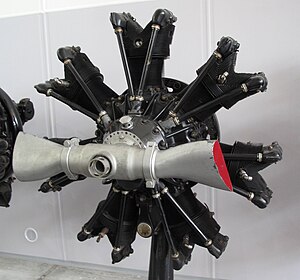
The BMW 132 was a nine-cylinder radial aircraft engine produced by BMW starting in 1933.

The Armstrong Siddeley Mongoose is a British five-cylinder radial aero engine produced by Armstrong Siddeley. Developed in the mid-1920s it was used in the Hawker Tomtit trainer and Parnall Peto seaplane amongst others. With a displacement of 540 cubic inches (9 litres) the Mongoose had a maximum power output of 155 horsepower (115 kilowatts).

The Walter Venus was a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft use, built in Czechoslovakia in the late 1920s.
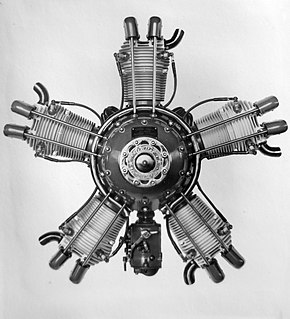
The Walter Vega was a five-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft use, built in Czechoslovakia in the late 1920s.

The Hispano-Suiza 14AB, a.k.a. Hispano-Suiza Type 80, was a 14-cylinder twin-row air-cooled radial engine. In 1929 the Hispano-Suiza company bought a license to produce the Wright Whirlwind engine. The technology from that engine was used to produce a number of different radial engines with greater displacements, power, and number of cylinders.
The Hirth HM 506 was a six-cylinder air-cooled inverted inline engine that was developed from the earlier four-cylinder HM 504. The HM 506 was a popular engine for light aircraft of the 1930s to 1940s and powered the Bücker Bü 133A model trainer. The engine featured a cast magnesium alloy crankcase.

The Hirth HM 60 was a four-cylinder inverted air-cooled inline aircraft engine designed in 1923 and first sold in 1924. The engine was of very high quality, and its sales success contributed to Hirth's rapid pre-war expansion. It was a popular engine for light aircraft delivering 80 hp (60 kW) at 2,300 rpm. Later Hirth engines built upon the HM 60's success and provided greater power with many of the same design features.

The Armstrong Siddeley Tiger was a British 14-cylinder air-cooled aircraft radial engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley in the 1930s from their Jaguar engine. The engine was built in a number of different versions but performance and dimensions stayed relatively unchanged. The Tiger VIII was the first British aircraft engine to use a two-speed supercharger.

The Kinner K-5 was a popular engine for light general and sport aircraft developed by Winfield B. 'Bert' Kinner. With the boom in civilian aviation after Charles Lindbergh's transatlantic flight the K-5 sold well. The K-5 was a rough running but reliable engine and the K-5 and its derivatives were produced in the thousands, powering many World War II trainer aircraft. The K-5 was followed by the B-5, R-5 and R-55. Military engines were designated R-370

The BMW X is a small five-cylinder radial engine for sport and training aircraft. Although this engine proved successful at several large-scale events in 1930, including that year's round-Europe flight, only a few were built.

The ABC Dragonfly was a British radial engine developed towards the end of the First World War. It was expected to deliver excellent performance for the time and was ordered in very large numbers. It proved, however, to be extremely unreliable and was abandoned when its faults were unable to be corrected.

British Salmson aero-engines refers to a series of small French designed, air-cooled radial aero engine that were produced by British Salmson Aero Engines Ltd, under license from Société des Moteurs Salmson, in Great Britain during the late 1920s and 1930s.

The Walter Scolar was a Czechoslovakian nine-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that first ran in 1936. With a displacement of 8 litres, it produced 132 kW at 2,500 rpm.

The Walter Pollux is a Czechoslovakian nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine, built by Walter Aircraft Engines for powering light aircraft and that first ran in 1936. The engine produces 240 kW (320 hp) at 1,800 rpm.

The Walter Regulus was a Czechoslovakian five-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that first ran in 1934. The engine produced 186 kW.

The Walter Bora was a Czechoslovakian nine-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that was developed in the 1930s by Walter Aircraft Engines.
The Clerget 11Eb was an 11-cylinder rotary aircraft engine of the World War I era designed by Pierre Clerget. Powering Sopwith types it was nominally rated at 200 horsepower (150 kW).
The Clerget 7Z was a seven-cylinder rotary aircraft engine of the World War I era designed by Pierre Clerget. First appearing in 1911 it was nominally rated at 80 horsepower (60 kW). 347 examples were jointly built in Britain by Gordon Watney & Co Ltd of Weybridge and Gwynnes Limited of Hammersmith.

The Guiberson A-1020 is a four-stroke diesel radial engine developed for use in aircraft and tanks.
The Franklin O-500 was an American air-cooled aircraft engine that first ran in the mid-1940s. The engine was of six-cylinder, horizontally-opposed layout and displaced 500 cu in (8 L). The power output was 215 hp (160 kW).