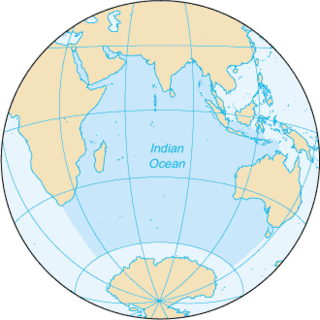
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or approx. 20% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean, or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has large marginal, or regional seas, such as the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea.

The Paleogene Period is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period 66 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Neogene Period 23.03 Mya. It is the first part of the Cenozoic Era of the present Phanerozoic Eon. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "Pe" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps.

William Michael Connolley is a British software engineer, writer, and blogger on climatology. Until December 2007 he was Senior Scientific Officer in the Physical Sciences Division in the Antarctic Climate and the Earth System project at the British Antarctic Survey, where he worked as a climate modeller. After that he became a software engineer for Cambridge Silicon Radio.

The Geological Society of America (GSA) is a nonprofit organization dedicated to the advancement of the geosciences.
The Early Cretaceous or the Lower Cretaceous is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.

Doidae is a small family of Lepidoptera with an exclusively New World distribution, with species occurring in Central America, the south-western United States, and northern South America.

Michael E. Cox is a British academic and international relations scholar. He is currently Emeritus Professor of International Relations at the London School of Economics (LSE) and Director of LSE IDEAS. He also teaches for the TRIUM Global Executive MBA Program, an alliance of NYU Stern and the London School of Economics and HEC School of Management.
The Gemmatimonadota are a phylum of bacteria established in 2003. The phylum contains two classes Gemmatimonadetes and Longimicrobia.

Urodidae, whose species are commonly known as false burnet moths, is a family of moths in the lepidopteran order. It is the type genus in the superfamily, Urodoidea, with three genera, one of which, Wockia, occurs in Europe.
Agathiphaga is a genus of moths, known as kauri moths. and is the only living genus in the family Agathiphagidae. This caddisfly-like lineage of primitive moths was first reported by Lionel Jack Dumbleton in 1952, as a new genus of Micropterigidae.
Betousa is a monotypic moth genus of the family Crambidae described by Francis Walker in 1865. Its only species, Betousa dilecta, was described by the same author in the same year. It is found on the Moluccas, Woodlark Island, St. Aignan, Ternate and Fergusson Island.
Myriostephes is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae. The genus was erected by Edward Meyrick in 1884.
Undulambia is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.
Symphonia is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.

Tirathaba is a genus of moths of the family Pyralidae described by Francis Walker in 1864.
Symphonia leucostictalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1906. It is found on New Guinea.
Undulambia fovecosta is a moth in the family Crambidae. It is found in Panama, Guatemala and Costa Rica.
A continent is a large geographical region defined by the continental shelves and the cultures on the continent. In the modern day, there are seven continents. However, there have been more continents throughout history. Vaalbara was the first supercontinent. Europe is the newest continent. Geologists have predicted that certain continents will appear, these being Pangaea Proxima, Novopangaea, Aurica, and Amasia.







