The V-2 rocket was a German early ballistic missile of World War II.
Contents
- Vehicles, craft, and ships
- Engines
- Biology
- Science and technology
- The arts
- Businesses and products
- Other
- See also
V2 or V-2 may also refer to:
The V-2 rocket was a German early ballistic missile of World War II.
V2 or V-2 may also refer to:
C5, C05, C V or C-5 may refer to:
O2, O-2, o2, or similar orthography may refer to:
D2, D02, D.II, D II or D-2 may refer to:
M2, M-2, M.2 or M02 may refer to:
A2, A02, A002, A², A.II or A-2 may refer to:
A3, A03 or A.III may refer to:
A7, A.7, A 7, A07 or A-7 may refer to:
N1, N.I, N-1, or N01 may refer to:
V1 can refer to the first version of anything.
A12, A.12 or A-12 may refer to:

A diesel–electric transmission, or diesel–electric powertrain, is a transmission system powered by diesel engines for vehicles in road, rail, and marine transport. Diesel–electric transmission is similar to petrol–electric transmission, which is powered by petrol engines.
C2 or a derivative (C-2, C2, etc.) may refer to:
S2 or S II may refer to:
C1, C01, C.I or C-1 may refer to:
D3, D03, D.III, D III or D-3 may refer to:
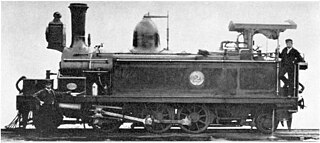
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Prairie.
i2, I-2, I 2 or I2 may refer to:
D4, D.IV, d4 or variants may refer to:

The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) Class V2 2-6-2 steam locomotives were designed by Sir Nigel Gresley for express mixed traffic work, and built at the LNER shops at Doncaster and Darlington between 1936 and 1944. The best known is the first of the class, 4771 Green Arrow, which is the sole survivor of the class.

The S-class or Srednyaya submarines were part of the Soviet Navy's underwater fleet during World War II. Unofficially nicknamed Stalinets, boats of this class were the most successful and achieved the most significant victories among all Soviet submarines. In all, they sank 82,770 gross register tons (GRT) of merchant shipping and seven warships, which accounts for about one-third of all tonnage sunk by Soviet submarines during the war.