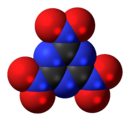
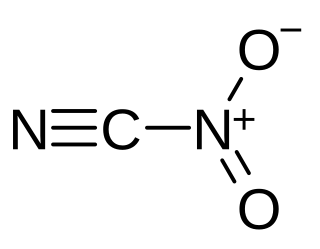RDX (abbreviation of "Research Department eXplosive") or hexogen, among other names, is an organic compound with the formula (O2N2CH2)3. It is a white solid without smell or taste, widely used as an explosive. Chemically, it is classified as a nitroamine alongside HMX, which is a more energetic explosive than TNT. It was used widely in World War II and remains common in military applications.

HMX, also called octogen, is a powerful and relatively insensitive nitroamine high explosive, chemically related to RDX. Like RDX, the compound's name is the subject of much speculation, having been variously listed as High Melting Explosive, Her Majesty's Explosive, High-velocity Military Explosive, or High-Molecular-weight RDX.

Oleum, or fuming sulfuric acid, is a term referring to solutions of various compositions of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid, or sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid. Oleum is identified by the CAS number 8014-95-7.
Tetrazine is a compound that consists of a six-membered aromatic ring containing four nitrogen atoms with the molecular formula C2H2N4. The name tetrazine is used in the nomenclature of derivatives of this compound. Three core-ring isomers exist: 1,2,3,4-tetrazines, 1,2,3,5-tetrazines, and 1,2,4,5-tetrazines, also known as v-tetrazines, as-tetrazines and s-tetrazines respectively.
Octanitrocubane (molecular formula: C8(NO2)8) is a high explosive that, like TNT, is shock-insensitive (not readily detonated by shock). The octanitrocubane molecule has the same chemical structure as cubane (C8H8) except that each of the eight hydrogen atoms is replaced by a nitro group (NO2).

Dinitrogen pentoxide is the chemical compound with the formula N2O5. It is one of the binary nitrogen oxides, a family of compounds that only contain nitrogen and oxygen. It exists as colourless crystals that sublime slightly above room temperature, yielding a colorless gas.

In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, C−H bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid.
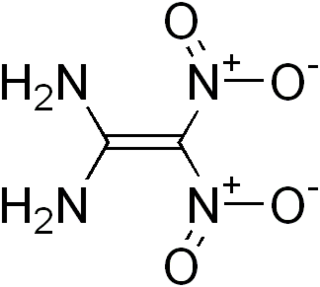
FOX-7 or 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene(DADNE) is an insensitive high explosive compound. It was first synthesized in 1998 by the Swedish National Defence Research Institute (FOS). The name FOX-7 is derived from the acronym of the Swedish Defence Research Agency (FOI), with the I replaced by an X to indicate an explosive, as in RDX and HMX.
An isocyanide is an organic compound with the functional group –N+≡C−. It is the isomer of the related nitrile (–C≡N), hence the prefix is isocyano. The organic fragment is connected to the isocyanide group through the nitrogen atom, not via the carbon. They are used as building blocks for the synthesis of other compounds.

Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is C3H3N3. They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common.

Heptazine, or tri-s-triazine or cyamelurine, is a chemical compound with formula C
6N
7H
3, that consist of a planar triangular core group or three fused triazine rings, with three hydrogen atoms at the corners. It is a yellow, weakly fluorescent solid with melting point over 300 °C. It is soluble in organic solvents such as acetonitrile, but is decomposed by water in the presence of light.
1,3,5-Triazine, also called s-triazine, is an organic chemical compound with the formula (HCN)3. It is a six-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring, one of several isomeric triazines. S-triazine—the "symmetric" isomer—and its derivatives are useful in a variety of applications.

Hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane, also called HNIW and CL-20, is a polycyclic nitroamine explosive with the formula C6H6N12O12. In the 1980s, CL-20 was developed by the China Lake facility, primarily to be used in propellants. It has a better oxidizer-to-fuel ratio than conventional HMX or RDX. It releases 20% more energy than traditional HMX-based propellants, and is widely superior to conventional high-energy propellants and explosives.

Hexazine is an allotrope of nitrogen composed of 6 nitrogen atoms arranged in a ring-like structure analogous to that of benzene. As a neutral-charged species, it would be the final member of the azabenzene (azine) series, in which all of the methine groups of the benzene molecule have been replaced with nitrogen atoms. The two last members of this series, hexazine and pentazine, have not been observed, although all other members of the azine series have.

4,4’-Dinitro-3,3’-diazenofuroxan (DDF) is a powerful experimental high explosive with performance comparable to that of other high-density high-explosives such as octanitrocubane. It is synthesised by oxidative coupling of 4-amino-3-(azidocarbonyl)furoxan followed by Curtius rearrangement and further oxidation.

HHTDD (hexanitrohexaazatricyclododecanedione) is a powerful but moisture sensitive explosive compound. It is essentially an open analogue of the cyclic nitroamine cage compounds such as CL-20. While it is highly explosive, with a velocity of detonation even higher than that of CL-20, HHTDD readily decomposes in the presence of even trace amounts of water, making it unsuitable for any practical applications.

Cyanuric triazide (C3N12 or (NCN3)3) is described as an environmentally friendly, low toxicity, and organic primary explosive with a detonation velocity of about 7,300 m s−1, and ignition temperature at 205 °C. Primary research on this compound focuses on its use as a high energy density compound.

TEX is a dense nitramine high explosive, that derives from the very powerful and sensitive high explosive CL-20. Though related to CL-20 in that is shares the same cage structure, TEX is more easily synthesized in good yield from inexpensive starting materials. Unlike CL-20, TEX is friction insensitive, bears a low impact sensitivity, and possesses a very low shock sensitivity and large critical diameter, making it an interesting explosive filler for insensitive munitions. Its systematic name, 4,10-dinitro-2,6,8,12-tetraoxa-4,10-diazatetracyclo[5.5.0.05,9.03,11]-dodecane derives from its tetracyclic structure.

Nitrosyl cyanide, a blue-green gas, is the compound with the molecular formula ONCN. The compound has been invoked as a product of the oxidation of cyanamide catalyzed by the enzyme glucose oxidase.
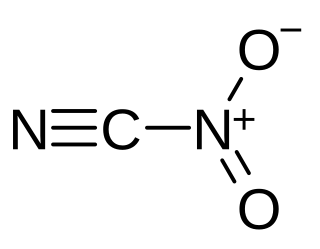
Nitryl cyanide is an energetic chemical compound with the formula NCNO2. Nitryl cyanide is a possible precursor to the theoretical explosive 2,4,6-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine.