
The University District is a neighborhood and a major district in central northeastern Seattle, Washington, comprising several distinct neighborhoods. The main campus of the University of Washington (UW) is located in the district, lending its name to both the district as well as University Way NE.

The Union Bay Natural Area (UBNA) in Seattle, Washington, also known as Union Bay Marsh, is the restored remainder of the filled former Union Bay and Union Bay Marsh. It is located at the east end of the main University of Washington campus, south of NE 45th Street and west of Laurelhurst. Ravenna Creek is connected to University Slough, thence to Union Bay, and Lake Washington. Drainage Canal is one of three or four areas of open water connected with Lake Washington around Union Bay Marsh. The canal extends from NE 45th Street, between the driving range and IMA Sports Field 1, south to the bay, ending southeast of the Husky Ballpark baseball grandstand. The Drainage Canal that carries Ravenna Creek past UBNA to Union Bay is locally sometimes called University Slough.

Northgate is a neighborhood in north Seattle, Washington, named for and surrounding Northgate Mall, the first covered mall in the United States. Its north-south principal arterials are Roosevelt Way NE and Aurora Avenue N, and its east-west principal arterials are NE Northgate Way and 130th Street. Minor arterials are College Way-Meridian Avenue N, 1st, 5th, and 15th avenues NE. Interstate 5 runs through the district. Besides the eponymous mall, the most characteristic distinctions of the area are North Seattle College (NSC) and the south fork of the Thornton Creek watershed and Seattle Kraken Iceplex center.

Magnuson Park is a park in the Sand Point neighborhood of Seattle, Washington, United States. At 350 acres (140 ha) it is the second-largest park in Seattle, after Discovery Park in Magnolia. Magnuson Park is located at the site of the former Naval Station Puget Sound, on the Sand Point peninsula with Pontiac and Wolf bays that juts into Lake Washington in northeast Seattle.

University Village is a shopping mall in northeastern Seattle, Washington, United States, located in the south corner of the Ravenna neighborhood to the north of the Downtown area. It is an open-air shopping center which offers restaurants, locally owned boutiques, and national retailers, and is a popular retail destination in the region for home furnishings, popular fashions, gift items, and restaurants. It is currently owned by multimillionaire Stuart Sloan.

Washington Park is a public park in Seattle, Washington, United States, most of which is taken up by the Washington Park Arboretum, a joint project of the University of Washington, the Seattle Parks and Recreation, and the nonprofit Arboretum Foundation. Washington Park also includes a playfield and the Seattle Japanese Garden in its southwest corner. To the north is Union Bay; to the west are Montlake and Madison Valley; to the south is the Washington Park neighborhood; and to the east is the Broadmoor Golf Club.

The Industrial District is a neighborhood and the principal industrial area of Seattle, Washington. It is bounded on the west by the Duwamish River and Elliott Bay, beyond which lies Delridge of West Seattle; on the east by Interstate 5, beyond which lies Beacon Hill; on the north by S King and S Dearborn Streets, beyond which lie Pioneer Square and southwest International District of Downtown; and on the south by the main lines of the BNSF Railway and Union Pacific Railroad, or about S Lucille Street, beyond which is Georgetown. SoDo is the name of the northwest portion of the neighborhood, named for its being South of Downtown. SoDo is the location of T-Mobile Park, home of the Seattle Mariners, and Lumen Field, home of the Seattle Seahawks and Seattle Sounders FC. Lumen Field was also the site of the former Kingdome.

Ravenna is a neighborhood in northeastern Seattle, Washington named after Ravenna, Italy. Though Ravenna is considered a residential neighborhood, it also is home to several businesses, many of which are located in the University Village, a shopping mall.

Lake City is a neighborhood and the northeast region of Seattle, centered along Lake City Way NE (SR-522), 7–8 miles (11–13 km) northeast of downtown Seattle. A broader definition of the Lake City area includes all the land between 15th Avenue NE and Lake Washington, and between NE 95th and 98th streets to the Seattle city limits at NE 145th Street. Lake City encompasses much of the Thornton Creek watershed, the focus of a long restoration campaign by citizens and Seattle Public Utilities staff to enhance the residential environment of Lake City.
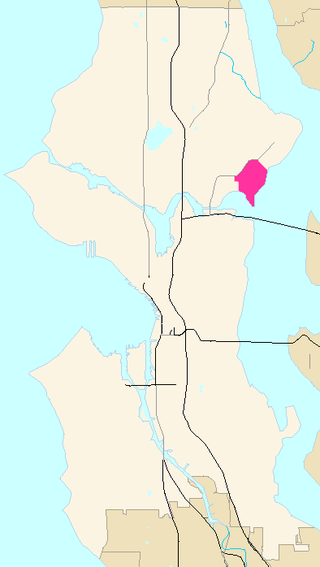
Laurelhurst is a residential neighborhood in northeastern Seattle, Washington, US. It is bounded on the northeast by Ivanhoe Place N.E., beyond which is Windermere; on the northwest by Sand Point Way N.E. and N.E. 45th Street, beyond which are Hawthorne Hills, Ravenna, and University Village; on the west by Mary Gates Memorial Drive N.E., beyond which is the East Campus of the University of Washington; on the southwest by Union Bay; and on the east by Lake Washington. Seattle Children's Hospital is located in its northwest corner. Once a seasonal campground of the Duwamish people, the neighborhood has been a part of Seattle since its annexation in 1910.

Licton Springs or North College Park is a neighborhood in the informal Northgate district of North Seattle. It is bounded by Interstate 5 to the east, beyond which is Maple Leaf neighborhood and the Northgate Mall; Aurora Avenue N to the west, beyond which is Greenwood; N 85th Street to the south, beyond which is Green Lake, and N Northgate Way to the north, beyond which is Haller Lake.

Matthews Beach is a neighborhood in Seattle, Washington; it and Meadowbrook are the southern neighborhoods of the annexed township of Lake City (1954). Matthews Beach lies about 2 miles (3.2 km) northeast of the University of Washington, about 8 miles (13 km) northeast of Downtown.

Rainier Beach is a set of neighborhoods in Seattle, Washington that are mostly residential. Also called Atlantic City, Rainier Beach can include Dunlap, Pritchard Island, and Rainier View neighborhoods.

Meadowbrook is a neighborhood in the Lake City district of Seattle, Washington. Meadowbrook is centered on open fields adjacent to the Community Center, Meadowbrook swimming pool, and Nathan Hale High School. It is bounded on the south by NE 95th Street and the Wedgwood neighborhood, on the north by NE 120th Street and Cedar Park, on the west by Lake City Way NE and Victory Heights, and on the east by 35th Avenue NE and Matthews Beach.

Cheshiahud and his family on Lake Union, Seattle, Washington, in the 1880s are, along with Princess Angeline, among the few late-19th century Dkhw'Duw'Absh about whom a little is known. In the University of Washington (UW) Library image archives, he is called Chudups John or Lake Union John. His family were among the few of the Duwamish people who did not move from Seattle to the Port Madison Reservation or other reservations. They lived on Portage Bay, part of Lake Union, when a photo was taken around 1885. According to the Duwamish Tribe, Lake John had a cabin and potato patch at the foot of Shelby Street. A commemorative plaque of unknown reliability is said to exist at the eastern foot of Shelby. This land was given to him by Seattle pioneer David Denny or the property was purchased—see below. Photographer Orion O. Denny recorded Old Tom and Madeline, c. 1904, further noted in the UW Library archives as Madeline and Old John, also known as Indian John or Cheshishon, who had a house on Portage Bay in the 1900s, south of what is now the UW campus although native people had been prohibited from residence in Seattle since the mid-1860s.
In the history of Seattle before white settlement, thirteen prominent villages existed in what is now the city of Seattle. The people living near Elliott Bay, and along the Duwamish, Black and Cedar Rivers were collectively known as the doo-AHBSH, or People of the Doo ("Inside"). Four prominent villages existed near what is now Elliott Bay and the (then-estuarial) lower Duwamish River. Before civil engineers rechanneled the Duwamish, the area had extensive tidelands, and had an abundance of seafoods.
The region now known as Seattle has been inhabited since the end of the last glacial period. Archaeological excavations at West Point in Discovery Park, Magnolia confirm that the Seattle area has been inhabited by humans for at least 4,000 years and probably much longer. West Point was called Oka-dz-elt-cu, Per-co-dus-chule, or Pka-dzEltcu. The village of tohl-AHL-too had been inhabited at least since the 6th century CE, as had hah-AH-poos—"where there are horse clams"—at the then-mouth of the Duwamish River in what is now the Industrial District. The Lushootseed (Skagit-Nisqually)-speaking Salish Dkhw'Duw'Absh and Xacuabš —ancestors of today's Duwamish Tribe—occupied at least 17 villages in the mid-1850s and lived in some 93 permanent longhouses (khwaac'ál'al) along the lower Duwamish River, Elliott Bay, Salmon Bay, Portage Bay, Lake Washington, Lake Sammamish, and the Duwamish River tributaries, the Black and Cedar Rivers.
The Duwamish tribe is a Native American tribe in western Washington, and the indigenous people of metropolitan Seattle. The Duwamish tribe today includes the People of the Inside (Dxw'Dəw?Abš), for Elliott Bay environs today; and the People of the Large Lake (Xacuabš), for those around Lake Washington of today.

















