
In United Nations Security Council resolution 661, adopted on 6 August 1990, reaffirming Resolution 660 (1990) and noting Iraq's refusal to comply with it and Kuwait's right of self-defence, the Council took steps to implement international sanctions on Iraq under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter. This was the second resolution by the Security Council over the invasion of Kuwait.

The Internal Settlement was an agreement which was signed on 3 March 1978 between Prime Minister of Rhodesia Ian Smith and the moderate African nationalist leaders comprising Bishop Abel Muzorewa, Ndabaningi Sithole and Senator Chief Jeremiah Chirau. After almost 15 years of the Rhodesian Bush War, and under pressure from the sanctions placed on Rhodesia by the international community, and political pressure from South Africa, the United Kingdom, and the United States, the Rhodesian government met with some of the internally based moderate African nationalist leaders in order to reach an agreement on the political future for the country.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1718 was adopted unanimously by the United Nations Security Council on October 14, 2006. The resolution, passed under Chapter VII, Article 41, of the UN Charter, imposes a series of economic and commercial sanctions on the Democratic People's Republic of Korea in the aftermath of that nation's claimed nuclear test of October 9, 2006.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 253, adopted unanimously on May 29, 1968, after reaffirming previous resolutions, the Council noted with concern that the measures taken so far have failed to bring the rebellion in Southern Rhodesia to an end and condemned the recent "inhuman executions carried out by the illegal regime in Southern Rhodesia which have flagrantly affronted the conscience of mankind". After further condemning the regime and calling upon the United Kingdom to end the rebellion in Southern Rhodesia the Council decided that all member states would:

United Nations Security Council Resolution 288, adopted unanimously on November 17, 1970, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the topic, the Council called upon the United Kingdom, as the legal administering Power of Southern Rhodesia, to bring an end to the illegal rebellion. The Council decided that the present sanctions against Rhodesia would remain in place and urged all states to implement all pertinent resolutions and not to grant any form of recognition to the regime.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 314, adopted on February 28, 1972, concerned that certain states were not complying with resolution 253, the Council decided that the sanctions against Southern Rhodesia set out in 253 would remain fully in force. It also urged all states to implement fully resolution 253 and declared that any legislation passed or act taken by any state with a view to permitting the importation of any commodity from Southern Rhodesia falling into the scope of 253 would undermine the sanctions and be contrary to the state's obligations under the United Nations Charter.

United Nations Security Council resolution 591, adopted unanimously on 28 November 1986, after recalling resolutions 418 (1977), 421 (1977), 473 (1980) and 558 (1984), the Council strengthened the mandatory arms embargo against apartheid South Africa imposed by Resolution 418, and made it more comprehensive. Resolution 591 sought to clarify vague terms from previous resolutions on the topic.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 320, adopted on 29 September 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions, the Council expressed concern that despite the previous resolutions, several states were covertly and overtly violating the sanctions on Southern Rhodesia. The Council requested that the committee which had been established in resolution 253, consider the type of action which should be taken "in view of the open and persistent refusal of South Africa and Portugal to implement sanctions" and asked for the report no later than 31 January 1973.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 388, adopted unanimously on April 6, 1976, reaffirmed previous resolutions on the topic, including the conclusion that the situation in Rhodesia constituted a threat to international peace and security. The council decided to expand its sanctions regime to include;

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1874 was adopted unanimously by the United Nations Security Council on 12 June 2009. The resolution, passed under Chapter VII, Article 41, of the UN Charter, imposes further economic and commercial sanctions on the Democratic People's Republic of Korea and encourages UN member states to search North Korean cargo, in the aftermath of an underground nuclear test conducted on 25 May 2009.
United Nations Security Council resolution 460, adopted on 21 December 1979, after taking note of the Lancaster House Agreement, the council decided to terminate measures taken against Southern Rhodesia in resolutions 232 (1966) and 253 (1968) and any subsequent resolutions. The resolution deplored the "loss of life, waste and suffering" over the past 14 years caused by the rebellion in southern Rhodesia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 463, adopted on 2 February 1980, after considering the latest developments in Southern Rhodesia and Resolution 460 (1979) in which it was noted that an agreement had produced a Constitution for a free and independent Zimbabwe and majority rule, the Council called on all parties to comply with the Lancaster House Agreement and the administering power, the United Kingdom, to fully implement the agreement.

United Nations Security Council resolution 787, adopted on 16 November 1992, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on the topic, the council called upon the parties in Bosnia and Herzegovina to consider the draft outline constitution as a basis for negotiating a political settlement of the conflict in the country, and went on to impose further international sanctions on the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 864, adopted unanimously on 15 September 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993), 834 (1993) and 851 (1993), the Council noted the continuing situation in Angola and went on to condemn and place international sanctions on UNITA.
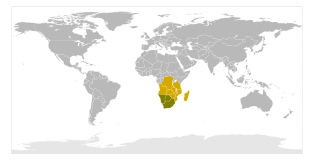
United Nations Security Council resolution 1295, adopted unanimously on 18 April 2000, after reaffirming Resolution 864 (1993) and all subsequent resolutions on Angola, particularly resolutions 1127 (1997), 1173 (1998) and 1237 (1999), the Council authorised a tightening of sanctions against UNITA and established a panel of experts to investigation violations of Security Council resolutions imposing measures against UNITA.

United Nations Security Council resolution 917, adopted unanimously on 6 May 1994, after recalling resolutions 841 (1993), 861 (1993), 862 (1993), 867 (1993), 873 (1993) and 875 (1993) and 905 (1994) on the situation in Haiti, the Council imposed further international sanctions on the country after the military authorities refused to implement the Governors Island Agreement to hand over power and instances of violations of human rights.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1409, adopted unanimously on 14 May 2002, after recalling all previous resolutions on Iraq, including resolutions 986 (1995), 1284 (1999), 1352 (2001), 1360 (2001) and 1382 (2001) concerning the Oil-for-Food Programme, the Council extended provisions relating to the export of Iraqi petroleum or petroleum products in return for humanitarian aid for a further 180 days and approved a list of revised sanctions against the country. Its adoption streamlined the sanctions program, with restrictions on shipping civilian goods to Iraq lifted though prohibitions on weapons and military goods remained.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1454, adopted on 30 December 2002, after recalling all previous resolutions on Iraq, including resolutions 661 (1991), 986 (1995), 1284 (1999), 1352 (2001), 1360 (2001), 1382 (2001), 1409 (2002) and 1447 (2002) concerning the Oil-for-Food Programme, the council adjusted the list of restricted goods and procedures for its implementation under the Oil-for-Food Programme. It was the final Security Council resolution adopted in 2002.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1689, adopted unanimously on June 20, 2006, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Liberia and West Africa, the Council decided to continue sanctions against the import of diamonds from the country for six months, though similar restrictions relating to timber imports were lifted.













