
The Cabombaceae are a family of aquatic, herbaceous flowering plants. A common name for its species is water shield. The family is recognised as distinct in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group IV system (2016). The family consists of two genera of aquatic plants, Brasenia and Cabomba, totalling six species.
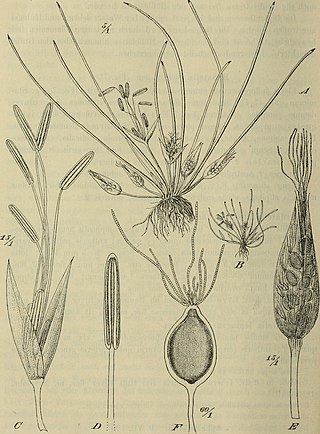
Hydatellaceae are a family of small, aquatic flowering plants. The family consists of tiny, relatively simple plants occurring in Australasia and India. It was formerly considered to be related to the grasses and sedges, but has been reassigned to the order Nymphaeales as a result of DNA and morphological analyses showing that it represents one of the earliest groups to split off in flowering-plant phylogeny, rather than having a close relationship to monocots, which it bears a superficial resemblance to due to convergent evolution. The family includes only the genus Trithuria, which has at least 13 species, although species diversity in the family has probably been substantially underestimated.

Trithuria is a genus of small ephemeral aquatic herb that represent the only members of the family Hydatellaceae found in India, Australia, and New Zealand. All 13 described species of Trithuria are found in Australia, with the exception of T. inconspicua and T. konkanensis, from New Zealand and India respectively. Until DNA sequence data and a reinterpretation of morphology proved otherwise, these plants were believed to be monocots related to the grasses (Poaceae). They are unique in being the only plants besides two members of Triuridaceae in which the stamens are centred and surrounded by the pistils; in Hydatellaceae the resulting 'flowers' may instead represent condensed inflorescences or non-flowers.

Wurmbea is a genus of perennial herbs in the family Colchicaceae, native to Africa and Australia. There are about 50 species, with about half endemic to each continent.

Tribonanthes a genus of Australian plants endemic to Western Australia in the bloodwort family, Haemodoraceae.

Haemodorum is a genus of herbs in the family Haemodoraceae, first described as a genus in 1798 by James Edward Smiith. The genus is native to New Guinea and Australia. The type species is Haemodorum corymbosum Vahl, first described by Martin Vahl in 1805.

Trithuria inconspicua is a small aquatic herb of the family Hydatellaceae that is only found in New Zealand.
Terry Desmond Macfarlane is a botanist and taxonomist, who has worked in both Australia and Peru. A senior research scientist at the Western Australian Herbarium, Macfarlane is associate editor of its journal Nuytsia and currently collaborates with researchers across Australia and in Canada, Germany, New Zealand, Russia, Spain and United Kingdom. He was also involved in the development of FloraBase, the Western Australian flora database.

Trithuria austinensis is a species of aquatic plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to Western Australia.

Trithuria australis is a species of aquatic plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to Western Australia.

Trithuria bibracteata is a species of aquatic plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to Western Australia.
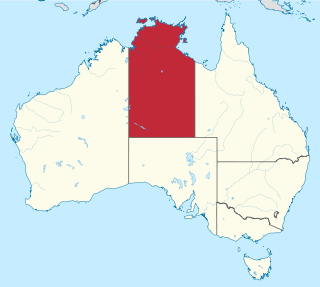
Trithuria cookeana is a species of aquatic plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to the Northern Territory, Australia.

Trithuria cowieana is a species of aquatic plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to the Northern Territory, Australia.
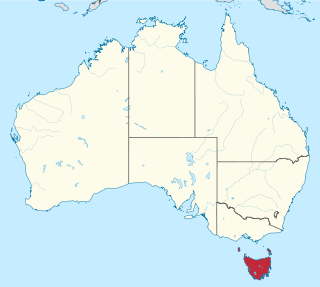
Trithuria filamentosa is a species of aquatic plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to Tasmania, Australia.

Trithuria konkanensis is a species of aquatic plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to India.

Trithuria lanterna is a species of plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to Australia.

Trithuria occidentalis is a species of plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to Western Australia.

Trithuria polybracteata is a species of plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to Western Australia.

Trithuria submersa is a species of plant in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to the Australian states New South Wales, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia.

Trithuria inconspicua subsp. brevistyla is a subspecies of Trithuria inconspicua in the family Hydatellaceae endemic to the South Island of New Zealand.













