Semiotics is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter.

Umberto Eco was an Italian medievalist, philosopher, semiotician, novelist, cultural critic, and political and social commentator. In English, he is best known for his popular 1980 novel The Name of the Rose, a historical mystery combining semiotics in fiction with biblical analysis, medieval studies and literary theory, as well as Foucault's Pendulum, his 1988 novel which touches on similar themes.

Kant and the Platypus: Essays on Language and Cognition (ISBN 0-15-601159-X) is a book by Umberto Eco which was published in Italian as Kant e l'ornitorinco in 1997. An English edition, translated by Alastair McEwen, appeared in 1999.

Eero Aarne Pekka Tarasti is a Finnish musicologist and semiotician, currently serving as Professor Emeritus of Musicology at the University of Helsinki. He has contributed significantly to the semiotics of music.

Thomas Albert Sebeok was a Hungarian-born American polymath, semiotician, and linguist. As one of the founders of the biosemiotics field, he studied non-human and cross-species signaling and communication. He is also known for his work in the development of long-time nuclear waste warning messages, in which he worked with the Human Interference Task Force to create methods for keeping the inhabitants of Earth away from buried nuclear waste that will still be hazardous 10,000 or more years in the future.
Urban semiotics is the study of meaning in urban form as generated by signs, symbols, and their social connotations.
Giorgio Prodi was an Italian medical scientist, oncologist and semiotician.

Jean-Marie Klinkenberg is a Belgian linguist and semiotician, professor at the State University of Liège, born in Verviers (Belgium) in 1944. Member of the interdisciplinary Groupe μ. President of the International Association for visual Semiotics.
International Association for Semiotic Studies is the major world organisation of semioticians, established in 1969.

Il costume di casa was originally an essay written by the Italian semiotician Umberto Eco, about "America's obsession with simulacra and counterfeit reality." It was later incorporated as the centrepiece of the anthology bearing the same name, a collection of articles and essays about Italian ideologies. The anthology contains a selection of essays taken from two Italian books by Eco: Il costume di casa and Sette anni di desiderio (1983). It was translated into English in 1986 as Faith in Fakes and later updated as Travels in Hyperreality in 1995.
Visual semiotics is a sub-domain of semiotics that analyses the way visual images communicate a message.
In a story, we detect an isotopy when there is a repetition of a basic meaning trait (seme); such repetition, establishing some level of familiarity within the story, allows for a uniform reading/interpretation of it. An example of a sentence containing an isotopy is I drink some water. The two words drink and water share a seme, and this gives homogeneity to the sentence.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to semiotics:

Aberrant decoding or aberrant reading is a concept used in fields such as communication and media studies, semiotics, and journalism about how messages can be interpreted differently from what was intended by their sender. The concept was proposed by Umberto Eco in an article published first in 1965 in Italian and in 1972 in English.
Film semiotics is the study of sign process (semiosis), or any form of activity, conduct, or any process that involves signs, including the production of meaning, as these signs pertain to moving pictures. Film semiotics is used for the interpretation of many art forms, often including abstract art.
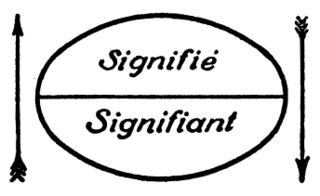
In semiotics, signified and signifier are the two main components of a sign, where signified is what the sign represents or refers to, known as the "plane of content", and signifier which is the "plane of expression" or the observable aspects of the sign itself. The idea was first proposed in the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, one of the two founders of semiotics.
Ethnosemiotics is a disciplinary perspective which links semiotics concepts to ethnographic methods.

Born from an exchange of ideas between Michel Costantini and Göran Sonesson during the congress of the International Association for Semiotic Studies held in Perpignan, in the south of France, in 1988, the International Association for Visual Semiotics, whose abbreviation is AISV-IAVS, was officially founded as an association under the French law in 1989 in Blois, France, where the first international congress was held in 1990.

Susan Petrilli is an Italian semiotician, professor of philosophy and theory of languages at the University of Bari, Aldo Moro, Italy, and the seventh Thomas A. Sebeok Fellow of the Semiotic Society of America. She is also International Visiting Research Fellow at the School of Psychology, the University of Adelaide, South Australia.

Paolo Fabbri was an Italian semiotician.










