
The pipe organ is a musical instrument that produces sound by driving pressurised air through the organ pipes selected from a keyboard. Because each pipe produces a single pitch, the pipes are provided in sets called ranks, each of which has a common timbre, volume, and construction throughout the keyboard compass. Most organs have many ranks of pipes of differing pitch, timbre, and volume that the player can employ singly or in combination through the use of controls called stops.

In music, the organ is a keyboard instrument of one or more pipe divisions or other means for producing tones. The organs have usually two or three, up to five, manuals for playing with the hands and a pedalboard for playing with the feet. With the use of registers, several groups of pipes can be connected to one manual.

An organ stop is a component of a pipe organ that admits pressurized air to a set of organ pipes. Its name comes from the fact that stops can be used selectively by the organist; each can be "on", or "off".

A pedalboard is a keyboard played with the feet that is usually used to produce the low-pitched bass line of a piece of music. A pedalboard has long, narrow lever-style keys laid out in the same semitone scalar pattern as a manual keyboard, with longer keys for C, D, E, F, G, A, and B, and shorter, raised keys for C♯, D♯, F♯, G♯ and A♯. Training in pedal technique is part of standard organ pedagogy in church music and art music.
The Voix celeste is an organ stop consisting of either one or two ranks of pipes slightly out of tune. The term celeste refers to a rank of pipes detuned slightly so as to produce a beating effect when combined with a normally tuned rank. It is also used to refer to a compound stop of two or more ranks in which all the ranks are detuned relative to each other.

The word "manual" is used instead of the word "keyboard" when referring to any hand-operated keyboard on a keyboard instrument that has a pedalboard, such as an organ; or when referring to one of the keyboards on an instrument that has more than one hand-operated keyboard, such as a two- or three-manual harpsichord.

A flue pipe is an organ pipe that produces sound through the vibration of air molecules, in the same manner as a recorder or a whistle, in a pipe organ. Air under pressure is driven through a flue and against a sharp lip called a labium, causing the column of air in the pipe to resonate at a frequency determined by the pipe length. Thus, there are no moving parts in a flue pipe. This is in contrast to reed pipes, whose sound is driven by beating reeds, as in a clarinet.

An organ pipe is a sound-producing element of the pipe organ that resonates at a specific pitch when pressurized air is driven through it. Each pipe is tuned to a note of the musical scale. A set of organ pipes of similar timbre comprising the complete scale is known as a rank; one or more ranks constitutes a stop.

A tremulant is a device on a pipe organ which varies the wind supply to the pipes of one or more divisions. This causes their amplitude and pitch to fluctuate, producing a tremolo and vibrato effect. A large organ may have several tremulants, affecting different ranks (sets) of pipes. Many tremulants are variable, allowing for the speed and depth of tremolo to be controlled by the organist. The tremulant has been a part of organ building for many centuries, dating back to Italian organs of the sixteenth century.
Bourdon, bordun, or bordone normally denotes a stopped flute type of flue pipe in an organ characterized by a dark tone, strong in fundamental, with a quint transient but relatively little overtone development. Its half-length construction makes it especially well suited to low pitches, and economical as well. The name is derived from the French word for 'bumblebee' or 'buzz'.

The musical instrument known as the regal or regalle is a small portable organ, furnished with beating reeds and having two bellows. The instrument enjoyed its greatest popularity during the Renaissance. The name "regal" was also sometimes given to the reed stops of a pipe organ, and more especially to the vox humana stop.
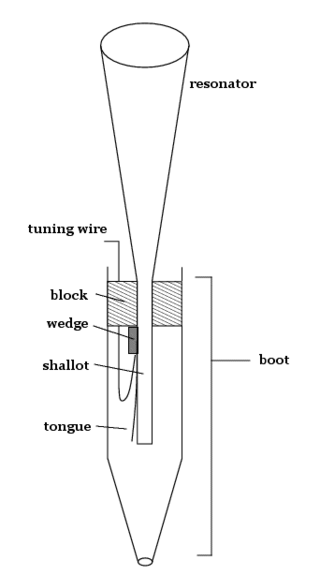
A reed pipe is an organ pipe that is sounded by a vibrating brass strip known as a reed. Air under pressure is directed towards the reed, which vibrates at a specific pitch. This is in contrast to flue pipes, which contain no moving parts and produce sound solely through the vibration of air molecules. Reed pipes are common components of pipe organs.
Gedackt is the name of a family of stops in pipe organ building. They are one of the most common types of organ flue pipe. The name stems from the Middle High German word gedact, meaning "capped" or "covered".
This article describes the process and techniques involved in the tuning of a pipe organ. Electronic organs typically do not require tuning.
The Human Voice is a monodrama first staged at the Comédie-Française in 1930, written two years earlier by Jean Cocteau. It is set in Paris, where a still-quite-young woman is on the phone with her lover of the last five years. He is to marry another woman the next day, which causes her to despair. The monologue triggers the woman's crippling depression.

The pipe organ is played from an area called the console or keydesk, which holds the manuals (keyboards), pedals, and stop controls. In electric-action organs, the console is often movable. This allows for greater flexibility in placement of the console for various activities. Some very large organs, such as the van den Heuvel organ at the Church of St. Eustache in Paris, have more than one console, enabling the organ to be played from several locations depending on the nature of the performance.
Registration is the technique of choosing and combining the stops of a pipe organ in order to produce a particular sound. Registration can also refer to a particular combination of stops, which may be recalled through combination action. The registration chosen for a particular piece will be determined by a number of factors, including the composer's indications, the time and place in which the piece was composed, the organ the piece is played upon, and the acoustic environment within which the organ resides.

Organ building is the profession of designing, building, restoring and maintaining pipe organs.
Vox humana is a reed stop on the pipe organ.











