
Vibrio cholerae is a species of Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe and comma-shaped bacteria. The bacteria naturally live in brackish or saltwater where they attach themselves easily to the chitin-containing shells of crabs, shrimps, and other shellfish. Some strains of V. cholerae are pathogenic to humans and cause a deadly disease cholera, which can be derived from the consumption of undercooked or raw marine life species.
El Tor is a particular strain of the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of cholera. Also known as V. cholerae biotype eltor, it has been the dominant strain in the seventh global cholera pandemic. It is distinguished from the classic strain at a genetic level, although both are in the serogroup O1 and both contain Inaba, Ogawa and Hikojima serotypes. It is also distinguished from classic biotypes by the production of hemolysins.

Vibrio is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Typically found in salt water, Vibrio species are facultative anaerobes that test positive for oxidase and do not form spores. All members of the genus are motile. They are able to have polar or lateral flagellum with or without sheaths. Vibrio species typically possess two chromosomes, which is unusual for bacteria. Each chromosome has a distinct and independent origin of replication, and are conserved together over time in the genus. Recent phylogenies have been constructed based on a suite of genes.

Pseudomonas fluorescens is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the Pseudomonas genus; 16S rRNA analysis as well as phylogenomic analysis has placed P. fluorescens in the P. fluorescens group within the genus, to which it lends its name.
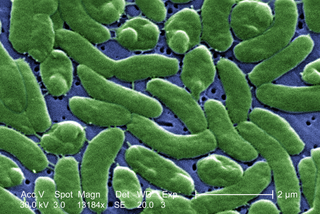
Vibrio vulnificus is a species of Gram-negative, motile, curved rod-shaped (bacillus), pathogenic bacteria of the genus Vibrio. Present in marine environments such as estuaries, brackish ponds, or coastal areas, V. vulnificus is related to V. cholerae, the causative agent of cholera. At least one strain of V. vulnificus is bioluminescent.

Aliivibrio fischeri is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a single polar flagella. Free-living A. fischeri cells survive on decaying organic matter. The bacterium is a key research organism for examination of microbial bioluminescence, quorum sensing, and bacterial-animal symbiosis. It is named after Bernhard Fischer, a German microbiologist.

Vibrio harveyi is a Gram-negative, bioluminescent, marine bacterium in the genus Vibrio. V. harveyi is rod-shaped, motile, facultatively anaerobic, halophilic, and competent for both fermentative and respiratory metabolism. It does not grow below 4 °C. V. harveyi can be found free-swimming in tropical marine waters, commensally in the gut microflora of marine animals, and as both a primary and opportunistic pathogen of marine animals, including Gorgonian corals, oysters, prawns, lobsters, the common snook, barramundi, turbot, milkfish, and seahorses. It is responsible for luminous vibriosis, a disease that affects commercially farmed penaeid prawns. Additionally, based on samples taken by ocean-going ships, V. harveyi is thought to be the cause of the milky seas effect, in which, during the night, a uniform blue glow is emitted from the seawater. Some glows can cover nearly 6,000 sq mi (16,000 km2).

Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a curved, rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium found in the sea and in estuaries which, when ingested, causes gastrointestinal illness in humans. V. parahaemolyticus is oxidase positive, facultatively aerobic, and does not form spores. Like other members of the genus Vibrio, this species is motile, with a single, polar flagellum.

The oxidase test is used to determine if an organism possesses the cytochrome oxidase enzyme. The test is used as an aid for the differentiation of Neisseria, Moraxella, Campylobacter and Pasteurella species. It is also used to differentiate pseudomonads from related species..
Vibrio natriegens is a Gram-negative marine bacterium. It was first isolated from salt marsh mud. It is a salt-loving organism (halophile) requiring about 2% NaCl for growth. It reacts well to the presence of sodium ions which appear to stimulate growth in Vibrio species, to stabilise the cell membrane, and to affect sodium-dependent transport and mobility. Under optimum conditions, and all nutrients provided, the doubling time of V. natriegens can be less than 10 minutes. In the laboratory, the growth medium can be easily changed, thus affecting the growth rate of a culture. V. natriegens is commonly found in estuarine mud. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified many strains of Vibrio natriegens from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island Area of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh.
Vibrio alginolyticus is a Gram-negative marine bacterium. It is medically important since it causes otitis and wound infection. It is also present in the bodies of animals such as pufferfish, where it is responsible for the production of the potent neurotoxin, tetrodotoxin.

Ballast water discharges by ships can have a negative impact on the marine environment. The discharge of ballast water and sediments by ships is governed globally under the Ballast Water Management Convention, since its entry into force in September 2017. It is also controlled through national regulations, which may be separate from the Convention, such as in the United States.
Bradyrhizobium elkanii is a species of legume-root nodulating, microsymbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacterium originally identified as DNA homology group II strains of B. japonicum . In 1988, it was discovered that only DNA homology group II strains caused a destructive bleaching of leaves, termed scientifically "microsymbiont-induced foliar chlorosis", which was widespread in soybean production fields of the southern United States . Whole cell fatty acid content together with antibiotic resistance profiles were major phenotypic differences that helped establish DNA homology group II strains as a new species, Bradyrhizobium elkanii .
Bucephalus mytili is a parasitic flatworm of the class Trematoda. It is a parasite of fish and a parasitic castrator of the mussel Mytilus edulis, where it destroys the mussel's gonads and causes the mussel to grow much larger than normal.

Vibrio anguillarum is a species of Gram-negative bacteria with a curved-rod shape and one polar flagellum. It is damaging to the economy of aquaculture sector and fishing industries.
Vibrio campbellii is a Gram-negative, curved rod-shaped, marine bacterium closely related to its sister species, Vibrio harveyi. It is an emerging pathogen in aquatic organisms.
Vibrio furnissii is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. Its type strain is ATCC 35016. V. furnissii is aerogenic (gas-producing), and uses L-rhamnose, L-arginine, L-arabinose, maltose, and D-mannitol, but not L-lysine, L-ornithine, or lactose. It has been isolated from patients with gastroenteritis, bacteremia, skin lesions, and sepsis.
Vibrio tapetis is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium, the causative agent of the brown ring disease that affects cultured clams. B1090 is the type strain.
Aquimarina mytili is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Aquimarina which has been isolated from the gut microflora of the mussel Mytilus coruscus which was collected from the Gwangyang Bay in Korea.
Colwellia mytili is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, aerobic and motile bacterium from the genus of Colwellia which has been isolated from the mussel Mytilus edulis from the South Sea in Korea.









