Related Research Articles
Behavior or behaviour is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary.

Marketing is the act of satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of business management and commerce.
Marketing research is the systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of qualitative and quantitative data about issues relating to marketing products and services. The goal is to identify and assess how changing elements of the marketing mix impacts customer behavior.

Psychological pricing is a pricing and marketing strategy based on the theory that certain prices have a psychological impact. In this pricing method, retail prices are often expressed as just-below numbers: numbers that are just a little less than a round number, e.g. $19.99 or £2.98. There is evidence that consumers tend to perceive just-below prices as being lower than they are, tending to round to the next lowest monetary unit. Thus, prices such as $1.99 may to some degree be associated with spending $1 rather than $2. The theory that drives this is that pricing practices such as this cause greater demand than if consumers were perfectly rational. Psychological pricing is one cause of price points.
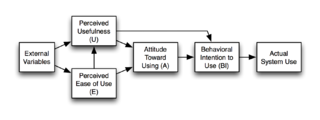
The technology acceptance model (TAM) is an information systems theory that models how users come to accept and use a technology.

Consumer behaviour is the study of individuals, groups, or organisations and all the activities associated with the purchase, use and disposal of goods and services. Consumer behaviour consists of how the consumer's emotions, attitudes, and preferences affect buying behaviour. Consumer behaviour emerged in the 1940–1950s as a distinct sub-discipline of marketing, but has become an interdisciplinary social science that blends elements from psychology, sociology, social anthropology, anthropology, ethnography, ethnology, marketing, and economics.
Marketing communications refers to the use of different marketing channels and tools in combination. Marketing communication channels focus on how businesses communicate a message to their desired market, or the market in general. It is also in charge of the internal communications of the organization. Marketing communication tools include advertising, personal selling, direct marketing, sponsorship, communication, public relations, social media, customer journey and promotion.
As part of consumer behavior, the buying decision process is the decision-making process used by consumers regarding the market transactions before, during, and after the purchase of a good or service. It can be seen as a particular form of a cost–benefit analysis in the presence of multiple alternatives.

Mental accounting is a model of consumer behaviour developed by Richard Thaler that attempts to describe the process whereby people code, categorize and evaluate economic outcomes. Mental accounting incorporates the economic concepts of prospect theory and transactional utility theory to evaluate how people create distinctions between their financial resources in the form of mental accounts, which in turn impacts the buyer decision process and reaction to economic outcomes. People are presumed to make mental accounts as a self control strategy to manage and keep track of their spending and resources. People budget money into mental accounts for savings or expense categories. People also are assumed to make mental accounts to facilitate savings for larger purposes. Mental accounting can result in people demonstrating greater loss aversion for certain mental accounts, resulting in cognitive bias that incentivizes systematic departures from consumer rationality. Through an increased understanding of mental accounting differences in decision making based on different resources, and different reactions based on similar outcomes can be greater understood.
In marketing and consumer behaviour, brand loyalty describes a consumer's persistent positive feelings towards a familiar brand and their dedication to purchasing the brand's products and/or services repeatedly regardless of deficiencies, a competitor's actions, or changes in the market environment. It can also be demonstrated with other behaviors such as positive word-of-mouth advocacy. Corporate brand loyalty is where an individual buys products from the same manufacturer repeatedly and without wavering, rather than from other suppliers. Loyalty implies dedication and should not be confused with habit, its less-than-emotional engagement and commitment. Businesses whose financial and ethical values rest in large part on their brand loyalty are said to use the loyalty business model.
Neuromarketing is a commercial marketing communication field that applies neuropsychology to market research, studying consumers' sensorimotor, cognitive, and affective responses to marketing stimuli. The potential benefits to marketers include more efficient and effective marketing campaigns and strategies, fewer product and campaign failures, and ultimately the manipulation of the real needs and wants of people to suit the needs and wants of marketing interests.
Buyer's remorse is the sense of regret after having made a purchase. It is frequently associated with the purchase of an expensive item such as a vehicle or real estate.
Deal-of-the-day is an ecommerce business model in which a website offers a single product for sale for a period of 24 to 36 hours. Potential customers register as members of the deal-a-day websites and receive online offers and invitations by email or social networks.
Customer engagement is an interaction between an external consumer/customer and an organization through various online or offline channels. According to Hollebeek, Srivastava and Chen, customer engagement is "a customer’s motivationally driven, volitional investment of operant resources, and operand resources into brand interactions," which applies to online and offline engagement.
A target market, also known as serviceable obtainable market (SOM), is a group of customers within a business's serviceable available market at which a business aims its marketing efforts and resources. A target market is a subset of the total market for a product or service.

Ayelet Gneezy is an associate professor of marketing at the Rady School of Management, UC San Diego.
A consumer-brand relationship, also known as a brand relationship, is the relationship that consumers think, feel, and have with a product or company brand. For more than half a century, scholarship has been generated to help managers and stakeholders understand how to drive favorable brand attitudes, brand loyalty, repeat purchases, customer lifetime value, customer advocacy, and communities of like-minded individuals organized around brands. Research has progressed with inspiration from attitude theory and, later, socio-cultural theories, but a perspective introduced in the early 1990s offered new opportunities and insights. The new paradigm focused on the relationships that formed between brands and consumers: an idea that had gained traction in business-to-business marketing scholarship where physical relationships formed between buyers and sellers.

Lynn R. Kahle is an American consumer psychologist and Professor Emeritus at the University of Oregon's Lundquist College of Business. From 2018 to 2020 he taught at the Lubin School of Business, Pace University in New York as a visiting scholar and professor.
Richard Paul Bagozzi is an Italian American behavioral and social scientist most known for his work in theory, methodology and empirical research. He is the Dwight F. Benton Professor Emeritus of Marketing at the University of Michigan.
Consumer value is used to describe a consumer's strong relative preference for certain subjectively evaluated product or service attributes.
References
- 1 2 "Utpal Dholakia". Jones Graduate School of Business at Rice University. April 7, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 "CV | Utpal Dholakia".
- 1 2 "Utpal Dholakia".
- ↑ "The Science Behind Behavior". Psychology Today.
- 1 2 "U. Dholakia". www.journals.elsevier.com.
- ↑ "Journal of Marketing". SAGE Publications Inc. July 4, 2018.
- ↑ "Journal of Public Policy & Marketing". 7 July 2018.
- ↑ "Scopus preview - Scopus - Author details (Dholakia, Utpal M.)". www2.scopus.com.
- ↑ "Utpal Dholakia - Google Scholar Citations". scholar.google.com.
- ↑ "Goal Setting and Goal Striving in Consumer Behavior".
- ↑ "The Scope and Persistence of Mere-Measurement Effects: Evidence from a Field Study of Customer Satisfaction Measurement".
- ↑ Bagozzi, Richard P.; Dholakia, Utpal M. (January 1, 2002). "Intentional social action in virtual communities". Journal of Interactive Marketing. 16 (2): 2–21. doi:10.1002/dir.10006. S2CID 144776087.
- ↑ Dholakia, Utpal M.; Bagozzi, Richard P.; Pearo, Lisa Klein (September 1, 2004). "A social influence model of consumer participation in network- and small-group-based virtual communities". International Journal of Research in Marketing. 21 (3): 241–263. doi:10.1016/j.ijresmar.2003.12.004.
- ↑ Tam, Leona; Dholakia, Utpal M. (March 1, 2011). "Delay and duration effects of time frames on personal savings estimates and behavior". Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes. 114 (2): 142–152. doi:10.1016/j.obhdp.2010.10.009.
- ↑ Tam, L.; Dholakia, U. (2014). "Saving in cycles: how to get people to save more money" (PDF). Psychological Science. 25 (2): 531–7. doi:10.1177/0956797613512129. PMID 24357616. S2CID 11551274. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-02-17.
- ↑ Dholakia, Utpal; Tam, Leona; Yoon, Sunyee; Wong, Nancy (June 1, 2016). "The Ant and the Grasshopper: Understanding Personal Saving Orientation of Consumers". Journal of Consumer Research. 43 (1): 134–155. doi:10.1093/jcr/ucw004 – via academic.oup.com.
- ↑ Greenburg, Zack O'Malley. "Groupon: Good For You, Bad For Business?". Forbes.
- ↑ arXiv, Emerging Technology from the. "Groupon, Daily Deals and the Complex Question of Business Failure". MIT Technology Review.
- ↑ Takahashi, Paul (January 31, 2019). "Francesca's CEO resigns as Houston retailer explores potential sale". HoustonChronicle.com.
- ↑ Dizik, Alina. "Small Businesses Are Returning to Groupon". WSJ.
- ↑ "IJRM-EMAC Steenkamp Award". Archived from the original on 2019-04-27. Retrieved 2019-08-26.