Related Research Articles
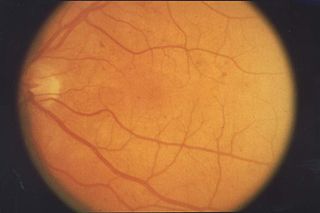
Retinopathy is any damage to the retina of the eyes, which may cause vision impairment. Retinopathy often refers to retinal vascular disease, or damage to the retina caused by abnormal blood flow. Age-related macular degeneration is technically included under the umbrella term retinopathy but is often discussed as a separate entity. Retinopathy, or retinal vascular disease, can be broadly categorized into proliferative and non-proliferative types. Frequently, retinopathy is an ocular manifestation of systemic disease as seen in diabetes or hypertension. Diabetes is the most common cause of retinopathy in the U.S. as of 2008. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working-aged people. It accounts for about 5% of blindness worldwide and is designated a priority eye disease by the World Health Organization.
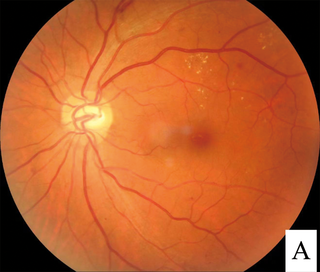
Diabetic retinopathy, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes mellitus. It is a leading cause of blindness in developed countries.

The National Eye Institute (NEI) is part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The mission of NEI is “to eliminate vision loss and improve quality of life through vision research.” NEI consists of two major branches for research: an extramural branch that funds studies outside NIH and an intramural branch that funds research on the NIH campus in Bethesda, Maryland. Most of the NEI budget funds extramural research.

In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.

In biology and other experimental sciences, an in silico experiment is one performed on computer or via computer simulation. The phrase is pseudo-Latin for 'in silicon', referring to silicon in computer chips. It was coined in 1987 as an allusion to the Latin phrases in vivo, in vitro, and in situ, which are commonly used in biology. The latter phrases refer, respectively, to experiments done in living organisms, outside living organisms, and where they are found in nature.
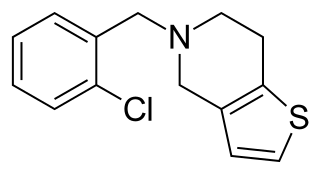
Ticlopidine, sold under the brand name Ticlid, is a medication used to reduce the risk of thrombotic strokes. It is an antiplatelet drug in the thienopyridine family which is an adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor inhibitor. Research initially showed that it was useful for preventing strokes and coronary stent occlusions. However, because of its rare but serious side effects of neutropenia and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura it was primarily used in patients in whom aspirin was not tolerated, or in whom dual antiplatelet therapy was desirable. With the advent of newer and safer antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel and ticagrelor, its use remained limited.

Electroretinography measures the electrical responses of various cell types in the retina, including the photoreceptors, inner retinal cells, and the ganglion cells. Electrodes are placed on the surface of the cornea or on the skin beneath the eye to measure retinal responses. Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) responses are measured with an EOG test with skin-contact electrodes placed near the canthi. During a recording, the patient's eyes are exposed to standardized stimuli and the resulting signal is displayed showing the time course of the signal's amplitude (voltage). Signals are very small, and typically are measured in microvolts or nanovolts. The ERG is composed of electrical potentials contributed by different cell types within the retina, and the stimulus conditions can elicit stronger response from certain components.
Astex Pharmaceuticals ("Astex") is a biotechnology company focused on the discovery and development of drugs in oncology and diseases of the central nervous system. Astex was founded in 1999 by Sir Tom Blundell, Chris Abell & Harren Jhoti, and is located in Cambridge, England.
Takeda Oncology is a biopharmaceutical company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical.

Fenofibrate, is an oral medication of the fibrate class used to treat abnormal blood lipid levels. It is less commonly used compared than statins because it treats a different type of cholesterol abnormality to statins. While statins have strong evidence for reducing heart disease and death, there is evidence to suggest that fenofibrate also reduces to the risk of heart disease and death. However, this seems only to apply to specific populations of people with elevated triglyceride levels and reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Its use is recommended together with dietary changes.

Calcium dobesilate is a vasoprotective. It is the calcium salt of dobesilic acid. It is a synthetic molecule with the ability to reduce capillary permeability in the body. In Switzerland the drug is sold by the pharmaceutical company OM Pharma under the trade name of Doxium in capsules containing 500 mg of active ingredient.
Nuvelo Inc. was a biopharmaceutical company engaged in the discovery, development and commercialization of drugs for acute cardiovascular disease, cancer and other debilitating medical conditions. On January 27, 2009, the company was acquired by ARCA Biopharma, Inc. in a reverse takeover transaction.

Melior Discovery, Inc. is a private biopharmaceutical company based in Exton, Pennsylvania, USA. The company specializes in drug repositioning and has established a proprietary phenotypic screening platform that it uses for this purpose. Melior also offers certain contract research organization (CRO) services comprising animal models representing different disease conditions. The Company has issued press releases disclosing partnerships with Pfizer, Merck & Co., Johnson & Johnson, and AstraZeneca, all citing the use of the company’s drug repositioning technology. Melior Discovery has also used its technology to discover its own drug candidates.
AstridBio Ltd. is a privately held Biotechnology company with office in Hungary. AstridBio's focus is biobanking software development, data management and analysis for genomics research. Its clients include academic research institutes, pharmaceutical and biotech companies.
Santaris Pharma A/S was a biopharmaceutical company founded in 2003 in Copenhagen, Denmark. The company also had a branch in San Diego, California that opened in 2009. Created by a merger between Cureon and Pantheco, Santaris developed RNA-targeted medicines using a Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) Drug Platform and Drug Development Engine.
Schrödinger, Inc. is an international scientific software company that specializes in developing computational tools and software for drug discovery and materials science.
Roivant Sciences is a healthcare company focused on applying technology to drug development. Roivant builds subsidiary biotech and healthcare technology companies.

Setanaxib is an experimental orally bioavailable dual inhibitor of NADPH oxidase isoforms NOX4 and NOX1. Setanaxib is a member of the pyrazolopyridine dione chemical series. The compound is the only specific NOX inhibitor that has entered into clinical trials.
Insilico Medicine is a biotechnology company based in Pak Shek Kok, Hong Kong in Hong Kong Science Park near the Chinese University of Hong Kong and in New York, at The Cure by Deerfield. The company combines genomics, big data analysis, and deep learning for in silico drug discovery.
Ali Maximilian Ertürk is a neuroscientist, inventor, and artist living in Munich, Germany. He is the director of a new Helmholtz Institute on Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (iTERM) in Munich since July 2019 and professor at the medical faculty. After his undergraduate study at Bilkent University in Ankara, he joined Max-Planck-Institute for Neurobiology for his PhD and Genentech Inc. for postdoctoral research.
References
- ↑ Ward, Andrew. "Big pharma seeks digital solution to productivity problem". Financial Times. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ↑ Goodman, Michael. "Verseon Corp – A New Twist on In Silico Drug Design". www.bio-itworld.com.
- ↑ Taylor, Nick Paul (2015-05-07). "U.S. biotech Verseon bucks trend by going to U.K. for $100M IPO". Fierce Biotech.
- ↑ Moran, Nuala (2015-05-08). "Long-term investors lure Verseon across pond for $100M IPO". BioWorld.
- ↑ "Investegate |AIM Announcements | AIM: Cancellation - Verseon Corporation". www.investegate.co.uk.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Goodman, Micheal (June 2016). "In Silico Drug Design: Finally Ready For Prime Time?" (PDF). In Vivo The Business & Medicine Report. 34/ NO. 6: 10–14.
- ↑ "How AI can Fundamentally Transform Drug Discovery and Nanomedicine". Nano Magazine - Latest Nanotechnology News.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Szymański, Paweł; Markowicz, Magdalena; Mikiciuk-Olasik, Elżbieta (2011-12-29). "Adaptation of High-Throughput Screening in Drug Discovery—Toxicological Screening Tests". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 13 (1): 427–452. doi: 10.3390/ijms13010427 . ISSN 1422-0067. PMC 3269696 . PMID 22312262.
- ↑ "Verseon Reports First Dosing in Phase 1 Trial on New Precision Oral Anticoagulant". www.businesswire.com. 2019-02-04.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "Blood Clot Treatment Found By Researchers At Verseon Corporation". Science World Report. 2016-12-12.
- ↑ "Diabetic Retinopathy" (PDF). CDC.gov. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- ↑ "Verseon Nominates VE-4840 as Primary Drug Candidate for Oral Prophylaxis and Treatment of Diabetic Eye Disease". PR Newswire. 2021-08-05.
- ↑ "Verseon presents oral drug candidate for diabetic eye disease that could replace eye injections". Drug Discovery Today. 2019-05-09.
- ↑ "Verseon Presents Anticancer Drug Candidates Targeting Multidrug Resistant Cancers". Business Wire. 2018-05-18.
- ↑ "Machine Learning Approach Against Cancer | Verseon". www.verseon.com.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "Verseon Developing Oral Treatment for HAE". HAEi News. 2017-09-28.