WAP, follistatin/kazal, immunoglobulin, kunitz and netrin domain containing 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WFIKKN2 gene. [5]
WAP, follistatin/kazal, immunoglobulin, kunitz and netrin domain containing 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WFIKKN2 gene. [5]
The WFIKKN1 protein contains a WAP domain, follistatin domain, immunoglobulin domain, two tandem Kunitz domains, and an NTR domain. This gene encodes a WFIKKN1-related protein which has the same domain organization as the WFIKKN1 protein. The WAP-type, follistatin type, Kunitz-type, and NTR-type protease inhibitory domains may control the action of multiple types of proteases. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. ##Evidence-Data-START## Transcript exon combination :: AY358142.1, AK127743.1 [ECO:0000332] RNAseq introns :: single sample supports all introns ERS025083, ERS025084 [ECO:0000348] ##Evidence-Data-END##

Myostatin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSTN gene. Myostatin is a myokine that is produced and released by myocytes and acts on muscle cells to inhibit muscle growth. Myostatin is a secreted growth differentiation factor that is a member of the TGF beta protein family.
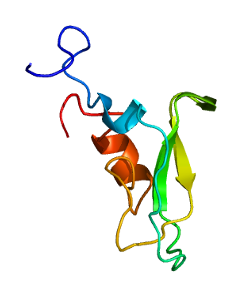
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor is a single-chain polypeptide which can reversibly inhibit factor Xa (Xa). While Xa is inhibited, the Xa-TFPI complex can subsequently also inhibit the FVIIa-tissue factor complex. TFPI contributes significantly to the inhibition of Xa in vivo, despite being present at concentrations of only 2.5 nM.
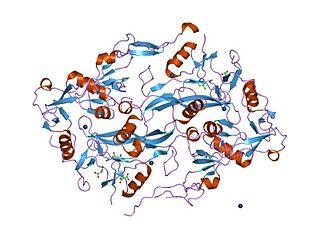
Follistatin also known as activin-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FST gene. Follistatin is an autocrine glycoprotein that is expressed in nearly all tissues of higher animals.

Activin receptor type-1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR1B gene.

Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor (PSTI) also known as serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 1 (SPINK1) or tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor (TATI) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPINK1 gene.

Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 2 is an enzyme inhibitor that in humans is encoded by the SPINT2 gene. SPINT2 is a transmembrane protein with two extracellular Kunitz domains to inhibit serine proteases. This gene is a presumed tumor suppressor by inhibiting HGF activator which prevents the formation of active hepatocyte growth factor. Mutations in SPINT2 could result in congenital sodium diarrhea (CSD).
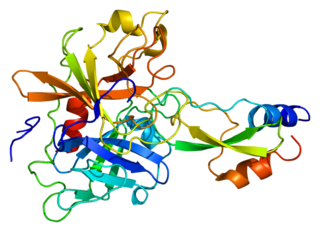
Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SPINT1 gene.
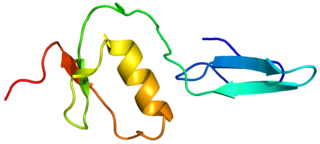
Follistatin-related protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FSTL3 gene.

Glia-derived nexin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINE2 gene.
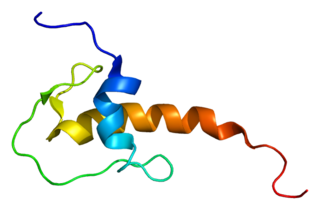
Lympho-epithelial Kazal-type-related inhibitor (LEKTI) also known as serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 5 (SPINK5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPINK5 gene.

Hepatocyte growth factor activator is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HGFAC gene.

Procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCOLCE gene.

Follistatin-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FSTL1 gene.

Eppin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPINLW1 gene.

WAP four-disulfide core domain protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WFDC1 gene.

Serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 2 also known as acrosin-trypsin inhibitor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPINK2 gene.

WAP, kazal, immunoglobulin, kunitz and NTR domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that is encoded by the WFIKKN1 gene. when found in humans.
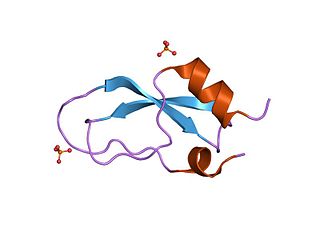
Kunitz domains are the active domains of proteins that inhibit the function of protein degrading enzymes or, more specifically, domains of Kunitz-type are protease inhibitors. They are relatively small with a length of about 50 to 60 amino acids and a molecular weight of 6 kDa. Examples of Kunitz-type protease inhibitors are aprotinin, Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein (APP), and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). Kunitz STI protease inhibitor, the trypsin inhibitor initially studied by Moses Kunitz, was extracted from soybeans.

Lympho-epithelial Kazal-type related inhibitor 2 (LEKTI-2) is a protein encoded by the SPINK9 gene in humans. SPINK9 is a member of a gene family cluster located on chromosome 5q33.1, which includes SPINK5 and SPINK6. LEKTI-2 is an inhibitor of KLK5.
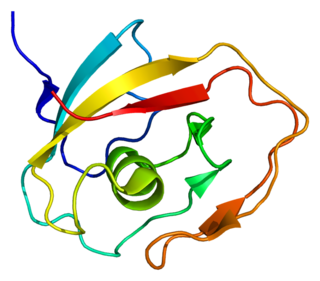
In molecular biology, the LCCL domain is a protein domain which has been named after several well-characterised proteins that were found to contain it, namely Limulus clotting factor C, Cochlin (Coch-5b2) and Lgl1 (CRISPLD2). It is an about 100 amino acids domain whose C-terminal part contains a highly conserved histidine in a conserved motif YxxxSxxCxAAVHxGVI. The LCCL module is thought to be an autonomously folding domain that has been used for the construction of various modular proteins through exon-shuffling. It has been found in various metazoan proteins in association with complement B-type domains, C-type lectin domains, von Willebrand type A domains, CUB domains, discoidin lectin domains or CAP domains. It has been proposed that the LCCL domain could be involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding. LCCL exhibits a novel fold.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.