A multi-user dungeon, also known as a multi-user dimension or multi-user domain, is a multiplayer real-time virtual world, usually text-based or storyboarded. MUDs combine elements of role-playing games, hack and slash, player versus player, interactive fiction, and online chat. Players can read or view descriptions of rooms, objects, other players, and non-player characters, and perform actions in the virtual world that are typically also described. Players typically interact with each other and the world by typing commands that resemble a natural language, as well as using a character typically called an avatar.
In multiplayer online games, a MUSH is a text-based online social medium to which multiple users are connected at the same time. MUSHes are often used for online social intercourse and role-playing games, although the first forms of MUSH do not appear to be coded specifically to implement gaming activity. MUSH software was originally derived from MUDs; today's two major MUSH variants are descended from TinyMUD, which was fundamentally a social game. MUSH has forked over the years and there are now different varieties with different features, although most have strong similarities and one who is fluent in coding one variety can switch to coding for the other with only a little effort. The source code for most widely used MUSH servers is open source and available from its current maintainers.

The World Wide Web is an information system that enables content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
AberMUD was the first popular open source MUD. It was named after the town Aberystwyth, where it was written. The first version was written in B by Alan Cox, Richard Acott, Jim Finnis, and Leon Thrane based at University of Wales, Aberystwyth for an old Honeywell mainframe and opened in 1987.
A talker is a chat system that people use to talk to each other over the Internet. Dating back to the 1980s, they were a predecessor of instant messaging. A talker is a communication system precursor to MMORPGs and other virtual worlds such as Second Life. Talkers are a form of online virtual worlds in which multiple users are connected at the same time to chat in real-time. People log in to the talkers remotely, and have a basic text interface with which to communicate with each other.

BatMUD is a medieval fantasy MUD, established in 1990. BatMUD is Finland-based and operated and owned by a non-profit organization, Balanced Alternative Techniques ry, officially registered 1994 in Helsinki, Finland.
DikuMUD is a multiplayer text-based role-playing game, which is a type of multi-user domain (MUD). It was written in 1990 and 1991 by Sebastian Hammer, Tom Madsen, Katja Nyboe, Michael Seifert, and Hans Henrik Stærfeldt at DIKU —the department of computer science at the University of Copenhagen in Copenhagen, Denmark.

Ancient Anguish, abbreviated AA, is a fantasy-themed MUD, a text-based online role-playing game. Founded in 1991 by Balz "Zor" Meierhans and Olivier "Drake" Maquelin, it opened to the public on February 2, 1992. It is free-to-play, but has been supported by player donations since 1994.

Discworld MUD is a popular MUD, a text-based online role-playing game, set in the Discworld as depicted in the Discworld series of books by Terry Pratchett.
LPMud, abbreviated LP, is a family of multi-user dungeon (MUD) server software. Its first instance, the original LPMud game driver, was developed in 1989 by Lars Pensjö. LPMud was innovative in its separation of the MUD infrastructure into a virtual machine and a development framework written in the programming language LPC.

Digital obsolescence is the risk of data loss because of inabilities to access digital assets, due to the hardware or software required for information retrieval being repeatedly replaced by newer devices and systems, resulting in increasingly incompatible formats. While the threat of an eventual "digital dark age" was initially met with little concern until the 1990s, modern digital preservation efforts in the information and archival fields have implemented protocols and strategies such as data migration and technical audits, while the salvage and emulation of antiquated hardware and software address digital obsolescence to limit the potential damage to long-term information access.
Lennart Augustsson is a Swedish computer scientist. He was formerly a lecturer at the Computing Science Department at Chalmers University of Technology. His research field is functional programming and implementations of functional programming languages.
Digital reference is a service by which a library reference service is conducted online, and the reference transaction is a computer-mediated communication. It is the remote, computer-mediated delivery of reference information provided by library professionals to users who cannot access or do not want face-to-face communication. Virtual reference service is most often an extension of a library's existing reference service program. The word "reference" in this context refers to the task of providing assistance to library users in finding information, answering questions, and otherwise fulfilling users’ information needs. Reference work often but not always involves using reference works, such as dictionaries, encyclopedias, etc. This form of reference work expands reference services from the physical reference desk to a "virtual" reference desk where the patron could be writing from home, work or a variety of other locations.
A MOO is a text-based online virtual reality system to which multiple users (players) are connected at the same time.

Michael Lawrie is a British computer security and social networking expert known for many things ranging from running MUDs to accidentally being the world's first Cybersquatter. He lives in Cambridge, England where he created the Cambridge Freecycle group, one of the largest in Europe.
Embedded Wizard is a graphical user interface tool developed and distributed by TARA Systems GmbH for creating graphical user interface (GUI) applications mainly for embedded systems. It provides a WYSIWYG front-end for editing graphics, effects and logic of the user interface and generates ANSI C code for particular target hardware. Embedded Wizard is independent of a specific graphics hardware or color format and supports object oriented programming.
DGD, Dworkin's Game Driver, is an LPMud server written by Felix A. "Dworkin" Croes. DGD pioneered important technical innovations in MUDs, particularly disk-based object storage, full world persistence, separation of concerns between driver and mudlib, runtime morphism, automatic garbage collection, lightweight objects and LPC-to-C compilation.

Xyllomer is a MUD, a text-based online role-playing game, founded in 1991 as PaderMUD. It was the first publicly accessible MUD to use Dworkin's Game Driver. It has been hosted in Germany throughout its history.
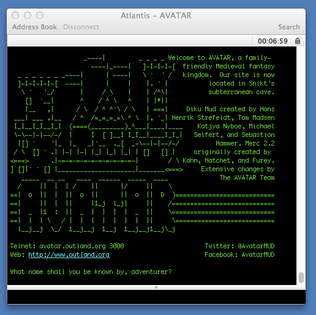
A.V.A.T.A.R. MUD is a free, online, massively multiplayer, fantasy, text-based role-playing game, set in a real-time virtual environment. It combines elements of role-playing games, hack and slash style computer games, adventure games and social gaming.







