Vijay Vasant Tambay | |
|---|---|
 Tambay c. 1970 | |
| Nickname | Uncle [1] |
| Born | 11 April 1943 |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch | |
| Service years | 1963–1973 |
| Rank | 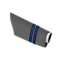 |
| Service number | 7662 F(P) |
| Unit | No.32 Squadron IAF |
| Conflicts | |
| Alma mater | Bishop Cotton School, Nagpur. |
| Spouse | Mrs Damayanti V. Tambay |
| Disappeared | 5 December 1971 (aged 28) Shorkot, Jhang District, Punjab province, Pakistan |
| Status | Missing for 54 years, 1 month and 14 days |
Flight Lieutenant Vijay Vasant Tambay (born 11 April 1943) was an officer of the Indian Air Force whose aircraft was shot down on 5 December 1971 over Shorkot in what was then West Pakistan while on a strike against the Pakistan Air Force Rafiqui Airbase during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971. [3]
Contents
Officially recorded by the Indian Air Force as killed in action, [4] Tambay is believed to be one of the five pilots reported by the Pakistan Observer to have been captured alive on 5 December 1971. [5] However, although a number of reports from eyewitnesses have subsequently suggested that Tambay was indeed captured alive, he was not repatriated at the end of the war, while the Pakistan Government denies having any Indian prisoners of war from the 1971 war, [6] making him one of the missing 54 Indian defence personnel from the war who are believed to remain in Pakistani custody. [3] [7] His uncle, Jayant Jatar, claimed that in January 1999 he was permitted by Tikka Khan, then Governor of Punjab, Pakistan, to see his nephew on condition that he inform only his immediate family. [3] He broke his silence in 2002, after the death of Tikka Khan. [3]