
The Iraq disarmament crisis was claimed as one of the primary issues that led to the multinational invasion of Iraq on 20 March 2003.

The United Nations Monitoring, Verification and Inspection Commission (UNMOVIC) was created through the adoption of United Nations Security Council resolution 1284 of 17 December 1999 and its mission lasted until June 2007.

This article describes the positions of world governments before the actual initiation of the 2003 invasion of Iraq, and not their current positions as they may have changed since then.

Opposition to the Iraq War significantly occurred worldwide, both before and during the initial 2003 invasion of Iraq by a United States–led coalition, and throughout the subsequent occupation. Individuals and groups opposing the war include the governments of many nations which did not take part in the invasion, including both its land neighbors Canada and Mexico, its NATO allies in Europe such as France and Germany, as well as China and Indonesia in Asia, and significant sections of the populace in those that took part in the invasion. Opposition to the war was also widespread domestically.

In March 2003 the United States government announced that "diplomacy has failed" and that it would proceed with a "coalition of the willing" to rid Iraq under Saddam Hussein of weapons of mass destruction the US and UK claimed it possessed. The 2003 invasion of Iraq began a few days later. Prior to this decision, there had been much diplomacy and debate amongst the members of the United Nations Security Council over how to deal with the situation. This article examines the positions of these states as they changed during 2002–2003.

Francisco Javier Solana de Madariaga CYC is a Spanish physicist and PSOE politician. After serving in the Spanish government as Foreign Affairs Minister under Felipe González (1992–1995) and as the Secretary General of NATO (1995–1999), leading the alliance during Operation Allied Force, he was appointed the European Union's High Representative for Common Foreign and Security Policy, Secretary General of the Council of the European Union and Secretary-General of the Western European Union and held these posts from October 1999 until December 2009.

The High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy/Vice-President of the European Commission (HR/VP) is the chief co-ordinator and representative of the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) within the European Union (EU). The position is currently held by Josep Borrell Fontelles.
The "letter of the eight" was an open letter, jointly signed by the prime ministers of five of the then fifteen members of the European Union together with three high representatives for the Central European countries that were to enter the union in 2004, published in the Wall Street Journal, The Times of London, and other international newspapers on 30 January 2003 under the title "Europe and America Must Stand United". It expressed indirect support for United States ambition of a régime change in Iraq in the lead-up to the 2003 invasion of Iraq. To most observers it demonstrated a total division within the EU in respect to foreign policy and attitudes towards international law.

The main event by far shaping the foreign policy of the United States during the presidency of George W. Bush (2001–2009) was the 9/11 terrorist attacks against the United States on September 11, 2001, and the subsequent war on terror. There was massive domestic and international support for destroying the attackers. With UN approval, US and NATO forces quickly invaded the attackers' base in Afghanistan and drove them out and the Taliban government that harbored them. It was the start of a 20-year quagmire that finally ended in failure with the withdrawal of United States troops from Afghanistan.
The following lists events in the year 2003 in Iraq.

Sir Matthew John Rycroft is a British civil servant and diplomat serving as Permanent Under-Secretary of State at the Home Office since 2020, appointed following the resignation of Sir Philip Rutnam. Rycroft previously served as Permanent Secretary at the Department for International Development (DFID) from 2018 to 2020 and as the Permanent Representative to the United Nations in New York from 2015 to 2018.

There are various rationales for the Iraq War that have been used to justify the 2003 invasion of Iraq and subsequent hostilities.
An arms embargo is a restriction or a set of sanctions that applies either solely to weaponry or also to "dual-use technology." An arms embargo may serve one or more purposes:
The 2003 United States–British–Spanish Draft Resolution on Iraq was, according to Ambassador John Negroponte, "a resolution to have the Council decide that Iraq is not complying, is out of compliance, with Resolution 1441". Initially introduced on February 24, 2003, and amended on March 7, 2003, the draft set a March 17 deadline for Iraq to demonstrate "full, unconditional, immediate and active cooperation in accordance with its disarmament obligations." The draft was based on information from the Iraqi defector "Curveball," who claimed Saddam Hussein was in possession of weapons of mass destruction, which Curveball later admitted was untrue. The widely discussed UN resolution was not brought up for formal vote after it became clear that it would not have passed due to opposition from France, Russia, and China. The United States invaded Iraq without UN support on March 20, 2003, initiating the Iraq War.

The legality of the Iraq War is a contested topic that spans both domestic and international law. Political leaders in the US and the UK who supported the invasion of Iraq have claimed that the war was legal. However, legal experts and other world leaders have argued that the war lacked justification and violated the United Nations charter.
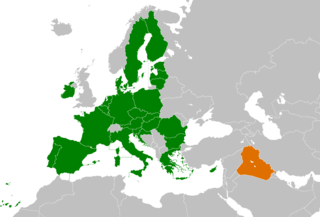
Iraq – European Union (EU) relations are the international relations between Iraq and the EU. Relations have been strained from the early 1990s but are now gradually progressing. From Brussels, Iraq has mostly been considered as falling under the U.S. area of responsibilities, independently from the close economic ties between certain European states and Saddam Hussein’s Iraq prior to the international sanctions regime, or the participation of five European countries in the U.S.-led invasion and occupation of the country. Should Turkey's accession to the EU take place, Iraq will border the European Union.

The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, commonly known as the Iran nuclear deal or Iran deal, is an agreement on the Iranian nuclear program reached in Vienna on 14 July 2015, between Iran and the P5+1 together with the European Union.

Federica Mogherini is an Italian politician who served as High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of the European Commission from 2014 to 2019. A member of the Democratic Party (PD), which is part of the Party of European Socialists, a political faction made up of centre-left national political parties in the European Union, the United Kingdom, and Norway. She previously served as Italy's Minister for Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation from February to October 2014 in the Renzi government. She was a member of the Chamber of Deputies (MP) from 2008 to 2014. In 2020, she was appointed rector of the College of Europe, a post-graduate university for European studies in Bruges (Belgium) and Natolin (Poland).

The COVID-19 pandemic has affected international relations and has caused diplomatic tensions, as well as resulted in a United Nations Security Council resolution demanding a global ceasefire.











