Related Research Articles

Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.

Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.

Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) in (via the gut) and out (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and between body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and bone. Bone acts as a calcium storage center for deposits and withdrawals as needed by the blood via continual bone remodeling.
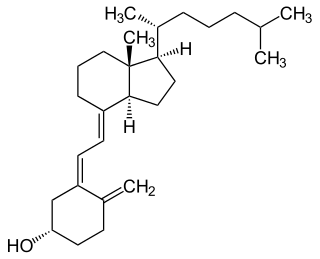
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 or colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is produced by the skin when exposed to UVB light; it is found in certain foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia. Those with a mild increase that has developed slowly typically have no symptoms. In those with greater levels or rapid onset, symptoms may include abdominal pain, bone pain, confusion, depression, weakness, kidney stones or an abnormal heart rhythm including cardiac arrest.

Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands or as response to external stimuli. Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are caused by inappropriately normal or elevated blood calcium excreted from the bones and flowing into the blood stream in response to increased production of parathyroid hormone. In healthy people, when blood calcium levels are high, parathyroid hormone levels should be low. With long-standing hyperparathyroidism, the most common symptom is kidney stones. Other symptoms may include bone pain, weakness, depression, confusion, and increased urination. Both primary and secondary may result in osteoporosis.

The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are used in medicine where they regulate skin health, immunity and bone disorders.
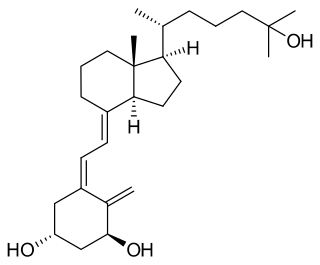
Calcitriol is a hormone and the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. It is also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. It binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the expression of many genes. Calcitriol increases blood calcium mainly by increasing the uptake of calcium from the intestines.

Calcipotriol, also known as calcipotriene, is a synthetic derivative of calcitriol, a form of vitamin D. It is used in the treatment of psoriasis. It is safe for long-term application in psoriatic skin conditions.

Vitamin D toxicity, or hypervitaminosis D, is the toxic state of an excess of vitamin D. The normal range for blood concentration in adults is 20 to 50 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL).
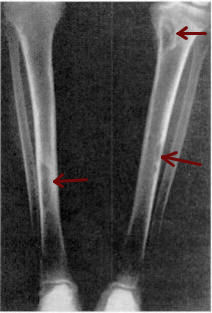
Osteitis fibrosa cystica is a skeletal disorder resulting in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue, and the formation of cyst-like brown tumors in and around the bone. Osteitis fibrosis cystica (OFC), also known as osteitis fibrosa, osteodystrophia fibrosa, and von Recklinghausen's disease of bone, is caused by hyperparathyroidism, which is a surplus of parathyroid hormone from over-active parathyroid glands. This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption. The hyperparathyroidism can be triggered by a parathyroid adenoma, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma, or renal osteodystrophy. Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium, from the bone into the bloodstream, causing both elevated blood calcium levels, and the structural changes which weaken the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea, moth-eaten appearance in the bones, appetite loss, and weight loss.

Secondary hyperparathyroidism is the medical condition of excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) by the parathyroid glands in response to hypocalcemia, with resultant hyperplasia of these glands. This disorder is primarily seen in patients with chronic kidney failure. It is sometimes abbreviated "SHPT" in medical literature.

Tertiary hyperparathyroidism is a condition involving the overproduction of the hormone, parathyroid hormone, produced by the parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are involved in monitoring and regulating blood calcium levels and respond by either producing or ceasing to produce parathyroid hormone.

The vitamin D receptor (VDR also known as the calcitriol receptor) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D, 1,25-(OH)2vitamin D3) binds to VDR, which then forms a heterodimer with the retinoid-X receptor. The VDR heterodimer then enters the nucleus and binds to Vitamin D responsive elements (VDRE) in genomic DNA. VDR binding results in expression or transrepression of many specific gene products. VDR is also involved in microRNA-directed post transcriptional mechanisms. In humans, the vitamin D receptor is encoded by the VDR gene located on chromosome 12q13.11.

Calcifediol, also known as calcidiol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (abbreviated 25(OH)D3), is a form of vitamin D produced in the liver by hydroxylation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) by the enzyme vitamin D 25-hydroxylase. Calcifediol can be further hydroxylated by the enzyme 25(OH)D-1α-hydroxylase, primarily in the kidney, to form calcitriol (1,25-(OH)2D3), which is the active hormonal form of vitamin D.

Cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1 (abbreviated CYP24A1) is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes encoded by the CYP24A1 gene. It is a mitochondrial monooxygenase which catalyzes reactions including 24-hydroxylation of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3). It has also been identified as vitamin D3 24-hydroxylase.(EC 1.14.15.16)
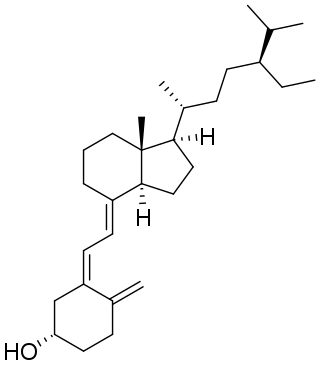
Vitamin D5 (sitocalciferol) is a form of vitamin D.

Alfacalcidol is an analogue of vitamin D used for supplementation in humans and as a poultry feed additive.

Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most significant compounds within this group are vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).

Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate, sold under the brand name Taclonex among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication of the synthetic vitamin D3 analog calcipotriol (also known as calcipotriene) and the synthetic corticosteroid betamethasone dipropionate for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. It is used in the form of ointment, topical suspension, gel, aerosol, and foam.
References
- ↑ Ashcroft DM, Po AL, Williams HC, Griffiths CE (April 2000). "Systematic review of comparative efficacy and tolerability of calcipotriol in treating chronic plaque psoriasis". BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 320 (7240): 963–7. doi:10.1136/bmj.320.7240.963. PMC 27334 . PMID 10753146.
- ↑ Martin KJ, González EA (November 2001). "Vitamin D analogues for the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism". American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 38 (5 Suppl 5): S34–40. doi:10.1053/ajkd.2001.28109. PMID 11689385.
- ↑ O'Neill JL, Feldman SR (May 2010). "Vitamine D analogue-based therapies for psoriasis". Drugs of Today. 46 (5): 351–60. doi:10.1358/dot.2010.46.5.1473264. PMID 20517536.
- ↑ Birlea SA, Costin GE, Norris DA (April 2008). "Cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the action of vitamin D analogs targeting vitiligo depigmentation". Current Drug Targets. 9 (4): 345–59. doi:10.2174/138945008783954970. PMID 18393827.
- 1 2 Bikle DD (March 2014). "Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications". Chemistry & Biology. 21 (3): 319–29. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.12.016. PMC 3968073 . PMID 24529992.