Vadym Slyusar | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 15 October 1964 (age 60) |
| Nationality | Ukrainian |
| Citizenship | Ukraine |
| Alma mater | Orenburg Air Defense high military school |
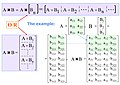
| Known for | Digital antenna array |
| Awards | Honored Scientist and Technician of Ukraine (2008) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Antenna theory Radar signal processing |
| Institutions | Central Scientific Research Institute of Armament and Military Equipment of the Armed Forces of Ukraine |
| Doctoral advisor | 17 Persons |
Vadym Slyusar (born 15 October 1964, vil. Kolotii, Reshetylivka Raion, Poltava region, Ukraine) is a Soviet and Ukrainian scientist, Professor, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Honored Scientist and Technician of Ukraine, founder of tensor-matrix theory of digital antenna arrays (DAAs), N-OFDM and other theories in fields of radar systems, smart antennas for wireless communications and digital beamforming.