Related Research Articles

Ulmus 'Exoniensis', the Exeter elm, was discovered near Exeter, England, in 1826, and propagated by the Ford & Please nursery in that city. Traditionally believed to be a cultivar of the Wych Elm U. glabra, its fastigiate shape when young, upward-curving tracery, small samarae and leaves, late leaf-flush and late leaf-fall, taken with its south-west England provenance, suggest a link with the Cornish Elm, which shares these characteristics.

Fine examples around the cathedral in 2007

The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Crispa' [:'curled', the leaf margin], sometimes known as the Fernleaf Elm, arose before 1800 and was first listed by Willdenow as U. crispa (1809). Audibert listed an U. campestrisLinn. 'Crispa', orme à feuilles crépues [:'frizzy-leaved elm'], in 1817, and an Ulmus urticaefolia [:'nettle-leaved elm'] in 1832; the latter is usually taken to be a synonym. Loudon considered the tree a variety of U. montana (1838). In the 19th century, Ulmus × hollandica cultivars, as well as those of Wych Elm, were often grouped under Ulmus montana. Elwes and Henry (1913) listed 'Crispa' as a form of wych elm, but made no mention of the non-wych samara.

The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Propendens', described by Schneider in 1904 as U. glabra (:minor) var. suberosa propendens, Weeping Cork-barked elm, was said by Krüssmann (1976) to be synonymous with the U. suberosa pendula listed by Lavallée without description in 1877. Earlier still, Loudon's Arboretum et Fruticetum Britannicum had included an illustration of a pendulous "cork-barked field elm", U. campestris suberosa. An U. campestris suberosa pendula was in nurseries by the 1870s.
The Wych Elm cultivar Ulmus glabra 'Albo-Variegata' was first mentioned by Weston in 1770 as U. glabra var. variegata. An U. campestris latifolia albo-variegataHort. was distributed by the Späth nursery, Berlin, from the 1890s to the 1930s.
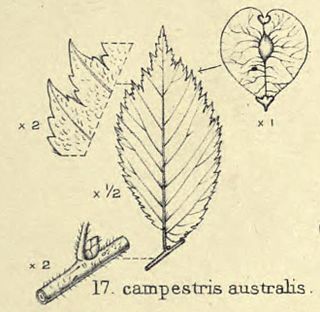
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Australis' [:'southern'], reputedly endemic to south-eastern France, Switzerland and Italy, is a little-known tree considered by various authorities to have been a variety of Ulmus minor or Ulmus × hollandica.
Ulmus glabra 'Cebennensis', also known as the Cevennes Elm, is a cultivar of the Wych Elm. The first known publication of the cultivar epithet was in the 1831-1832 catalogue from the Audibert brothers plant nursery at Tonelle, near Tarascon in France. The cultivar was given the name Ulmus campestris var. cebennensis.

The dwarf wych elm cultivar Ulmus glabra 'Nana', a very slow growing shrub that with time forms a small tree, is of unknown origin. It was listed in the Simon-Louis 1869 catalogue as Ulmus montana nana. Henry (1913), referring his readers to an account of the Kew specimen in the journal Woods and Forests, 1884, suggested that it may have originated from a witch's broom. It is usually classified as a form of Ulmus glabra and is known widely as the 'Dwarf Wych Elm'. However, the ancestry of 'Nana' has been disputed in more recent years, Melville considering the specimen once grown at Kew to have been a cultivar of Ulmus × hollandica.
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Ramulosa' [: 'twiggy'], Floetbeck elm, was raised in the Floetbeck nurseries, Hamburg, by James Booth & Son, and was first mentioned by Loudon in Arboretum et Fruticetum Britannicum (1838) as Ulmus montana glabra var. ramulosaBooth, but without description. It does not, however, appear in Booth's 1838 list. Loudon listed the tree in a group including Downton Elm, Scampston Elm, and Ludlow Elm, so Green's wych cultivar attribution appears to be an error.
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Rubra' was reputedly cloned from a tree found by Vilmorin in a wood near Verrières-le-Buisson in the 1830s. It was listed in the 1869 Catalogue of Simon-Louis, Metz, France, as Ulmus campestris rubra, and by Planchon in de Candolle's Prodromus Systematis Naturalis Regni Vegetabilis (1873) as Ulmus libero-rubra: 'Orme à liber rouge' [:elm with red inner bark]. Elwes and Henry (1913) and Bean (1936) listed it as Ulmus montana [:U. glabraHuds.] var. libro-rubro, the former stating that the tree appeared "identical" to Simon-Louis's Ulmus campestris rubra. A specimen in the Zuiderpark, The Hague, was identified in 1940 as a wych elm cultivar, U. glabraHuds.libero rubro.
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Rugosa' [:'wrinkled', the leaves], was first listed in Audibert's Tonelle (1817), as "U. campestris Linn. 'Rugosa' = orme d'Avignon [Avignon elm] ", but without description. A description followed in the Revue horticole, 1829. Green (1964) identified this cultivar with one listed by Hartwig and Rümpler in Illustrirtes Gehölzbuch (1875) as Ulmus montana var. rugosaHort.. A cultivar of the same name appeared in Loddiges' catalogue of 1836 and was identified by Loudon in Arboretum et Fruticetum Britannicum (1838) as Ulmus montana var. rugosaMasters, Masters naming the tree maple-bark elm. Ulmus montana was used at the time both for wych cultivars and for some cultivars of the Ulmus × hollandica group.
The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Cucullata', the Hooded elm, was listed by Loddiges of Hackney, London, in their catalogue of 1823 as Ulmus campestris cucullata, and later by Loudon in Arboretum et Fruticetum Britannicum (1838), as U. campestris var. cucullata.

The hybrid elm cultivar Ulmus × hollandica 'Superba' is one of a number of intermediate forms arising from the crossing of the Wych Elm U. glabra with a variety of Field Elm U. minor. Boulger tentatively (1881) and Green more confidently (1964) equated it with a hybrid elm cultivated in the UK by Masters at Canterbury in the early 19th century, known as "Masters' Canterbury Seedling" or simply the Canterbury Elm. Loudon examined a specimen sent by Masters and considered it a hybrid, calling it U. montana glabra major.
The hybrid elm Ulmus × hollandica 'Viscosa' is probably one of a number of cultivars arising from the crossing of the Wych Elm U. glabra with a variety of Field Elm U. minor. The tree was listed by Loddiges, in his catalogue of 1836 and two years later by Loudon in Arboretum et Fruticetum Britannicum 3: 1378, 1838, as U. viscosa. An early specimen in the Herbarium Dumortier named U. viscosaAudibert was later sunk by Melville as U. × hollandica.

The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Scampstoniensis', the Scampston Elm or Scampston Weeping Elm, is said to have come from Scampston Hall, Yorkshire, England, before 1810. Loudon opined that a tree of the same name at the Royal Horticultural Society's Garden in 1834, 18 feet (5.5 m) high at 8 years old "differed little from the species". Henry described the tree, from a specimen growing in Victoria Park, Bath, as "a weeping form of U. nitens" [:Ulmus minor ]; however Green considered it "probably a form of Ulmus × hollandica". Writing in 1831, Loudon said that the tree was supposed to have originated in America. U. minor is not, however, an American species, so if the tree was brought from America, it must originally have been taken there from Europe. There was an 'American Plantation' at Scampston, which may be related to this supposition. A number of old specimens of 'Scampstoniensis' in this plantation were blown down in a great gale of October 1881; younger specimens were still present at Scampston in 1911.
Ulmus glabra 'Australis' is a Wych Elm cultivar described by Loudon in 1838, from a tree in the Royal Horticultural Society garden, as U. montana var. australisHort..

The hybrid elm cultivar Ulmus × hollandica 'Fastigiata' was first listed and described as Ulmus glabra fastigiata, a narrow-crowned elm with large smooth leaves, by Petzold and Kirchner in Arboretum Muscaviense (1864). C. Berndt of the Berndt Nursery, Zirlau, Schweidnitz, described an elm of the same name in Mitteilungen der Deutschen Dendrologischen Gesellschaft, that he had received in 1903 "from a renowned nursery in Holstein" as Ulmus montana fastigiata macrophylla. A tree of that name had been listed by Dieck in 1885 without description. Berndt reported that his U. glabra fastigiata was "easy to confuse with U. montana superba", a tree "known in the Magdeburg region as Ulmus praestans", a statement confirming that, like that cultivar, his tree was a form of U. × hollandica. Karl Gustav Hartwig who received specimens of U. praestans from Kiessling of the Magdeburg city nursery in 1908, concluded (1912) that U. glabra fastigiataKirchner was indistinguishable in leaf or habit from U. praestans. An U. campestris glabra fastigiataArb. Musc. [ = Kirchner] was distributed by the Hesse Nursery, Weener, Germany, in the 1930s, where it was listed separately from U. praestans.
The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Viminalis Betulaefolia' (:'birch-leaved') is an elm tree of uncertain origin. An U. betulaefolia was listed by Loddiges of Hackney, London, in the catalogue of 1836, an U. campestris var. betulaefolia by Loudon in Arboretum et Fruticetum Britannicum (1838), and an U. betulifoliaBooth by the Lawson nursery of Edinburgh. Henry described an U. campestris var. betulaefolia at Kew in 1913, obtained from Fulham nurseryman Osborne in 1879, as "scarcely different from var. viminalis ". Melville considered the tree so named at Kew a form of his U. × viminalis, while Bean (1988), describing U. 'Betulaefolia', likewise placed it under U. 'Viminalis' as an apparently allied tree. Loudon and Browne had noted that some forms of 'Viminalis' can be mistaken for a variety of birch. An U. campestris betulaefolia was distributed by Hesse's Nurseries, Weener, Germany, in the 1930s.

The Wych Elm cultivar Ulmus glabra 'Concavaefolia', a form with up-curling leaves, was listed in Beissner's Handbuch der Laubholz-Benennung (1903) as Ulmus montana cucullataHort. [:'hooded', the leaf], a synonym of the Ulmus scabraMill. [:glabraHuds.] var. concavaefolia of herbarium specimens. An Ulmus campestris cucullata, of uncertain species, had appeared in Loddiges' 1823 list, but Loudon's brief description (1838) of concave- and hooded-leaved elms was insufficient for later botanists to distinguish them. The earliest unambiguous description appears to be that of Petzold and Kirchner in Arboretum Muscaviense (1864).

The wych elm cultivar Ulmus glabraHuds. 'Superba', Blandford Elm, with unusually large leaves, was raised by Gill's of Blandford Forum, Dorset, in the early 1840s as Ulmus montana superba and was quickly distributed to other UK nurseries. It was confirmed as a form of wych, and first described, by Lindley in The Gardeners' Chronicle, 1845, later descriptions being added by Gill (1845) and Morren (1848), who called it U. montana var. superba. Morren had adopted the name 'Superba' from the Fulham nurseryman Osborne in 1844, who supplied him with the tree – presumably one of the nurseries supplied by Gill. Morren states that 'Superba', already in cultivation in England, was introduced to Belgium by Denis Henrard of Saint Walburge, Liège, that in 1848 it had been present in Belgium for only three years, and that this variety was the one described as 'Superba' by Osborne, whom Henrard had visited at his nursery in Fulham in September 1844. 'Blandford Elm', with leaves of the same dimensions, was soon for sale in the USA.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Robertson, J., 'The Black Irish Elm' (letter, 18 Feb. 1837), Gardener's Magazine, vol. 13 (1837), p.237
- 1 2 Loddiges, Conrad, & Sons, Catalogue of Plants, 15th edn. (1830), p.61
- 1 2 3 Arboretum et Fruticetum Britannicum, 3: 1398, 1838
- ↑ Green, Peter Shaw (1964). "Registration of cultivar names in Ulmus". Arnoldia. Arnold Arboretum, Harvard University. 24 (6–8): 41–80. Retrieved 16 February 2017.
- ↑ Elwes, Henry John; Henry, Augustine (1913). The Trees of Great Britain & Ireland. 7. pp. 1847–1929.
- ↑ Bean, W. J. (1981). Trees and shrubs hardy in Great Britain, 7th edition. Murray, England.
- 1 2 Katalog (PDF). 108. Berlin, Germany: L. Späth Baumschulenweg. 1902–1903. pp. 132–133.
- ↑ 'Cineria' leaves, herbariaunited.org, specimen 295176
- 1 2 Hanham, F. (1857). A Manual for the Park (Royal Victoria Park, Bath). Longman, London.
- ↑ Saunders, William; Macoun, William Tyrrell (1899). Catalogue of the trees and shrubs in the arboretum and botanic gardens at the central experimental farm (2 ed.). pp. 74–75.