
The sea lettuces comprise the genus Ulva, a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus Ulva is Ulva lactuca, lactuca being Latin for "lettuce". The genus also includes the species previously classified under the genus Enteromorpha, the former members of which are known under the common name green nori.

Ulva lactuca, also known by the common name sea lettuce, is an edible green alga in the family Ulvaceae. It is the type species of the genus Ulva. A synonym is U. fenestrata, referring to its "windowed" or "holed" appearance, Despite the name, it is not a lettuce

Ulvaria is a genus of green algae in the family Ulvaceae. It is similar to Ulva, but rather than being two cells thick, it is only one, despite its darker colour.

Caulerpa lentillifera or sea grape is a species of ulvophyte green algae from coastal regions in the Asia-Pacific. This seaweed is one of the favored species of edible Caulerpa due to its soft and succulent texture. It is traditionally eaten in the cuisines of Southeast Asia, Oceania, and East Asia. It was first commercially cultivated in the Philippines in the 1950s, followed by Japan in 1968. Both countries remain the top consumers of C. lentillifera. Its cultivation has since spread to other countries, including Vietnam, Taiwan, and China. C. lentillifera, along with C. racemosa, are also known as sea grapes or green caviar in English.

Ulva intestinalis is a green alga in the family Ulvaceae, known by the common names sea lettuce, green bait weed, gutweed, and grass kelp. Until they were reclassified by genetic work completed in the early 2000s, the tubular members of the sea lettuce genus Ulva were placed in the genus Enteromorpha.

Codium fragile, known commonly as green sea fingers, dead man's fingers, felty fingers, forked felt-alga, stag seaweed, sponge seaweed, green sponge, green fleece, sea staghorn, and oyster thief, is a species of seaweed in the family Codiaceae. It originates in the Pacific Ocean near Japan and has become an invasive species on the coasts of the Northern Atlantic Ocean.

Ulva linza is a green alga in the family Ulvaceae that can be found in British Isles.
Ulva atroviridis is a species of blackish-green coloured seaweed in the family Ulvaceae that can be found in Port Nolloth of Cape Province in South Africa and in Namibia.
Ulva brevistipita is a species of blackish-green coloured seaweed in the family Ulvaceae that can be found in Australia and New Zealand.
Ulva bifrons is a species of blackish-green coloured seaweed in the family Ulvaceae that can be found in Sezimbra, Portugal, in France and Spain, and Balearic islands.

Ulva clathrata is a species of seaweed in the family Ulvaceae that can be found in such European countries as Azores, Belgium, Ireland, Netherlands, and the United Kingdom. It is also common in Asian and African countries such as Israel, Kenya, Mauritius, South Africa, Tanzania, Japan, Portugal and Tunisia. It has distribution in the Americas as well including Alaska, Argentina, Brazil, Cuba, Grenada, Hispaniola, and Venezuela. Besides various countries it can be found in certain gulfs, oceans and seas such as the Gulf of Maine and Gulf of Mexico, Indian Ocean and European waters.

Ulva conglobata is a species of seaweed in the family Ulvaceae that can be found on Jeju Island of Korea, Qingdao province of China and Yokohama, Japan.
Ulva crassa is a species of blackish-green coloured seaweed in Ulvaceae family that is endemic to New Zealand. The name comes from Latin meaning thick.

Blidingia marginata is a species of seaweed in the Kornmanniaceae family.
Monostroma kuroshiense, a green alga in the division Chlorophyta, is a green seaweed endemic to Kuroshio Coast of Japan. This high-value seaweed is called Hitoegusa or Hirohano hitoegusa (ヒロハノヒトエグサ) in Japanese. Previously this algae was known in binomen Monostroma latissimum, but the latest scientific research based on multilocal phylogeny discovered that this is a new species. The algae is named after Kuroshio Current, naming is done by phycologist Felix Bast This algae is commercially cultivated in East Asia and South America for the edible product "hitoegusa-nori" or "hirohano-hitoegusa nori", popular sushi wraps. Monostroma oligosaccharides with degree of polymerization 6 prepared by agarase digestion from Monostroma nitidum polysaccharides have been shown to be an effective prophylactic agent during in vitro and in vivo tests against Japanese encephalitis viral infection. The sulfated oligosaccharides from Monostroma seem to be promising candidates for further development as antiviral agents. The genus Monostroma is the most widely cultivated genus among green seaweeds.
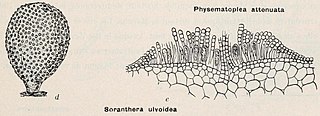
Soranthera ulvoidea, sometimes called the studded sea balloon, is a species of brown algae in the family Chordariaceae. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Soranthera. The generic name Soranthera is from the Greek soros (heap) and antheros (blooming). The specific epithet ulvoidea refers to certain resemblances the algae has with Ulva. The name in Japanese is 千島袋のり / ちしまふろくのり literally meaning "Kuril Islands bag nori".

Halosaccion glandiforme, also known as sea sacs or sea grapes, is a species of red algae.











