Longtan Dam is a large roller-compacted concrete (RCC) gravity dam on the Hongshui River in Tian'e County of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China, a tributary of the Xi River and the Pearl River. The dam is 216.2 metres (709.3 ft) high and 849 m (2,785 ft) long; it is the tallest of its type in the world. The dam is intended for hydroelectric power production, flood control and navigation. The dam contains seven surface spillways, two bottom outlets and an underground power station. The Longtan ship lift, part of the dam complex, will be the tallest ship lift system in the world.

The Robert-Bourassa generating station, formerly known as La Grande-2 (LG-2), is a hydroelectric power station on the La Grande River that is part of Hydro-Québec's James Bay Project in Canada. The station can generate 5,616 MW and its 16 units were gradually commissioned between 1979 and 1981. Annual generation is in the vicinity of 26500 GWh.
The Xiaowan Dam is an arch dam on the Lancang (Mekong) River in Nanjian County, Yunnan Province in southwest China. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 4,200 MW power station. Constructed between 2002 and 2010 by Huaneng Power International at a cost of ¥32 billion, it is the world's second highest arch dam at 292 m (958 ft). It is also third highest among dams of all types behind Jinping-I and Nurek and the third largest hydroelectric power station in China.

The Ertan Dam is an arch dam on the Yalong River, a tributary of the Yangtze River in Sichuan Province, in southwest China.

The Oroville–Thermalito Complex is a group of reservoirs, structures, and facilities located in and around the city of Oroville in Butte County, California. The complex serves not only as a regional water conveyance and storage system, but is the headwaters for, and therefore perhaps is the most vital part of, the California Department of Water Resources' State Water Project, as one of the largest publicly built and operated water and power development and conveyance systems.

Tanbara Dam is a rock-fill embankment dam impounding the headwaters of the Hotchi River, a Tone River tributary in Gunma Prefecture of Japan. It is located 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) north of Numata. It creates the upper reservoir for the 1,200 megawatts (1,600,000 hp) Tamahara Pumped Storage Power Station (玉原発電所). Construction began in 1973 and the dam was complete in 1981 while the power station was commissioned in 1986. It is 116 metres (381 ft) tall and withholds a reservoir with a storage capacity of 14,800,000 m3 (11,999 acre⋅ft). Of that capacity, 13,000,000 cubic metres (11,000 acre⋅ft) is active for power generation. The lower reservoir for the pumped-storage power station is created by the Fujiwara Dam, located 4 km (2 mi) to the northwest on another Tone River tributary. Power is generated during periods of high energy demand and pumping occurs during times when energy demand is low such as at night. The power station contains four 300 megawatts (400,000 hp) reversible Francis turbine pump-generators which serve to both pump water and generate electricity. The upper Tamahara Reservoir is at an elevation of 1,177 metres (3,862 ft) and the lower Fujiwara Reservoir is at 651 metres (2,136 ft) which affords the power station an effective hydraulic head of 518 metres (1,699 ft). When pumping, the pump-generators can move up to 210 cubic metres per second (7,400 cu ft/s) of water and when generating, they discharge up to 276 cubic metres per second (9,700 cu ft/s).
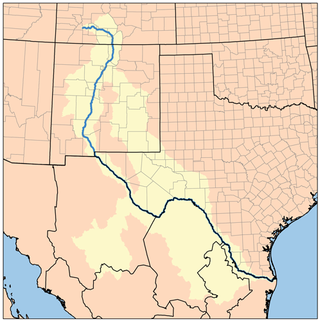
The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates 193,000 acres (780 km2) along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some 25,000 acres (100 km2) on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s.

The Siah Bisheh Pumped Storage Power Plant, also spelled Siyāhbisheh and Siah Bishe, is located in the Alborz Mountain range near the village of Siah Bisheh and 48 km (30 mi) south of Chalus in Mazandaran Province, Iran. The power plant uses the pumped-storage hydroelectric method to generate electricity during periods of high energy demand, making it a peaking power plant, intended to fulfill peak electricity demand in Tehran 60 km (37 mi) to the south. When complete it will have an installed generating capacity of 1,040 megawatts (1,390,000 hp) and a pumping capacity of 940 megawatts (1,260,000 hp). Planning for the project began in the 1970s and construction began in 1985. It was delayed from 1992 until 2001 and the first generator went online in May 2013. The remaining generators were commissioned by 1 September 2015. The power plant is the first pumped-storage type in Iran and will also use the country's first concrete-face rock-fill dam – two of them.

Seimare Dam, also known as Hini Mini or spelled Seymareh, is an arch dam on the Seimare River in Badreh County, Ilam Province, Iran. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation. Studies for the dam were carried out in the mid to late 1970s and construction began on the diversion works in 1997. In 2006, concrete placement began and on 19 May 2011, the dam began to impound the river. The dam's first generator became operational in 2013. The power plant, located downstream, houses three 160 MW Francis turbine-generators with an installed capacity of 480 MW.

The Kannagawa Hydropower Plant (神流川発電所) is an under construction pumped-storage hydroelectric power plant near Minamiaiki in Nagano Prefecture and Ueno in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. The power plant utilizes the Minamiaiki River along with an upper and lower reservoir created by two dams, the upper Minamiaiki Dam and the lower Ueno Dam. The power station in between the two dams will contain six 470 megawatts (630,000 hp) pump-generators for a total installed capacity of 2,820 megawatts (3,780,000 hp). Unit 1 commenced commercial operation in 2005 and Unit 2 in 2012. When completed, the plant will have the third-largest pumped-storage power capacity in the world.
The Dachaoshan Dam is a gravity dam on the Lancang (Mekong) River in Yunnan Province, China. The sole purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production as it supplies water to a power station containing six 225 MW generators for a total installed capacity of 1,350 MW.

The Fengman Dam is a concrete gravity dam 20 km (12 mi) from Jilin City on the Second Songhua River in Jilin Province, China. The main purposes of the dam are hydroelectric power generation and flood control. Construction of the dam began in 1937 and was complete in 1953. The dam is owned and operated by Northeast China Grid Company Limited.

The Amagase Dam (天ヶ瀬ダム) is an arch dam on the Uji River just upstream from Uji, Kyoto Prefecture, Japan. The main purpose of the dam is flood control but it supports a hydroelectric power station and creates the lower reservoir for the Kisenyama Pumped Storage Plant. The dam itself serves a 92 MW power station while the pumped-storage power station upstream has a 466 MW capacity. Construction on the dam began in 1955 and it was complete in 1964. The pumped-storage power station became operational in 1970. Both plants are owned by Kansai Electric Power Company.

The Ramganga Dam, also known as the Kalagarh Dam, is an embankment dam on the Ramganga River 3 km (2 mi) upstream of Kalagarh in Pauri Garhwal district, Uttarakhand, India. It is located within the Jim Corbett National Park.
The Koteshwar Dam is a gravity dam on the Bhagirathi River, located 22 km (14 mi) downstream of the Tehri Dam in Tehri District, Uttarakhand, India. The dam is part of the Tehri Hydropower Complex and serves to regulate the Tehri Dam's tailrace for irrigation and create the lower reservoir of the Tehri Pumped Storage Power Station. In addition, the dam has a 400 MW run-of-the-river power station. The project was approved in 2000 and its first generator was commissioned on 27 March 2011, the second on 30 March 2011. The construction site had been inundated in September 2010 by floods. The diversion tunnel was later blocked heaving/collapse of the hill in December 2010. The spillway was commissioned in Jan, 2011. The last two generators were made operational in March 2012.
The Guxian Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Luo River, a tributary of the Yellow River, in Luoning County, Henan Province, China. The primary purpose of the dam is flood control but it also generates hydroelectricity and provides water for irrigation. The 125 m (410 ft) tall dam withholds a reservoir of 1,175,000,000 m3 (952,588 acre⋅ft) and provides 848,000,000 m3 (687,485 acre⋅ft) in flood storage. The dam's power station contains three 20 MW Francis turbine-generators for a total installed capacity of 60 MW. Construction on the dam began in 1958 but was suspended several times afterwards. It recommenced in 1978 and the reservoir began to fill in 1991. The dam's generators were commissioned in 1992 and the project complete in 1993. The dam's spillway is controlled by five tainter gates and has a maximum discharge capacity of 11,436 m3/s (403,859 cu ft/s). Flip buckets are used at the spillway base to dissipate water. On the right side of the spillway there are two intermediate orifice openings controlled by hydraulic press-operated radial gates. Two bottom outlets are set on the spillway's left side, also controlled by hydraulic press-operated radial gates. To the left of the bottom outlets is the power station.
The Panjiakou Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Luan River in Qianxi County, Hebei Province, China. The primary purpose of the dam is to provide water for the cities of Tianjin and Tangshan, located to the south. The dam also provides flood control and its power plant has an installed capacity of 420 MW which includes a 270 MW pumped storage power station.
The Daguangba Dam is a multi-purpose dam on the Changhua River in Hainan Province, China. It is located 35 km (22 mi) east of Dongfang. As the primary component of the Daguangba Multipurpose Project, the dam was constructed between 1990 and 1995. It serves to provide water for both hydroelectric power generation and agriculture. It supports a 240 MW power station and supplies water for the irrigation of 12,700 ha. It is also the largest dam and hydroelectric power station in Hainan.

Wujie Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Zhuoshui River in Ren'ai Township, Nantou County, Taiwan. The dam was built in two stages, from 1919 to 1922 and 1927–1934, and serves primarily to divert water from the Zhuoshui River to a storage reservoir at Sun Moon Lake and its associated hydroelectric projects. During the Japanese occupation of Taiwan it was known as Bukai Dam.
The Lubuge Dam is a rock-fill embankment dam on the Huangni River, a tributary of the Nanpan River, located near Lubugexiang in Luoping County on the border of Guizhou and Yunnan Provinces, China. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 600 MW power station. Construction on the project began in 1982 and it was completed in 1991. Funded by the World Bank, it was the first loan offered by the bank to China's power sector.