
Brayley is a lunar impact crater located in the southwest part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after British geographer Edward W. Brayley in 1935. It has a circular rim and a low rise in the center. There are no notable craters overlapping the rim or interior. The sinuous rille Rima Brayley passes to the north of Brayley.

Abul Wafa is an impact crater located near the lunar equator on the far side of the Moon, named after the Persian mathematician and astronomer Abu al-Wafa' Buzjani. To the east are the crater pair Ctesibius and Heron. In the northeast lies the larger crater King, and to the southwest is Vesalius.

Al-Khwarizmi is a lunar impact crater located on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the southeast of the crater Moiseev, and northeast of Saenger.

Amici is a lunar impact crater that is located on the rugged far side of the Moon. It lies to the south of the larger crater Icarus, to the north of McKellar.

Encke is a lunar impact crater that is located on the western edge of the Mare Insularum, to the south-southeast of the crater Kepler. The small crater Kunowsky lies to the east-southeast on the mare.

Borman is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies across the southeast section of the mountainous inner ring, within the walled basin named Apollo.

Brown is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southeast part of the Moon, to the southwest of the prominent ray crater Tycho. Northwest of Brown is the crater Wilhelm, and to the west is Montanari. This crater was named after Ernest William Brown, and is distinct from crater D. Brown, a satellite crater of the Apollo crater.

Barringer is a lunar impact crater that is located on the southern hemisphere on the Far side of the Moon, named after geologist Daniel Barringer. It is attached to the north-northeastern rim of the walled basin named Apollo, and lies to the southeast of Plummer. South of Barringer, on the floor of the Apollo basin, is the crater Scobee.

Barbier is a lunar impact crater that is located on the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It forms a matched pair with Cyrano to the north-northwest, and it lies to the southeast of the huge walled plain Gagarin. Southwest of Barbier is the crater Sierpinski, and to the southeast is the Mare Ingenii.

Bečvář is a lunar impact crater that is located near the equator on the far side of the Moon. It was named after Czechoslovakian astronomer Antonín Bečvář. It lies to the northeast of the crater Necho, within that feature's ray system. To the north-northeast is the crater Gregory.

Buisson is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It is named after the French physicist Henri Buisson. Nearly attached to the southeast rim is the crater Vesalius. To the southwest is Einthoven. The rim of this crater is somewhat worn, and is lowest in the north. There is a low central ridge across the midpoint.

Firmicus is a lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, so that from Earth it appears oval in shape due to foreshortening. It is, however, very nearly circular. The crater is located to the west of the Mare Undarum, and northeast of the similar-sized crater Apollonius. To the north of Firmicus are the craters van Albada and Auzout. Attached to its northwest rim is the Lacus Perseverantiae, a miniature lunar mare.

Coriolis is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. The crater floor is bisected by the lunar equator, and it lies about three crater diameters northwest of the crater Daedalus.

File: Franz is a small lunar impact crater identified during the Apollo mission in August 1971 and located along the eastern edge of the Sinus Amoris, a bay that forms a northern extension to the Mare Tranquillitatis. Its diameter is 25 km. It was named after German astronomer Julius Heinrich Franz. It lies to the southwest of the prominent crater Macrobius. To the north is the smaller Carmichael, and to the northwest is the diminutive Theophrastus.

Widmannstätten is a lunar impact crater in the southern part of the Mare Smythii, near the eastern limb of the Moon. The rim of this crater has a wide gap along the western side, where it is joined to the larger Kiess. There is also a gap in the northern rim where the crater floor is joined to the adjacent lunar mare. The dark interior floor of this formation has been flooded by lava, leaving a level interior surface and a shallow surviving rim.

Dobrovolʹskiy is a small lunar impact crater on the Moon's far side. The northwest part of its rim is intruded upon by the somewhat larger crater Shirakatsi, and the outer rampart of that feature covers most of the interior floor of Dobrovolʹskiy. Very little of the original floor now survives, with a small section near the southern inner wall. The remainder of the crater rim is somewhat circular and only mildly worn.
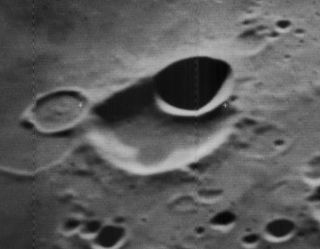
Resnik is a small lunar impact crater that is located within the interior of the huge walled plain Apollo, on the Moon's far side. Apollo is a double-ringed formation with a central floor that has been flooded with basaltic lava. Resnik is located at the northern edge of the dark area of the surface. It lies to the southwest of the smaller crater McAuliffe.

McAuliffe is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the Moon's far side. It lies within the inner ring of the double-ringed walled plain Apollo, about one crater diameter to the northeast of the crater Resnik. To the southeast of it lies the crater pair of Jarvis and McNair.

Shirakatsi is an impact crater that is located on the Moon's far side. It is attached to the southern exterior rim of the larger crater Perepelkin, and overlies the northwestern rim of Dobrovol'skiy.

Lobachevskiy is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, beyond the eastern limb. It was named after Russian mathematician Nikolai Lobachevsky in 1961. This crater lies to the southeast of the larger crater Fleming. Less than a crater diameter to the east-northeast lies Guyot.
























