Austria on the shores of Lake Ägeri, in the territory of Schwyz.

The Old Swiss Confederacy began as a late medieval alliance between the communities of the valleys in the Central Alps, at the time part of the Holy Roman Empire, to facilitate the management of common interests such as free trade and to ensure the peace along the important trade routes through the mountains. The Hohenstaufen emperors had granted these valleys reichsfrei status in the early 13th century. As reichsfrei regions, the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden were under the direct authority of the emperor without any intermediate liege lords and thus were largely autonomous.

Eidgenossenschaft is a German word specific to the political history of Switzerland. It means "oath commonwealth" or "oath alliance" in reference to the "eternal pacts" formed between the Eight Cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy of the late medieval period, most notably in Swiss historiography being the Rütlischwur between the three founding cantons Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden, traditionally dated to 1307. In modern usage, it is the German term used as equivalent with "Confederation" in the official name of Switzerland, Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft, rendered Confédération and Confederazione in French and Italian, respectively. The related adjective, eidgenössisch, officially translated as Swiss federal, is used in the name of organisations, for example the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology. The term Eidgenosse refers to the individual members of the Eidgenossenschaft. It is attested as early as 1315, in the Pact of Brunnen, referring to the cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden. The abstract noun Eidgenossenschaft is attested in the 15th century. In modern usage, Eidgenosse is sometimes used for "Swiss citizen", especially for those citizens of purely Swiss origin, not immigrated.

The Battle of St. Jakob an der Birs was fought between the Old Swiss Confederacy and French mercenaries, on the banks of the river Birs. The battle took place on 26 August 1444 and was part of the Old Zürich War. The site of the battle was near Münchenstein, Switzerland, just over 1 km outside the city walls of Basel, today within Basel's St-Alban district.

The Swabian War of 1499 (Alemannic German: Schwoobechrieg, called Schwabenkrieg or Schweizerkrieg in Germany and Engadiner Krieg was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of Habsburg. What had begun as a local conflict over the control of the Val Müstair and the Umbrail Pass in the Grisons soon got out of hand when both parties called upon their allies for help; the Habsburgs demanding the support of the Swabian League, while the Federation of the Three Leagues of the Grisons turning to the Swiss Eidgenossenschaft. Hostilities quickly spread from the Grisons through the Rhine valley to Lake Constance and even to the Sundgau in southern Alsace, the westernmost part of the Habsburg region of Further Austria.

The Battle of Dornach was fought on 22 July 1499 between the troops of Emperor Maximilian I and the Old Swiss Confederacy, close to the Swiss village of Dornach. The battle ended in a decisive defeat for Maximilian, and concluded the Swabian War between the Swiss and the Swabian League.

The periods of Restoration and Regeneration in Swiss history lasted from 1814 to 1847. "Restoration" is the period of 1814 to 1830, the restoration of the Ancien Régime (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte on the centralist Helvetic Republic from 1798 and the partial reversion to the old system with the Act of Mediation of 1803. "Regeneration" is the period of 1830 to 1848, when in the wake of the July Revolution the "restored" Ancien Régime was countered by the liberal movement. In the Protestant cantons, the rural population enforced liberal cantonal constitutions, partly in armed marches on the cities. This resulted in a conservative backlash in the Catholic cantons in the 1830s, raising the conflict to the point of civil war by 1847.

The Rütli Oath is the legendary oath taken at the foundation of the Old Swiss Confederacy by the representatives of the three founding cantons, Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden. It is named after the site of the oath taking, the Rütli, a meadow above Lake Uri near Seelisberg. Recorded in Swiss historiography from the 15th century, the oath is notably featured in the 19th century play William Tell by Friedrich Schiller.
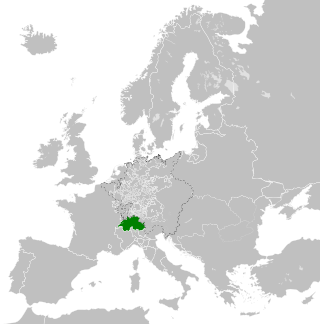
The Old Swiss Confederacy, also known as Switzerland or the Swiss Confederacy, was a loose confederation of independent small states, initially within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland.

The Battle of Calven1 took place on 22 May 1499 at the exit of the Val Müstair in the Grisons to the Vinschgau in County of Tyrol between the forces of King Maximilian I of the House of Habsburg and those of the free federation of the Three Leagues of the Grisons. It was the decisive battle in the southern Grisons of the Swabian War; after the defeat of the Habsburg troops, the king had to abandon his attempts to control the Engadin and the Val Müstair. The focus of operations in the Swabian War subsequently shifted again to the northern border of the Old Swiss Confederacy.

The Battle of Frastanz between an army of the Old Swiss Confederacy and the troops of King Maximilian I of the Holy Roman Empire took place on 20 April 1499. In one of the many raids of the Swabian War, an expedition of Habsburg troops had plundered some villages in the Swiss Confederacy, who responded by sending an army to Vorarlberg. At Frastanz, a few kilometers south-east of Feldkirch, the Habsburg troops had blocked the entry to the Montafon valley with a strong wooden fortification called a Letzi. The Swiss used a flanking maneuver to bypass the Letzi and after a hard battle routed Maximilian's army. Many Landsknechte drowned in the river Ill.
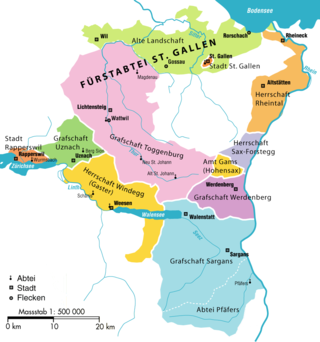
The County of Sargans was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1458 until the French Revolutionary War in 1798, Sargans became a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy, administered jointly by the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Lucerne, Zürich, Glarus and Zug.
The Bundeslied or Tellenlied is a patriotic song of the Old Swiss Confederacy. Its original composition dates to the Burgundian Wars period (1470s). The oldest extant manuscript text was written in 1501, the first publication in print dates to 1545. It consists of stanzas of six lines each, with a rhyming scheme of A-A-B-C-C-B. It is one of the oldest existing records of the legend of Swiss national hero William Tell.

The English name of Switzerland is a compound containing Switzer, an obsolete term for the Swiss, which was in use during the 16th to 19th centuries. The English adjective Swiss is a loan from French Suisse, also in use since the 16th century.
Burkhard VII. Münch was a knight and life peer, a renowned late member of the Landskron branch of the Münch family. His reputation rests primarily on his death at the Battle of St. Jakob an der Birs. Burkhard's death spelled the end of the family Münch of Landskron, which ended completely when his brother Johann IX. died in 1461.

The territorial evolution of Switzerland occurred primarily with the acquisition of territory by the historical cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy and its close associates. This gradual expansion took place in two phases, the growth from the medieval Founding Cantons to the "Eight Cantons" during 1332–1353, and the expansion to the "Thirteen Cantons" of the Reformation period during 1481–1513.

Wilhelm Oechsli was a Swiss historian.

At the Diet of Wormsin 1495, the foundation stone was laid for a comprehensive reform (Reichsreform) of the Holy Roman Empire. Even though several elements of the reforms agreed by the Imperial Diet (Reichstag) at Worms did not last, they were nevertheless highly significant in the further development of the empire. They were intended to alter its structure and constitutional ordinances in order to resolve the problems of imperial government that had become evident.

Bernau Castle is a ruined castle in the municipality of Leibstadt in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It was mostly destroyed in a fire in July 1844 leaving only a few ruined walls still visible.


















