The Phoenix was an experimental version of the Bristol Aeroplane Company's Pegasus engine, adapted to run on the Diesel cycle. Only a few were built between 1928 and 1932, although samples fitted to a Westland Wapiti held the altitude record for diesel-powered aircraft at 27,453 ft from 11 May 1934 until World War II. The primary advantage of the Phoenix was better fuel efficiency at cruise, by up to 35%.

The Nakajima Sakae was a two-row, 14-cylinder air-cooled radial engine used in a number of combat aircraft of the Imperial Japanese Navy and Imperial Japanese Army before and during World War II.

The Armstrong Siddeley Mongoose is a British five-cylinder radial aero engine produced by Armstrong Siddeley. Developed in the mid-1920s it was used in the Hawker Tomtit trainer and Parnall Peto seaplane amongst others. With a displacement of 540 cubic inches (9 litres) the Mongoose had a maximum power output of 155 horsepower (115 kilowatts).

The Armstrong Siddeley Serval was a British ten-cylinder aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley in the late 1920s. Following company tradition, the engine was named for the serval.

The Walter Venus was a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft use, built in Czechoslovakia in the late 1920s.
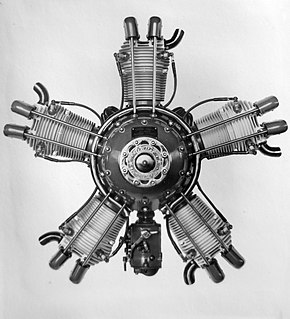
The Walter Vega was a five-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft use, built in Czechoslovakia in the late 1920s.

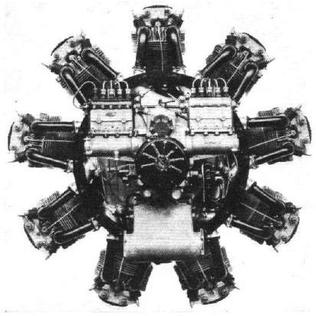
The Gnome et Rhône 18L was a French-designed twin-row 18-cylinder air-cooled radial engine. The 18L was a large step up in terms of displacement, power and number of cylinders. The majority of Gnome-Rhone engines were either 7, 9 or 14 cylinders. The engine proved not to be a success, and it was dropped in 1939 due to a poor power-to-weight ratio.

The Armstrong Siddeley Tiger was a British 14-cylinder air-cooled aircraft radial engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley in the 1930s from their Jaguar engine. The engine was built in a number of different versions but performance and dimensions stayed relatively unchanged. The Tiger VIII was the first British aircraft engine to use a two-speed supercharger.

The Siddeley Tiger was an unsuccessful British aero engine developed shortly after the end of World War I by Siddeley-Deasy. Problems encountered during flight testing caused the project to be cancelled.

The Armstrong Siddeley Ounce was a small two-cylinder aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley in 1920. The engine was originally conceived as a test piece but ran very well and was put into production for early ultralight aircraft and use in target drones. The Ounce used two cylinders from the preceding Jaguar I radial engine.
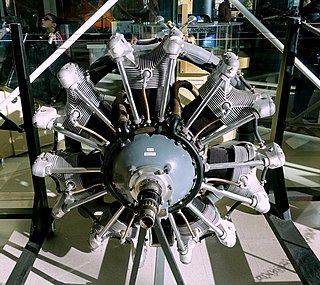
The Jacobs R-915 or Jacobs L-6 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States, production started in 1936.
The Jacobs R-830 or L-5 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States, production started in 1935.

The Alvis Pelides was an unflown British air-cooled radial aero engine first developed in 1936. The Pelides Major was a projected but unbuilt development as were the Alcides, Alcides Major and the Maeonides Major, the Alvis aircraft engine range taking their names from Greek mythology.

The Curtiss H-1640 Chieftain was an unusual American 12-cylinder radial aero engine designed and built by the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company in the mid-1920s.

The Walter Scolar was a Czechoslovakian nine-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that first ran in 1936. With a displacement of 8 litres, it produced 132 kW at 2,500 rpm.

The Walter Pollux is a Czechoslovakian nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine, built by Walter Aircraft Engines for powering light aircraft and that first ran in 1936. The engine produces 240 kW (320 hp) at 1,800 rpm.

The Walter Regulus was a Czechoslovakian five-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that first ran in 1934. The engine produced 186 kW.

The Walter Polaris was a Czechoslovakian three-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that was developed in the 1930s.

The Walter Mars was a Czechoslovakian 14-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering aircraft, a licensed built Gnome-Rhône 14M.

The Walter Castor was a Czechoslovakian seven-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering aircraft that was developed in the late 1920s. The Super Castor was a nine-cylinder development. Castor I production began in 1928, Castor II in 1932 and the Castor III in 1934.


















