
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, phase and frequency of an analog signal.

Chrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal. Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B′ − Y′ (blue − luma) and V = R′ − Y′ (red − luma). Each of these difference components may have scale factors and offsets applied to it, as specified by the applicable video standard.

The National Television System Committee (NTSC) developed the analog television format encoding system that was introduced in North America in 1954 and stayed in use until digital conversion. It is one of three major analog format television standards, the others being PAL and SECAM. All the countries using NTSC are currently in the process of conversion, or have already converted to the ATSC standard, or to DVB, ISDB or DTMB.

Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields per second, and associated with CCIR analogue broadcast television systems B, D, G, H, I or K. The articles on analog broadcast television systems further describe frame rates, image resolution, and audio modulation.

SECAM, also written SÉCAM, is an analog color television system first used in France. It was one of three major analog color television standards, the others being PAL and NTSC. This page primarily discusses the SECAM colour encoding system. The articles on broadcast television systems and analog television further describe frame rates, image resolution, and audio modulation. SECAM video is composite video because the luminance and chrominance are transmitted together as one signal.

Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode ray tube (CRT) systems which were later replaced by flat panel displays of several types.
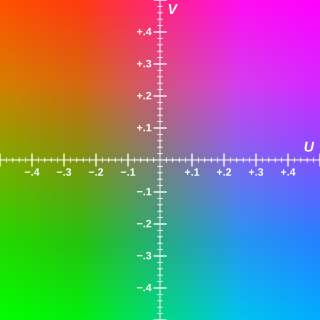
YUV is a color encoding system typically used as part of a color image pipeline. It encodes a color image or video taking human perception into account, allowing reduced bandwidth for chrominance components, compared to a "direct" RGB-representation. Historically, the terms YUV and Y′UV were used for a specific analog encoding of color information in television systems. Today, the term YUV is commonly used in the computer industry to describe file-formats that are encoded using YCbCr.

Colorburst is an analog video, composite video signal generated by a video-signal generator used to keep the chrominance subcarrier synchronized in a color television signal. By synchronizing an oscillator with the colorburst at the back porch (beginning) of each scan line, a television receiver is able to restore the suppressed carrier of the chrominance (color) signals, and in turn decode the color information. The most common use of colorburst is to genlock equipment together as a common reference with a vision mixer in a television studio using a multi-camera setup.

Composite video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video as a single channel. Video information is encoded on one channel, unlike the higher-quality S-Video and the even higher-quality component video. In all of these video formats, audio is carried on a separate connection.

S-Video is a signaling standard for standard definition video, typically 480i or 576i. By separating the black-and-white and coloring signals, it achieves better image quality than composite video, but has lower color resolution than component video. S-Video was introduced with JVC's S-VHS format in 1987.

Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.

ITU-R Recommendation BT.601, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 601 or BT.601 is a standard originally issued in 1982 by the CCIR for encoding interlaced analog video signals in digital video form. It includes methods of encoding 525-line 60 Hz and 625-line 50 Hz signals, both with an active region covering 720 luminance samples and 360 chrominance samples per line. The color encoding system is known as YCbCr 4:2:2.

Component video is an analog video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals. Component video can be contrasted with composite video in which all the video information is combined into a single signal that is used in analog television. Like composite, component-video cables do not carry audio and are often paired with audio cables.

Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video interfaces first standardized by SMPTE in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s.

SMPTE color bars are a television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in North America. The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) refers to the pattern as Engineering Guideline (EG) 1-1990. Its components are a known standard. Comparing it as received to the known standard gives video engineers an indication of how an NTSC video signal has been altered by recording or transmission and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce NTSC chrominance and luminance information correctly.

A vectorscope is a special type of oscilloscope used in both audio and video applications. Whereas an oscilloscope or waveform monitor normally displays a plot of signal vs. time, a vectorscope displays an X-Y plot of two signals, which can reveal details about the relationship between these two signals. Vectorscopes are highly similar in operation to oscilloscopes operated in X-Y mode; however those used in video applications have specialized graticules, and accept standard television or video signals as input.

Dot crawl is a visual defect of color analog video standards when signals are transmitted as composite video, as in terrestrial broadcast television. It consists of moving checkerboard patterns which appear along horizontal color transitions. It results from intermodulation or crosstalk between chrominance and luminance components of the signal, which are imperfectly multiplexed in the frequency domain. The term is more associated with the NTSC analog color TV system, with the PAL equivalent being Chroma dots. Although the interference patterns are slightly different depending on the system used, they have the same cause and the same general principles apply.

A PCM adaptor is a device that encodes digital audio as video for recording on a videocassette recorder. The adapter also has the ability to decode a video signal back to digital audio for playback. This digital audio system was used for mastering early compact discs.
Differential gain is a kind of linearity distortion which affects the color saturation in TV broadcasting.
This glossary defines terms that are used in the document "Defining Video Quality Requirements: A Guide for Public Safety", developed by the Video Quality in Public Safety (VQIPS) Working Group. It contains terminology and explanations of concepts relevant to the video industry. The purpose of the glossary is to inform the reader of commonly used vocabulary terms in the video domain. This glossary was compiled from various industry sources.
















