
United Nations Security Council Resolution 678, adopted on 29 November 1990, after reaffirming resolutions 660, 661, 662, 664, 665, 666, 667, 669, 670, 674 and 677, the council noted that despite all the United Nations efforts, Iraq continued to defy the Security Council.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1373, adopted unanimously on 28 September 2001, is a counterterrorism measure passed following the 11 September terrorist attacks on the United States. The resolution was adopted under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, and is therefore binding on all UN member states.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1718 was adopted unanimously by the United Nations Security Council on October 14, 2006. The resolution, passed under Chapter VII, Article 41, of the UN Charter, imposes a series of economic and commercial sanctions on the Democratic People's Republic of Korea in the aftermath of that nation's claimed nuclear test of October 9, 2006.
The ISIL (Da'esh) and Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee is a committee of the United Nations Security Council tasked with implementing international sanctions against the Islamic State and al-Qaeda. It was established as the Al-Qaida and Taliban Sanctions Committee on 15 October 1999, pursuant to Security Council Resolution 1267, which designated al-Qaeda and the Taliban as terrorist organizations. Following the creation of a separate Taliban Sanctions Committee on 17 June 2011, it was renamed the Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee. The scope of the sanctions regime was expanded to include the Islamic State on 17 December 2015 pursuant to Resolution 2253.
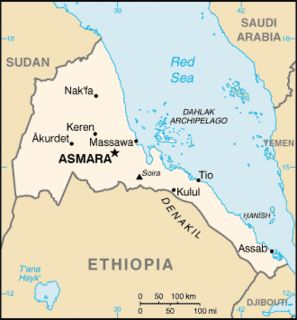
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1907, adopted on December 23, 2009, imposed an arms embargo on Eritrea, travel bans on its leaders, and froze the assets of some of the country's political and military officials after accusing the Eritrean government of aiding Al-Shabaab in Somalia and reportedly refusing to withdraw troops from its disputed border with Djibouti, following a conflict in 2008. The African Union and other organisations had been calling on the Security Council to sanction Eritrea for several months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1572, adopted unanimously on 15 November 2004, after recalling Resolution 1528 (2004) on the situation in Côte d'Ivoire, the council imposed an arms embargo on the country following recent violence and threatened further sanctions if Ivorian parties did not comply with their political commitments.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1952, adopted unanimously on November 29, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1807 (2008), 1857 (2008) and 1896 (2009), the Council renewed an arms embargo and related targeted sanctions for a further period until November 30, 2011.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1970 was a measure adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on 26 February 2011. It condemned the use of lethal force by the government of Muammar Gaddafi against protesters participating in the Libyan Civil War, and imposed a series of international sanctions in response.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1982, adopted unanimously on May 17, 2011, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Sudan, the Council extended the mandate of an expert panel monitoring the arms embargo and other sanctions against the country until February 19, 2012.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2014 was unanimously adopted on 21 October 2011.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1841 was unanimously adopted on 15 October 2008.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2231 was a 20 July 2015 resolution endorsing the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action on the nuclear program of Iran. It sets out an inspection process and schedule while also preparing for the removal of United Nations sanctions against Iran. The 15 nations on the Security Council unanimously endorsed the resolution, which had been negotiated by the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—plus Germany, the European Union, and Iran.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2249 was unanimously adopted on 20 November 2015. It notably calls upon all Member States to redouble their efforts against both ISIL and the al-Nusra Front as well as other al-Qaeda affiliates as designated by the Security Council.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2564 was unanimously adopted on 25 February 2021. It calls for a nationwide sanctions in Yemen. According to the resolution, the Security Council renews ban on destabilizing actors in Yemen, but Houthis reject latest resolution.

On 14 April 2015, the United Nations Security Council adopted Resolution 2216 on Yemen. Fourteen members of the Council voted in favor, while only Russian Federation abstained. The Resolution imposed "sanctions on individuals undermining the stability of Yemen, calling all Yemeni parties, in particular the Houthis, to end violence and refrain from further unilateral actions that threatened the political transition."

The United Nations Security Council Resolution 2201 was unanimously adopted on 15 February 2015. The Security Council condemned the actions of the Houthis and demanded them to withdraw from the state institutions and release Yemeni president Abdrabbo Mansour Hadi.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2624, adopted on 28 February 2022, extended for one year arms embargo on Yemen and sanctions including travel ban and asset freeze against those destabilizing the stability of the country. The security council also extended the mandate of the Panel of Experts on Yemen.












