
ITV Digital was a British digital terrestrial television broadcaster which launched a pay-TV service on the world's first digital terrestrial television network. Its main shareholders were Carlton Communications plc and Granada plc, owners of multiple licences of the ITV network. Starting as ONdigital in 1998, the service was rebranded as ITV Digital in July 2001.
The Digibox is a device marketed by Sky UK in the UK and Ireland to enable home users to receive digital satellite television broadcasts from the Astra satellites at 28.2° east. An Internet service was also available through the device, similar in some ways to the American MSN TV, before being discontinued in 2015. The first Digiboxes shipped to consumers in October 1998 when Sky Digital was launched, and the hardware reference design has been relatively unchanged since then. Compared to other satellite receivers, they are severely restricted. As of 2020, Sky Digiboxes have become largely outmoded, superseded by Sky's latest-generation Sky Q boxes and Sky Glass televisions; the previous generation Sky+HD boxes are still in use, however.

Sky UK Limited, trading as Sky, is a British broadcaster and telecommunications company that provides television, internet, fixed line and mobile telephone services to consumers and businesses in the United Kingdom. It is a subsidiary of Sky Group and, from 2018 onwards, part of Comcast. It is the UK's largest pay-TV broadcaster, with 12.7 million customers as of the end of 2019 for its digital satellite TV platform. Sky's flagship products are Sky Q and the internet-based Sky Glass, and its flagship channels are Sky Showcase, Sky Max, and Sky Atlantic.

Top Up TV was a pay TV service in the United Kingdom that was launched in March 2004, operating on the digital terrestrial television platform. The service aimed to "top up" Freeview customers by providing additional content and services through encrypted TV channels unavailable to other viewers.
Cisco Videoscape was a majority owned subsidiary of News Corp, which develops software for the pay TV industry. NDS Group was established in 1988 as an Israeli start up company. It was acquired by Cisco in 2012 before being sold back to the private equity company Permira in 2018 for US$1 billion. The company is currently headquartered in Staines, United Kingdom.
Pirate decryption is the decryption, or decoding, of pay TV or pay radio signals without permission from the original broadcaster. The term "pirate" is used in the sense of copyright infringement. The MPAA and other groups which lobby in favour of intellectual property regulations have labelled such decryption as "signal theft" even though there is no direct tangible loss on the part of the original broadcaster, arguing that losing out on a potential chance to profit from a consumer's subscription fees counts as a loss of actual profit.

A conditional access module (CAM) is an electronic device, usually incorporating a slot for a smart card, which equips an integrated digital television or set-top box with the appropriate hardware facility to view conditional access content that has been encrypted using a conditional access system. They are normally used with direct-broadcast satellite (DBS) services, although digital terrestrial pay TV suppliers also use CAMs. PC Card form factor is used as the Common Interface form of Conditional Access Modules for DVB broadcasts. Major CAM manufacturers are Airmod.tech and SMIT. Airmod, created in 2022, regroup CAM formerly managed by Neotion and SmarDTV.
Television encryption, often referred to as scrambling, is encryption used to control access to pay television services, usually cable, satellite, or Internet Protocol television (IPTV) services.
Conditional access (CA) is a term commonly used in relation to software and to digital television systems. Conditional access is an evaluation to ensure the person who is seeking access to content is authorized to access the content. Access is managed by requiring certain criteria to be met before granting access to the content.
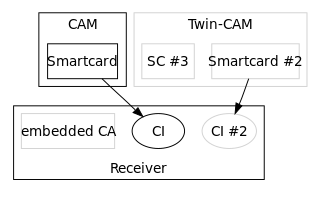
In Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is a technology which allows decryption of pay TV channels. Pay TV stations want to choose which encryption method to use. The Common Interface allows TV manufacturers to support many different pay TV stations, by allowing to plug in exchangeable conditional-access modules (CAM) for various encryption schemes.

Sky+ is a discontinued personal video recorder (PVR) and subscription service from the satellite television provider Sky in the UK and Ireland. Launched in September 2001, it allows customers to record, pause and instantly rewind live TV. The system performs these functions using an internal hard drive inside the Sky+ set top box, an upgrade over the standard Digibox.
Freesat from Sky (FsfS) was a British satellite television service from Sky UK. It offered over 240 free-to-air (FTA) channels in its EPG. This is a greater number than its competitors, Freesat, which has 200+, and Freeview, which has 70+. It also had up to six HD channels and used to have Sky Active interactive data service. Sky was not actively promoting the service and the service has quietly been discontinued for new customers as of 2021.
Sky+ HD was the brand name of the HDTV service launched by Sky plc on 22 May 2006 in the United Kingdom and Ireland to enable high definition channels on Sky to be viewed. For the first two years after launch, the service was branded Sky HD. The service requires the user to have a Sky+ HD Digibox and an HD ready TV. A subscription to the original HD pack carries an extra fee of £10.25 a month in addition to the standard Sky subscription, allowing customers to view HD channels corresponding to the channel packs subscribed to. Additional Pay-Per-View events on Sky Box Office HD are not available to customers unless they subscribe to the Sky HD pack.
Card sharing, also known as control word sharing, is a method of allowing multiple clients or digital television receivers to access a subscription television network with only one valid subscription card. This is achieved by electronically sharing a part of the legitimate conditional access smart card's output data, enabling all recipients to gain simultaneous access to scrambled DVB streams, held on the encrypted television network.

Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter.

Sky Multichannels was a package of analogue television services offered by BSkyB on the Astra satellites at 19.2° east from 1 September 1993 to 27 September 2001, which started off with 15 channels before expanding to over 40.

Sky Ireland Limited is a subsidiary of Comcast-owned Sky UK and supplies television, internet and telephony services in Ireland.
Addressability is the ability of a digital device to individually respond to a message sent to many similar devices. Examples include pagers, mobile phones and set-top boxes for pay TV. Computer networks are also addressable via the MAC address on Ethernet network cards, and similar networking protocols like Bluetooth. This allows data to be sent in cases where it is impractical to control exactly where or to which devices the message is physically sent.
Satellite television varies in the different regions around the world.
Synamedia Ltd. is a video technology provider headquartered in Staines-upon-Thames, UK. Its products cover content distribution and delivery, video processing, advanced advertising, broadband offerings, and video security.








