The Eastern Highlands, also known as the Manica Highlands, is a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The Eastern Highlands extend north and south for about 300 kilometres (190 mi) through Zimbabwe's Manicaland Province and Mozambique's Manica Province.
The Nguru Mountains are a mountain range in Morogoro Region, Tanzania, Africa. The Nguru Mountains are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains. The mountains are predominantly covered with rainforest, home to 83 species of birds and African violets. There are a number of forest reserves in the mountains.
The Viphya Mountains, also known as the Viphya Plateau or Viphya Highlands, are a mountain range in Malawi's Northern Region.
The Kipengere Range, also known as the Livingstone Mountains, lies entirely in Njombe Region in southwest Tanzania at the northern end of Lake Nyasa. Near Lake Nyasa they are known as the Kinga Mountains. It is a plateau-like ridge of mountains running southeastwards from the basin of the Great Ruaha River in the north to that of the Ruhuhu River in the south, and forms part of the eastern escarpment of the East African Rift. The range is mostly clad in montane grasslands, renowned for their botanical diversity and displays of flowers, with montane evergreen forests mostly in stream valleys.

The Udzungwa Mountains are a mountain range in south-central Tanzania. The mountains are mostly within Iringa Region, south of Tanzania's capital Dodoma. The Udzungwa Mountains are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains, and are home to a biodiverse community of flora and fauna with large numbers of endemic species.
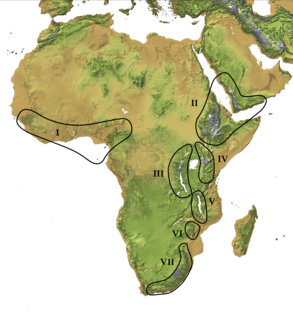
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.
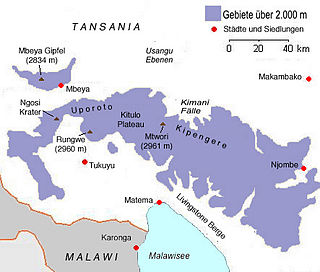
Mount Rungwe is a volcanic mountain in Mbeya Region, in Tanzania's Southern Highlands. At an altitude of 2,981 metres (9,780 ft), it is southern Tanzania's second-highest peak. Rungwe's volcano is currently inactive.

Tukuyu, known as Neu Langenburg during the German colonial rule, is a small hillside town that lies about 36 miles (58 km) south of the city of Mbeya, at an elevation of around 5,000 ft (1,500 m) in the highland Rungwe District of southern Tanzania, East Africa. Tukuyu town has a moderate to cool temperature ranging from 10° C in May/June to mid 20°C in around November. The town and surrounding areas are green all year round due to the almost year-round convectional rains resulting from Lake Nyasa(Lake Malawi).Tukuyu town is divided into several wards include; Kawetere, Msasani, Bulyaga and Bagamoyo.

The Cameroonian Highlands forests, also known as the Cameroon Highlands forests, are a montane tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion located on the range of mountains that runs inland from the Gulf of Guinea and forms the border between Cameroon and Nigeria. This is an area of forest and grassland which has become more populous as land is cleared for agriculture.

The South Malawi montane forest-grassland mosaic is an ecoregion of Malawi.
The Poroto Mountains are a mountain range in the Mbeya Region of Tanzania. They are located east of the city of Mbeya. The Poroto Mountains are a northwestward extension of the Kipengere Range, and part of the Southern Highlands. The Poroto mountains are volcanic in origin, part of the geological Rungwe Volcanic Province.

Kiwira River is a river located in Rungwe District and Kyela District of Mbeya Region, Tanzania.

Kitulo National Park is a protected area of montane grassland and montane forest on the Kitulo Plateau in the southern highlands of Tanzania. The park is at an elevation of 2,600 metres (8,500 ft) between the peaks of the Kipengere and Poroto mountains and covers an area of 412.9 square kilometres (159.4 sq mi), lying in Mbeya Region and Njombe Region. The park is administered by Tanzania National Parks (TANAPA) and is the first national park in tropical Africa to be established primarily to protect its flora.
The Southern Highlands is a highland region in southwestern Tanzania, at the northern end of Lake Malawi. The highlands include portions of Mbeya, Njombe, Rukwa, Ruvuma, and Songwe regions, bordering Malawi, Mozambique, and Zambia. Mbeya is the largest city in the highlands.

The Eastern Arc forests is a montane tropical moist forest ecoregion of eastern Africa. The ecoregion comprises several separate highland areas above 800 meters in Kenya, and (mostly) Tanzania.

The South Malawi montane forest-grassland mosaic is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, and Zambia.
The Misuku Hills are a mountain range in Malawi's Northern Region.
The Ukaguru Mountains are a mountain range in central Tanzania. The mountains are in Morogoro region, east of Tanzania's capital Dodoma. The mountains are named for the Kaguru people. The Ukaguru Mountains are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains, and are home to a biodiverse community of flora and fauna with large numbers of endemic species.

The Victoria Basin forest–grassland mosaic is an ecoregion that lies mostly in Uganda and extends into neighboring countries. The ecoregion is centered north and west of Lake Victoria, with an outlier on the border of Ethiopia and South Sudan.
The Njesi Highlands are a range of mountains in northern Mozambique.