
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating the body's adaptive immunity, they help prevent sickness from an infectious disease. When a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been vaccinated, herd immunity results. Herd immunity protects those who may be immunocompromised and cannot get a vaccine because even a weakened version would harm them. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the elimination of diseases such as polio and tetanus from much of the world. However, some diseases, such as measles outbreaks in America, have seen rising cases due to relatively low vaccination rates in the 2010s – attributed, in part, to vaccine hesitancy.
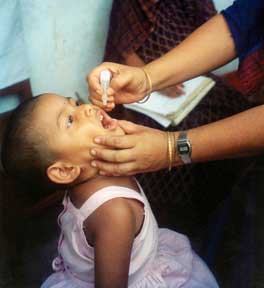
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all children be fully vaccinated against polio. The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the world, and reduced the number of cases reported each year from an estimated 350,000 in 1988 to 33 in 2018.

A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, collectively referred to as the cutis. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be abbreviated as SC, SQ, sub-cu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut.Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors.

Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have larger and more numerous blood vessels than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster absorption than subcutaneous or intradermal injections. Medication administered via intramuscular injection is not subject to the first-pass metabolism effect which affects oral medications.
Vaccine hesitancy is a delay in acceptance, or refusal of vaccines despite the availability of vaccine services. The term covers outright refusals to vaccinate, delaying vaccines, accepting vaccines but remaining uncertain about their use, or using certain vaccines but not others. The scientific consensus that vaccines are generally safe and effective is overwhelming. Vaccine hesitancy often results in disease outbreaks and deaths from vaccine-preventable diseases. Therefore, the World Health Organization characterizes vaccine hesitancy as one of the top ten global health threats.

The International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), also known as the Carte Jaune or Yellow Card, is an official vaccination report created by the World Health Organization (WHO). As a travel document, it is a kind of medical passport that is recognised internationally and may be required for entry to certain countries where there are increased health risks for travellers.
Feline vaccination is animal vaccination applied to cats. Vaccination plays a vital role in protecting cats from infectious diseases, some of which are potentially fatal. They can be exposed to these diseases from their environment, other pets, or even humans.

COVID-19 vaccination in Switzerland is an ongoing immunization campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country.

Israel's COVID-19 vaccination programme, officially named "Give a Shoulder", began on 19 December 2020, and has been praised for its speed, having given twenty percent of the Israeli population the first dose of the vaccines' two dose regimen in the span of three weeks.

The National COVID-19 Immunisation Programme, abbreviated as NIP or PICK, is a national vaccination campaign that is currently being implemented by the Malaysian government as an approach in curbing the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and to end the COVID-19 pandemic in Malaysia by successfully achieving the highest immunisation rate among its citizens and non-citizens that are residing in Malaysia. It is the largest immunisation programme implemented in the history of the country and it is being administrated by The Special Committee For Ensuring Access To COVID-19 Vaccine Supply (JKJAV) since early 2021.

The COVID-19 vaccination campaign in the United States is an ongoing mass immunization campaign for the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first granted emergency use authorization to the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine on December 10, 2020; mass vaccinations began on December 14, 2020. The Moderna vaccine was granted emergency use authorization on December 17, 2020, and the Janssen vaccine was granted emergency use authorization on February 27, 2021. By April 19, 2021, all U.S. states had opened vaccine eligibility to residents aged 16 and over. On May 10, 2021, the FDA approved the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for adolescents aged 12 to 15. On August 23, 2021, the FDA granted full approval to the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine for individuals aged 16 and over.
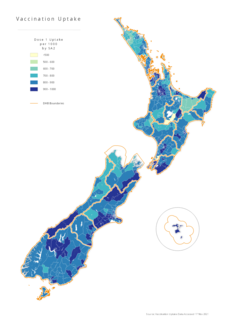
COVID-19 vaccination in New Zealand began on 20 February 2021, and will continue throughout the pandemic with the goal of vaccinating all willing New Zealanders aged 5 or older. Those aged 5 to 11 require a parent, caregiver or legal guardian accompany them to their appointment and provide consent for them to be vaccinated. As of 1 September, anyone in New Zealand, regardless of their immigration status, is eligible to be vaccinated.

A COVID-19 vaccine card is a record often given to those who have received a COVID-19 vaccine showing information such as the date(s) one has received the shot(s) and the brand of vaccine one has received, sometimes including the lot number. The card also contains information identifying the recipient and the location where the shot was given. Depending on the country, it could serve as an official document verifying one has received vaccination, which could be required by some institutions, such as a school or workplace, when boarding a cruise ship, or when crossing an international border, as proof that one has been vaccinated.

The COVID-19 vaccination campaign in Ukraine is an ongoing mass immunization campaign for the COVID-19 pandemic in Ukraine.

COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in the United States is the sociocultural phenomenon of individuals refusing or displaying hesitance towards receiving the COVID-19 vaccine. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in the United States can be considered as part of the broader history of vaccine hesitancy.

Anti-vaccination activists and other people in many countries have spread a variety of unfounded conspiracy theories and other misinformation about COVID-19 vaccines based on misunderstood or misrepresented science, religion, exaggerated claims about side effects, a story about COVID-19 being spread by 5G, misrepresentations about how the immune system works and when and how COVID-19 vaccines are made, and other false or distorted information. This misinformation has proliferated and may have made many people averse to vaccination. This has led to governments and private organisations around the world introducing measures to incentivize/coerce vaccination, such as lotteries, mandates and free entry to events, which has in turn led to further misinformation about the legality and effect of these measures themselves.

COVID-19 vaccine mandates have been enacted by numerous states and municipalities in the United States, and also by private entities. In September 2021, President Joe Biden announced that the federal government would take steps to mandate COVID-19 vaccination for certain entities under the authority of the federal government or federal agencies.
The Biden Administration COVID-19 action plan, also called the Path out of the Pandemic, is a substantial increase in the use of vaccination mandates as part of the U.S. federal government response to the COVID-19 pandemic announced by President Joe Biden on September 9, 2021, to be carried out by officials in the Biden administration. The plan included various announced prospective efforts, as well as the issuance of several executive orders.
My Vaccine Pass is a vaccine certificate issued by the New Zealand Government that serves as an official record of one's COVID-19 vaccination status. The vaccine pass is required to enter hospitality venues, community, sport and faith-based gatherings, as a result of the COVID-19 Protection Framework having come into effect on 3 December 2021.

The COVID-19 Response (Vaccinations) Legislation Act 2021 is an Act of Parliament to provide a legal framework for the New Zealand Government's COVID-19 Protection Framework and vaccination mandates. The bill was introduced under urgency and passed in law on 23 November 2021. While the bill was supported by the Labour Government and their Green coalition partners, it was opposed by the opposition National, ACT, and Māori parties, which criticised the rushed and divisive nature of the legislation and claimed that vulnerable communities would be adversely affected.











