
A Vietnam veteran is an individual who performed active military, naval, or air service in the Republic of Vietnam during the Vietnam War.

The Vietnam War was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975.

The G.I. Bill, formally known as the Servicemen's Readjustment Act of 1944, was a law that provided a range of benefits for some of the returning World War II veterans. The original G.I. Bill expired in 1956, but the term "G.I. Bill" is still used to refer to programs created to assist some of the U.S. military veterans.

The Gulf of Tonkin incident was an international confrontation that led to the United States engaging more directly in the Vietnam War. It consisted of a confrontation on August 2, 1964, when United States forces were carrying out covert operations close to North Vietnamese territorial waters and North Vietnamese forces responded. The United States government falsely claimed that a second incident occurred on August 4, 1964, between North Vietnamese and United States ships in the waters of the Gulf of Tonkin. Originally, US military claims blamed North Vietnam for the confrontation and the ostensible, but in fact imaginary, incident on August 4. Later investigation revealed that the second attack never happened; the American claim is that it was based mostly on erroneously interpreted communications intercepts.

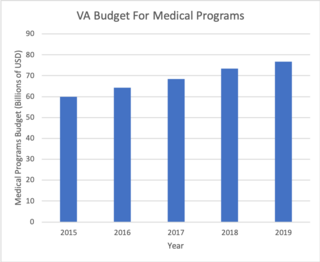
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing lifelong healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers and outpatient clinics located throughout the country. Non-healthcare benefits include disability compensation, vocational rehabilitation, education assistance, home loans, and life insurance. The VA also provides burial and memorial benefits to eligible veterans and family members at 135 national cemeteries.
The National Defense Service Medal (NDSM) is a service award of the United States Armed Forces established by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1953. It is awarded to every member of the U.S. Armed Forces who has served during any one of four specified periods of armed conflict or national emergency from June 27, 1950 through December 31, 2022. Combat or "in theater" service is not a requirement for the award.

The Republic of Vietnam Campaign Medal, also known as the Vietnam Campaign Medal, is a South Vietnamese military campaign medal which was created in 1949, and awarded to French military personnel during the First Indochina War. During the Vietnam War, the South Vietnamese government awarded the Republic of Vietnam Campaign Medal with Device to members of the South Vietnamese military for wartime service and on March 24, 1966, to members of the U.S. military for support of operations in Vietnam. In May 1966, other allied foreign military personnel became eligible for the award.
The Vietnam Service Medal is a military award of the United States Armed Forces established on 8 July 1965 by order of President Lyndon B. Johnson. The medal is awarded to recognize service during the Vietnam War by all members of the U.S. Armed Forces provided they meet the award requirements.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the component of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) led by the Under Secretary of Veterans Affairs for Health that implements the healthcare program of the VA through a nationalized healthcare service in the United States, providing healthcare and healthcare-adjacent services to Veterans through the administration and operation of 146 VA Medical Centers (VAMC) with integrated outpatient clinics, 772 Community Based Outpatient Clinics (CBOC), and 134 VA Community Living Centers Programs. It is the largest division in the Department, and second largest in the entire federal government, employing over 350,000 employees. All VA hospitals, clinics and medical centers are owned by and operated by the Department of Veterans Affairs as opposed to private companies, and all of the staff employed in VA hospitals are government employees. Because of this, Veterans that qualify for VHA healthcare do not pay premiums or deductibles for their healthcare but may have to make copayments depending on what procedure they are having. VHA is distinct from the U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System of which it is not a part.
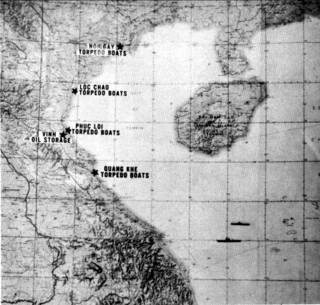
Operation Pierce Arrow was a U.S. bombing campaign at the beginning of the Vietnam War.
The Veterans' Preference Act is a United States federal law passed in 1944. It required the federal government to favor returning war veterans when hiring new employees in an attempt to recognize their service, sacrifice, and skills.

The Veterans Benefits Administration (VBA) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. It is responsible for administering the department's programs that provide financial and other forms of assistance to veterans, their dependents, and survivors. Major benefits include Veterans' compensation, Veterans' pension, survivors' benefits, rehabilitation and employment assistance, education assistance, home loan guaranties, and life insurance coverage.

The United States Court of Appeals for Veterans Claims is a federal court of record that was established under Article I of the United States Constitution, and is thus referred to as an Article I tribunal (court). The court has exclusive national jurisdiction to provide independent federal judicial oversight and review of final decisions of the Board of Veterans' Appeals.

A veteran's pension or "wartime pension" is a pension for veterans of the United States Armed Forces, who served in the military but did not qualify for military retired pay from the Armed Forces. It was established by the United States Congress and given to veterans who meet the eligibility requirements. Along with payments, they are also given additional benefits depending on their eligibility and needs.
The Vietnam Era Veterans' Readjustment Assistance Act of 1974 is an Act of Congress originally about Vietnam-era veterans, disabled veterans, and any other veterans who served active duty time in a war event that qualifies for a campaign badge.

Gulf War syndrome or Gulf War illness is a chronic and multi-symptomatic disorder affecting military veterans of both sides of the 1990–1991 Persian Gulf War. A wide range of acute and chronic symptoms have been linked to it, including fatigue, muscle pain, cognitive problems, insomnia, rashes and diarrhea. Approximately 250,000 of the 697,000 U.S. veterans who served in the 1991 Gulf War have enduring chronic multi-symptom illness, a condition with serious consequences.

George Stephen Morrison was a United States Navy rear admiral and naval aviator. Morrison was commander of United States naval forces during the Gulf of Tonkin Incident of August 1964, which sparked an escalation of American involvement in the Vietnam War. He was the father of Jim Morrison, the lead singer of the rock band The Doors, who died on July 3, 1971.

A SIGINT Activity Designator identifies a signals intelligence (SIGINT) line of collection activity associated with a signals collection station, such as a base or a ship. For example, the SIGAD for Menwith Hill in the UK is USD1000. SIGADs are used by the signals intelligence agencies of the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand.

The Gulf of Tonkin Resolution or the Southeast Asia Resolution, Pub. L. 88–408, 78 Stat. 384, enacted August 10, 1964, was a joint resolution that the United States Congress passed on August 7, 1964, in response to the Gulf of Tonkin incident.

The George E. Wahlen Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) is located in Salt Lake City, Utah. The George E. Wahlen VA Hospital is a 121-bed short-term acute care hospital and is designated as a medical training and research facility. For the scale of operations in 2019, the George E. Wahlen VA had over 2,500 employees, treated over 66,000 veterans, and accommodated nearly 390,000 outpatient visits. Of the veterans treated here in 2019, 24,514 served in the Gulf War, 25,714 served in the Vietnam War, 1,290 in World War II, 3,377 served in the Korean War, and 7,286 were women. During 2019, the George E. Wahlen VA federal budget allocation was approximately $668 million. The George E. Wahlen Medical Center is one of five heart transplant centers in the United States. The facility is encompassed within the Veterans Integrated Service Network 19 within the Rocky Mountain Region.















