
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek galaxias (γαλαξίας), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a thousand stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies.

The M81 Group is a galaxy group in the constellations Ursa Major and Camelopardalis that includes the galaxies Messier 81 and Messier 82, as well as several other galaxies with high apparent brightnesses. The approximate center of the group is located at a distance of 3.6 Mpc, making it one of the nearest groups to the Local Group. The group is estimated to have a total mass of ×1012M☉. The M81 Group, the Local Group, and other nearby groups all lie within the Virgo Supercluster.

The Uppsala General Catalogue of Galaxies (UGC) is a catalogue of 12,921 galaxies visible from the northern hemisphere. It was first published in 1973.

An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure.

The Pinwheel Galaxy is a face-on spiral galaxy located 21 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 and was communicated that year to Charles Messier, who verified its position for inclusion in the Messier Catalogue as one of its final entries.

A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is sometimes classified as a dwarf galaxy; others consider it a full-fledged galaxy. Dwarf galaxies' formation and activity are thought to be heavily influenced by interactions with larger galaxies. Astronomers identify numerous types of dwarf galaxies, based on their shape and composition.
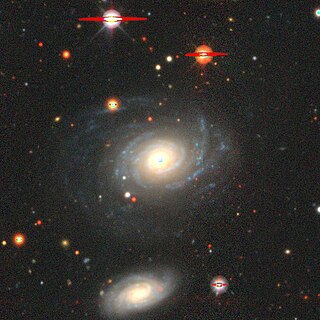
NGC 1 is an intermediate spiral galaxy of the morphological type Sbc, located in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered on 30 September 1861 by Heinrich d'Arrest.

The Tadpole Galaxy, also known as UGC 10214 and Arp 188, is a disrupted barred spiral galaxy located 420 million light-years from Earth in the northern constellation Draco. Its most dramatic feature is a trail of stars about 280,000 light-years long. Its size has been attributed to a merger with a smaller galaxy that is believed to have occurred about 100 million years ago. The galaxy is filled with bright blue star clusters triggered by the merger, some containing as many as one million stars. It is the largest disrupted spiral galaxy of its sort.

NGC 3370 (also known as UGC 5887 or Silverado Galaxy) is a spiral galaxy about 82.2 ± 5.9 million light-years (25.2 ± 1.8 megaparsecs) away in the constellation Leo. It is nearly comparable to our Milky Way both in diameter with a D25 isophotal size about 77,300 ly (23.69 kpc) comparing to the Milky Way Galaxy's 87,400 ly (26.8 kpc) diameter, and as well as in mass (1011 M☉). NGC 3370 exhibits an intricate spiral arm structure surrounding a poorly defined nucleus. It is a member of the NGC 3370 Group of galaxies, which is a member of the Leo II Groups, a series of galaxies and galaxy clusters strung out from the right edge of the Virgo Supercluster.

NGC 2363 is a star-forming region in the Magellanic galaxy NGC 2366 which is located in the constellation Camelopardalis. It contains NGC 2363-V1, a luminous blue variable star which is 6,300,000 times more luminous than the Sun and one of the most luminous stars known. It can be seen in this Hubble Space Telescope image as the bright isolated star in the dark void on the left of the nebula.

Hanny's Voorwerp, is a type of astronomical object called a quasar ionization echo. It was discovered in 2007 by Dutch schoolteacher Hanny van Arkel while she was participating as a volunteer in the Galaxy Zoo project, part of the Zooniverse group of citizen science websites. Photographically, it appears as a bright blob close to spiral galaxy IC 2497 in the constellation Leo Minor.

Arp 273 is a pair of interacting galaxies, 300 million light years away in the constellation Andromeda. It was first described in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies, compiled by Halton Arp in 1966. The larger of the spiral galaxies, known as UGC 1810, is about five times more massive than the smaller galaxy. It has a disc that is tidally distorted into a rose-like shape by the gravitational pull of the companion galaxy below it, known as UGC 1813. The smaller galaxy shows distinct signs of active star formation at its nucleus, and "it is thought that the smaller galaxy has actually passed through the larger one."

UGC 5497 is a dwarf galaxy, located about 12 million light years away in the constellation Ursa Major. It is a member of the M81 Group.

UGC 2885 is a large barred spiral galaxy of type SA(rs)c in the constellation Perseus. It is 232 million light-years (71 Mpc) from Earth and measures 463,000 ly (142,000 pc) across, making it one of the largest known spiral galaxies. It is also a possible member of the Pisces-Perseus supercluster.

UGC 8335 is a pair of strongly interacting spiral galaxies. They have been distorted by extreme tidal forces, creating prominent tidal tails and a bridge of gas and stars between the galaxies.

NGC 218, also known as UGC 480, is a spiral galaxy located approximately 500 million light-years from the Sun in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered on October 17, 1876 by Édouard Stephan, and is interacting with the galaxy PGC 2726.

NGC 511, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5103 or UGC 936, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 499 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 26 October 1876 by French astronomer Édouard Stephan.

NGC 515, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5201 or UGC 956, is a lenticular galaxy located approximately 228 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 13 September 1784 by astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 522, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5218 or UGC 970, is a spiral galaxy located approximately 122 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 25 September 1862 by astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest.

The Virgo III Groups, or Virgo III Cloud, are a series of at least 75 galactic clusters and individual galaxies stretching approximately 40 megalight-years off the eastern edge of the Virgo Supercluster. Parts of it are in the constellations Virgo, Libra, and Serpens Caput. It is located approximately 65 Mly (19,929,090.60 pc) to 85 Mly (26,061,118.47 pc) from the Solar System, at a right ascension of 13h 30m to 15h 20m.




















