Pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound similar to pyridine. One of the three diazines, it has the nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine and pyridazine. In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U).

Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.
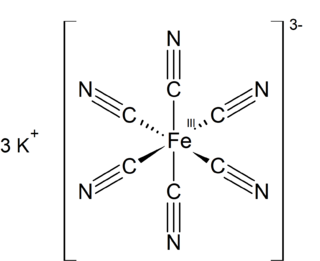
Potassium ferricyanide is the chemical compound with the formula K3[Fe(CN)6]. This bright red salt contains the octahedrally coordinated [Fe(CN)6]3− ion. It is soluble in water and its solution shows some green-yellow fluorescence. It was discovered in 1822 by Leopold Gmelin,

Robert Bruce Merrifield was an American biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1984 for the invention of solid phase peptide synthesis.
Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2. It is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Pyrazine is less basic than pyridine, pyridazine and pyrimidine.

Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) describes any of several compounds of with the formula CrCl3 • xH2O, where x can be 0, 5, and 6. The anhydrous compound with the formula CrCl3 is a violet solid. The most common form of the trichloride is the dark green hexahydrate, CrCl3 • 6H2O. Chromium chlorides find use as catalysts and as precursors to dyes for wool.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl
2. It is a moderately volatile colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

DABCO (1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) is a bicyclic organic compound with the formula N2(C2H4)3. This colorless solid is a highly nucleophilic tertiary amine base, which is used as a catalyst and reagent in polymerization and organic synthesis.
Quinazoline is an organic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is an aromatic heterocycle with a bicyclic structure consisting of two fused six-membered aromatic rings, a benzene ring and a pyrimidine ring. It is a light yellow crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Also known as 1,3-diazanaphthalene, quinazoline received its name from being an aza derivative of quinoline. Though the parent quinazoline molecule is rarely mentioned by itself in technical literature, substituted derivatives have been synthesized for medicinal purposes such as antimalarial and anticancer agents. Quinazoline is a planar molecule. It is isomeric with the other diazanaphthalenes of the benzodiazine subgroup: cinnoline, quinoxaline, and phthalazine. Over 200 biologically active quinazoline and quinoline alkaloids are identified.

Sodium periodate is an inorganic salt, composed of a sodium cation and the periodate anion. It may also be regarded as the sodium salt of periodic acid. Like many periodates it can exist in two different forms: sodium metaperiodate, which has the formula NaIO4, and sodium orthoperiodate, normally this means sodium hydrogen periodate (Na2H3IO6) but the fully reacted sodium orthoperiodate salt, Na5IO6, can also be prepared. Both salts are useful oxidising agents.

Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is an organofluorine compound with the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It is a structural analogue of acetic acid with all three of the acetyl group's hydrogen atoms replaced by fluorine atoms and is a colorless liquid with a vinegar-like odor.
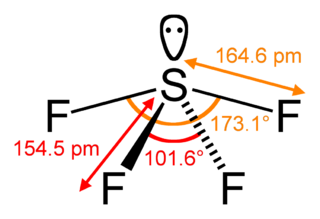
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.

Indium(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula InCl3. This salt is a white, flaky solid with applications in organic synthesis as a Lewis acid. It is also the most available soluble derivative of indium.
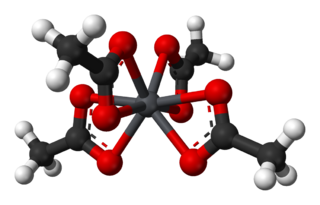
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is a chemical compound with chemical formula Pb(C2H3O2)4. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis.
Antimony trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF3. Sometimes called Swarts' reagent, is one of two principal fluorides of antimony, the other being SbF5. It appears as a white solid. As well as some industrial applications, it is used as a reagent in inorganic and organofluorine chemistry.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.

Hypofluorous acid, chemical formula HOF, is the only known oxyacid of fluorine and the only known oxoacid in which the main atom gains electrons from oxygen to create a negative oxidation state. The oxidation state of the oxygen in hypofluorites is 0. It is also the only hypohalous acid that can be isolated as a solid. HOF is an intermediate in the oxidation of water by fluorine, which produces hydrogen fluoride, oxygen difluoride, hydrogen peroxide, ozone and oxygen. HOF is explosive at room temperature, forming HF and O2:

Tetrakis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]borate is an anion with chemical formula [{3,5-(CF3)2C6H3}4B]−, which is commonly abbreviated as [BArF4]−, indicating the presence of fluorinated aryl (ArF) groups. It is sometimes referred to as Kobayashi's anion in honour of Hiroshi Kobayashi who led the team that first synthesised it. More commonly it is affectionately nicknamed "BARF." The BARF ion is also abbreviated BArF24−, to distinguish it from the closely related BArF−
20, [(C6F5)4B]−.
Trifluoromethylation in organic chemistry describes any organic reaction that introduces a trifluoromethyl group in an organic compound. Trifluoromethylated compounds are of some importance in pharmaceutical industry and agrochemicals. Several notable pharmaceutical compounds have a trifluoromethyl group incorporated: fluoxetine, mefloquine, Leflunomide, nulitamide, dutasteride, bicalutamide, aprepitant, celecoxib, fipronil, fluazinam, penthiopyrad, picoxystrobin, fluridone, norflurazon, sorafenib and triflurazin. A relevant agrochemical is trifluralin. The development of synthetic methods for adding trifluoromethyl groups to chemical compounds is actively pursued in academic research.













