
Alamethicin is a channel-forming peptide antibiotic, produced by the fungus Trichoderma viride. It belongs to peptaibol peptides which contain the non-proteinogenic amino acid residue Aib. This residue strongly induces formation of alpha-helical structure. The peptide sequence is

Teicoplanin is an semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic with a spectrum of activity similar to vancomycin. Its mechanism of action is to inhibit bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis. It is used in the prophylaxis and treatment of serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis.
In organic chemistry, polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone and methylene groups: [−C(=O)−CH2−]n. First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity.
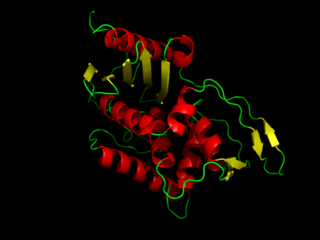
DD-Transpeptidase is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the R-L-αα-D-alanyl moiety of R-L-αα-D-alanyl-D-alanine carbonyl donors to the γ-OH of their active-site serine and from this to a final acceptor. It is involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, namely, the transpeptidation that crosslinks the peptide side chains of peptidoglycan strands.
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be made by bacteria inside these organisms. While there exist a wide range of peptides that are not synthesized by ribosomes, the term nonribosomal peptide typically refers to a very specific set of these as discussed in this article.

Clavulanic acid is a β-lactam drug that functions as a mechanism-based β-lactamase inhibitor. While not effective by itself as an antibiotic, when combined with penicillin-group antibiotics, it can overcome antibiotic resistance in bacteria that secrete β-lactamase, which otherwise inactivates most penicillins.
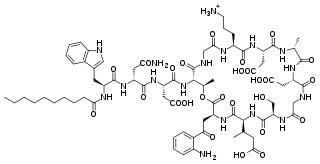
Daptomycin, sold under the brand name Cubicin among others, is a lipopeptide antibiotic used in the treatment of systemic and life-threatening infections caused by Gram-positive organisms.
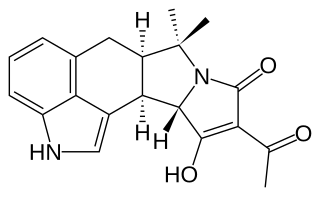
Cyclopiazonic acid (α-CPA), a mycotoxin and a fungal neurotoxin, is made by the molds Aspergillus and Penicillium. It is an indole-tetramic acid that serves as a toxin due to its ability to inhibit calcium-dependent ATPases found in the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. This inhibition disrupts the muscle contraction-relaxation cycle and the calcium gradient that is maintained for proper cellular activity in cells.
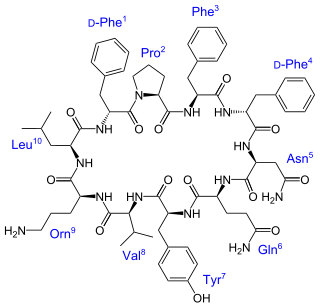
Tyrocidine is a mixture of cyclic decapeptides produced by the bacteria Brevibacillus brevis found in soil. It can be composed of 4 different amino acid sequences, giving tyrocidine A–D. Tyrocidine is the major constituent of tyrothricin, which also contains gramicidin. Tyrocidine was the first commercially available antibiotic, but has been found to be toxic toward human blood and reproductive cells. The function of tyrocidine within its host B. brevis is thought to be regulation of sporulation.
Polyketide synthases (PKSs) are a family of multi-domain enzymes or enzyme complexes that produce polyketides, a large class of secondary metabolites, in bacteria, fungi, plants, and a few animal lineages. The biosyntheses of polyketides share striking similarities with fatty acid biosynthesis.
Blasticidin S is an antibiotic that is used in biology research for selecting cells in cell culture. Cells of interest can express the blasticidin resistance genes BSD or bsr, and can then survive treatment with the antibiotic. Blasticidin S is a nucleoside analogue antibiotic, resembling the nucleoside cytidine. Blasticidin works against human cells, fungi, and bacteria, all by disrupting protein translation. It was originally described by Japanese researchers in the 1950s seeking antibiotics for rice blast fungus.
Zwittermicin A is an antibiotic that has been identified from the bacterium Bacillus cereus UW85. It is a molecule of interest to agricultural industry because it has the potential to suppress plant disease due to its broad spectrum activity against certain gram positive and gram negative prokaryotic micro-organisms. The molecule is also of interest from a metabolic perspective because it represents a new structural class of antibiotic and suggests a crossover between polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide biosynthetic pathways. Zwittermicin A is linear aminopolyol.
Streptogramin B is a subgroup of the streptogramin antibiotics family. These natural products are cyclic hexa- or hepta depsipeptides produced by various members of the genus of bacteria Streptomyces. Many of the members of the streptogramins reported in the literature have the same structure and different names; for example, pristinamycin IA = vernamycin Bα = mikamycin B = osteogrycin B.

Echinomycin is a peptide antibiotic. It is a dimer of two peptides creating a cyclic structure. It contains a bicyclic aromatic chromophore that is attached to the dimerized cyclic peptide core and a thioacetal bridge. It intercalates into DNA at two specific sites, thereby blocking the binding of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1alpha).

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.

The cyclothiazomycins are a group of natural products, classified as thiopeptides, which are produced by various Streptomyces species of bacteria.
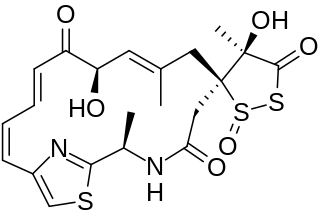
Leinamycin is an 18-membered macrolactam produced by several species of Streptomyces atroolivaceus. This macrolactam has also been shown to exhibit antitumor properties as well as antimicrobial properties against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The presence of a spiro-fused 1,3-dioxo-1,2-dithiolane moiety was a unique structural property at the time of this compound's discovery and it plays an important role in leinamycin's antitumor and antibacterial properties due to its ability to inhibit DNA synthesis.

C-1027 or lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks.

Pyoluteorin is a natural antibiotic that is biosynthesized from a hybrid nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) and polyketide synthase (PKS) pathway. Pyoluteorin was first isolated in the 1950s from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains T359 and IFO 3455 and was found to be toxic against oomycetes, bacteria, fungi, and against certain plants. Pyoluteorin is most notable for its toxicity against the oomycete Pythium ultimum, which is a plant pathogen that causes a global loss in agriculture. Currently, pyoluteorin derivatives are being studied as an Mcl-1 antagonist in order to target cancers that have elevated Mcl-1 levels.

Dihydromaltophilin, or heat stable anti-fungal factor (HSAF), is a secondary metabolite of Streptomyces sp. and Lysobacter enzymogenes. HSAF is a polycyclic tetramate lactam containing a single tetramic acid unit and a 5,5,6-tricyclic system. HSAF has been shown to have anti-fungal activity mediated through the disruption of the biosynthesis of Sphingolipid's by targeting a ceramide synthase unique to fungi.
















