Alternate history or alternative history (AH) is a genre of speculative fiction consisting of stories in which one or more historical events occur differently. These stories usually contain "what if" scenarios at crucial points in history and present outcomes other than those in the historical record. The stories are conjectural but are sometimes based on fact. Alternate history has been seen as a subgenre of literary fiction, science fiction, or historical fiction; alternate history works may use tropes from any or all of these genres. Another term occasionally used for the genre is "allohistory".
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians have studied that topic using particular sources, techniques, and theoretical approaches. Scholars discuss historiography by topic—such as the historiography of the United Kingdom, that of Canada, the British Empire, early Islam, and China—and different approaches and genres, such as political history and social history. Beginning in the nineteenth century, with the development of academic history, there developed a body of historiographic literature. The extent to which historians are influenced by their own groups and loyalties—such as to their nation state—remains a debated question.

Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus in the Persian Empire. He is known for having written the book The Histories, a detailed record of his "inquiry" on the origins of the Greco-Persian Wars. He is widely considered to have been the first writer to have treated historical subjects using a method of systematic investigation—specifically, by collecting his materials and then critically arranging them into an historiographic narrative. On account of this, he is often referred to as "The Father of History", a title first conferred on him by the first-century BC Roman orator Cicero.

Anatomically modern humans are thought to have arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Settled life, which involves the transition from foraging to farming and pastoralism, began in South Asia around 7,000 BCE; during this period, domestication of wheat and barley, rapidly followed by that of goats, sheep, and cattle occurred. By 4,500 BCE, settled life had become more widely prevalent, and eventually evolved into the Indus Valley Civilization. Considered a cradle of civilisation, the Indus Valley civilisation, which spread and flourished in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent from 3300 to 1300 BCE, was the first major civilisation in South Asia. A sophisticated and technologically advanced urban culture developed in the Mature Harappan period, from 2600 to 1900 BCE. Indus Valley Civilisation was noted for developing new techniques in handicraft, carnelian products, seal carving, metallurgy, urban planning, baked brick houses, efficient drainage systems, water supply systems and clusters of large non-residential buildings. This civilisation collapsed at the start of the second millennium BCE and was later followed by the Iron Age Vedic Civilisation.

In the history of the United Kingdom, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian period, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the Belle Époque era of Continental Europe. In terms of moral sensibilities and political reforms, this period began with the passage of the Reform Act 1832. There was a strong religious drive for higher moral standards led by the nonconformist churches, such as the Methodist, and the Evangelical wing of the established Church of England. Britain's relations with the other Great Powers were driven by the colonial antagonism of the Great Game with Russia, climaxing during the Crimean War; a Pax Britannica of international free trade was maintained by the country's naval and industrial supremacy. Britain embarked on global imperial expansion, particularly in Asia and Africa, which made the British Empire the largest empire in history. National self-confidence peaked.

A museum is an institution that cares for (conserves) a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from serving researchers and specialists to serving the general public. The goal of serving researchers is increasingly shifting to serving the general public.

Ancient history as a term refers to the aggregate of past events from the beginning of writing and recorded human history and extending as far as the post-classical history. The phrase may be used either to refer to the period of time or the academic discipline.

The Kingdom of Great Britain, officially called simply Great Britain, was a sovereign state in western Europe from 1 May 1707 to 31 December 1800. The state came into being following the Treaty of Union in 1706, ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single parliament and government that was based in Westminster. The former kingdoms had been in personal union since James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland in 1603 following the death of Elizabeth I, bringing about the "Union of the Crowns". After the accession of George I to the throne of Great Britain in 1714, the kingdom was in a personal union with the Electorate of Hanover.
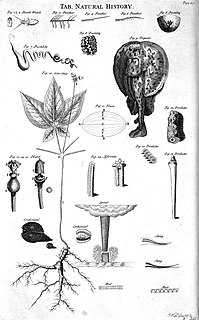
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms including animals, fungi and plants in their environment; leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is called a naturalist or natural historian.

Lawrence Wendell Pfohl better known by the ring name Lex Luger, is an American retired professional wrestler, television producer and football player currently working with WWE on their wellness policy. He is best known for his work with Jim Crockett Promotions, World Championship Wrestling (WCW), and the World Wrestling Federation.

The Delhi Sultanate was a sultanate based mostly in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526). Five dynasties ruled over the Delhi Sultanate sequentially: the Mamluk dynasty (1206–90), the Khalji dynasty (1290–1320), the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1414), the Sayyid dynasty (1414–51), and the Lodi dynasty (1451–1526). The sultanate is noted for being one of the few states to repel an attack by the Mongols, and enthroned one of the few female rulers in Islamic history, Razia Sultana, who reigned from 1236 to 1240.

The Natural History Museum in London is a natural history museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road.
The Billboard 200 is a record chart ranking the 200 most popular music albums and EPs in the United States. It is published weekly by Billboard magazine. It is frequently used to convey the popularity of an artist or groups of artists. Often, a recording act will be remembered by its "number ones", those of their albums that outperformed all others during at least one week. The chart grew from a weekly top 10 list in 1956 to become a top 200 in May 1967, and acquired its present title in March 1992. Its previous names include the Billboard Top LPs (1961–72), Billboard Top LPs & Tape (1972–84), Billboard Top 200 Albums (1984–85) and Billboard Top Pop Albums.

History is a history-based digital cable and satellite television network that is owned by A&E Networks, a joint venture between Hearst Communications and the Walt Disney Television division of the Walt Disney Company. In addition to its self-named flagship channel, History provides sister channels such as History en Español and Military History.
This is a list of known albums and DVDs belonging to the Now That's What I Call Music! series. They are categorised by series (country), then ordered by date.