
South West Africa was a territory under South African administration from 1915 to 1966, and under South African occupation from 1966 to 1990. Renamed Namibia by the United Nations in 1968, it became independent under this name on 21 March 1990.
The history of Namibia has passed through several distinct stages from being colonised in the late nineteenth century to Namibia's independence on 21 March 1990.

A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".

A United Nations resolution is a formal text adopted by a United Nations (UN) body. Although any UN body can issue resolutions, in practice most resolutions are issued by the Security Council or the General Assembly, in the form of United Nations Security Council resolutions and United Nations General Assembly resolutions, respectively.
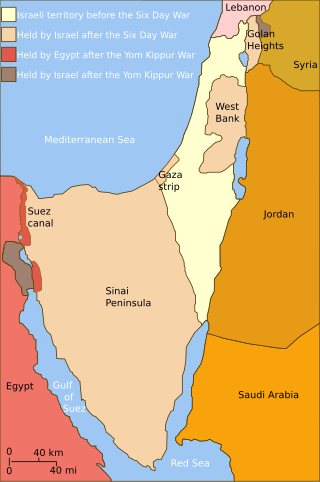
United Nations Security Council Resolution 338 was a three-line resolution adopted by the UN Security Council on 22 October 1973, which called for a ceasefire in the Yom Kippur War in accordance with a joint proposal by the United States and the Soviet Union. It was passed at the 1747th Security Council meeting by 14 votes to none, with China abstaining.

The United Nations Transition Assistance Group (UNTAG) was a United Nations (UN) peacekeeping force deployed from April 1989 to March 1990 in Namibia, known at the time as South West Africa, to monitor the peace process and elections there. Namibia had been occupied by South Africa since 1915, first under a League of Nations mandate and later illegally. Since 1966, South African forces had been combating an insurgency by the People's Liberation Army of Namibia (PLAN), the military wing of the Namibian-nationalist South West African People's Organization (SWAPO). The UN Security Council passed Resolution 435 in 1978, which set out a plan for elections administered by South Africa but under UN supervision and control after a ceasefire. However, only in 1988 were the two parties able to agree to a ceasefire. As UNTAG began to deploy peacekeepers, military observers, police, and political workers, hostilities were briefly renewed on the day the transition process was supposed to begin. After a new round of negotiations, a second date was set and the elections process began in earnest. Elections for the constitutional assembly took place in November 1989. They were peaceful and declared free and fair; SWAPO won a majority of the seats. The new constitution was adopted four months later and it was followed by Namibia's official independence and the successful conclusion of UNTAG.
Chapter VI of the United Nations Charter deals with peaceful settlement of disputes. It requires countries with disputes that could lead to war to first of all try to seek solutions through peaceful methods such as "negotiation, enquiry, mediation, conciliation, arbitration, judicial settlement, resort to regional agencies or arrangements, or other peaceful means of their own choice." If these methods of alternative dispute resolution fail, then they must refer it to the UN Security Council. Under Article 35, any country is allowed to bring a dispute to the attention of the UN Security Council or the General Assembly. This chapter authorizes the Security Council to issue recommendations but does not give it power to make binding resolutions; those provisions are contained in Chapter VII. Chapter VI is analogous to Articles 13-15 of the Covenant of the League of Nations which provide for arbitration and for submission of matters to the Council that are not submitted to arbitration. United Nations Security Council Resolution 47 and United Nations Security Council Resolution 242 are two examples of Chapter VI resolutions which remain unimplemented.

Louis Alexander Pienaar was a South African lawyer and diplomat. He was the last white Administrator of South-West Africa, from 1985 through Namibian independence in 1990. Pienaar later served as a minister in F W de Klerk's government until 1993. He married Isabel Maud van Niekerk on 11 December 1954.
United Nations Commissioner for South West Africa was a post created by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 1966 to assert the UN's direct responsibility for South West Africa which was then under illegal occupation by apartheid South Africa.
The Western Contact Group (WCG), representing three of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council - France, United Kingdom and United States - and including Canada and West Germany, launched a joint diplomatic effort in 1977 to bring an internationally acceptable transition to independence for Namibia, after a decade of illegal occupation by apartheid of South Africa.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 435, adopted on September 29, 1978, put forward proposals for a cease-fire and UN-supervised elections in South African-controlled South West Africa which ultimately led to the independence of Namibia. Importantly, it established the United Nations Transition Assistance Group (UNTAG) which oversaw the election and the South African withdrawal.
The 1978 Settlement Proposal in Namibia, devised by the Contact Group of Western States, mandated the United Nations Transition Assistance Group (UNTAG) under United Nations Security Council Resolution 435 to assist a UN Special Representative appointed by the UN Secretary-General 'to ensure the early independence of Namibia through free and fair elections under the supervision and control of the United Nations'.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 393, adopted on July 30, 1976, after a letter from a representative from Zambia, the Council condemned a recent attack by South Africa in Zambian territory, resulting in the destruction of property and loss of life. The resolution went on to express concern at South Africa's occupation and use of South West Africa as a base for attacking neighbouring African countries, and that the continuation of this would constitute a threat to international peace and security.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 428, adopted unanimously on May 6, 1978, after hearing representations from the People's Republic of Angola, Zambia and the South West Africa People's Organisation (SWAPO), the Council reminded Member States to refrain from using threats and use of force in their international relations. Reiterating Resolution 387 (1976), the present resolution condemned South Africa for its armed invasion of Angola via South West Africa (Namibia).

United Nations Security Council resolution 629, adopted unanimously on 16 January 1989, after recalling resolutions 431 (1978), 435 (1978) and 628 (1989), the council noted that the parties to the Brazzaville Protocol agreed that 1 April 1989 be established as the date of the South African withdrawal from Angola and therefore lead the way to the independence of Namibia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 643, adopted unanimously on 31 October 1989, after reaffirming resolutions 435 (1978) and 629 (1989), 632 (1989) and 640 (1989), as well as noting a report by the Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar, the council expressed its full intention to implement Resolution 435 of 29 September 1978 regarding the situation in Namibia.

The Australian Services Contingent was the Australian Army contribution to the United Nations Transition Assistance Group (UNTAG) peacekeeping mission to Namibia in 1989 and 1990. Australia sent two contingents of over 300 engineers each to assist the Special Representative of the Secretary General, Martti Ahtisaari, in overseeing free and fair elections in Namibia for a Constituent Assembly in what was the largest deployment of Australian troops since the Vietnam War.
Operation Merlyn was a military operation by the South African Defence Force (SADF), South West African Territorial Force (SWATF) and South West African Police (SWAPOL) during the South African Border War and Angolan Civil War in April 1989. The aim of the operation was to prevent the incursion of PLAN (SWAPO) insurgents into South West Africa/Namibia from bases in Angola. These incursions were in violation of a ceasefire which came into effect on 1 April 1989 via the implementation of United Nations Security Council Resolution 435 and the Tripartite Accord. Initially, these PLAN incursions were tackled by South West African police units and eventually by SADF and SWATF units, released to assist the police having been confined to their bases by the peace agreements. These incursions and the conflict that occurred ended after hastily arranged talks resulted in the Mount Etjo Declaration and an eventual ceasefire.
The Namibia exception identifies the advisory opinion issued on 21 June 1971 by the International Court of Justice (I.C.J), the principal judicial organ of the United Nations (UN). The opinion refers to the "Legal Consequences for States of the Continued Presence of South Africa in Namibia notwithstanding Security Council Resolution 276 (1970)".

Mexico and Namibia established diplomatic relations in 1990. Both nations are members of the United Nations.










