
In zoology, a scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of an animal's skin to provide protection. In lepidopterans, scales are plates on the surface of the insect wing, and provide coloration. Scales are quite common and have evolved multiple times through convergent evolution, with varying structure and function.

Placoderms are vertebrate animals of the class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates, and the rest of the body was scaled or naked depending on the species.

Galeaspida is an extinct taxon of jawless marine and freshwater fish. The name is derived from galea, the Latin word for helmet, and refers to their massive bone shield on the head. Galeaspida lived in shallow, fresh water and marine environments during the Silurian and Devonian times in what is now Southern China, Tibet and Vietnam. Superficially, their morphology appears more similar to that of Heterostraci than Osteostraci, there being currently no evidence that the galeaspids had paired fins. A galeaspid Tujiaaspis vividus from the Silurian period of China was described in 2022 as having a precursor condition to the form of paired fins seen in Osteostraci and gnathostomes. Earlier than this, Galeaspida were already in fact regarded as being more closely related to Osteostraci, based on the closer similarity of the morphology of the braincase.

Dunkleosteus is an extinct genus of large arthrodire ("jointed-neck") fish that existed during the Late Devonian period, about 382–358 million years ago. It was a pelagic fish inhabiting open waters, and one of the first apex predators of any ecosystem.

Bothriolepis was a widespread, abundant and diverse genus of antiarch placoderms that lived during the Middle to Late Devonian period of the Paleozoic Era.

Rhenanida is an order of scaly placoderms. Unlike most other placoderms, the rhenanids' armor was made up of a mosaic of unfused scales and tubercles. The patterns and components of this "mosaic" correspond to the plates of armor in other, more advanced placoderms, suggesting that the ancestral placoderm had armor made of unfused components, as well.
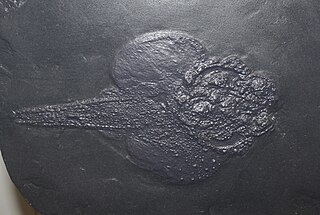
Gemuendina stuertzi is a placoderm of the order Rhenanida, of the seas of Early Devonian Germany. In life, Gemuendina resembled a scaly ray with an upturned head, or a large-finned stargazer. G. stuertzi is often invoked as an example of convergent evolution- with its flat body and huge, wing-like pectoral fins it has a strong, albeit superficial similarity to rays. Unlike rays, however, both Gemuendina`s eyes and nostrils were placed atop the head, facing upward. Furthermore, G. stuertzi's upturned mouth would have enabled it to suction prey that swam overhead, rather than swallow sediment or suction prey out of the substrate like modern rays.

Acanthothoraci is an extinct group of chimaera-like placoderms closely related to the rhenanid placoderms. Superficially, the acanthoracids resembled scaly chimaeras and (relatively) heavily armored ptyctodonts. They were distinguished from chimaeras by their large scales and plates, a pair of large spines that emanate from their chests, tooth-like beak plates, and the typical bone-enhanced placoderm eyeball. They were distinguished from other placoderms by differences in skull anatomy and by patterns on the skull plates and thoracic plates that are unique to this order.

The ptyctodontids ("folded-teeth") are placoderms of the order Ptyctodontida, containing the family Ptyctodontidae. With their big heads, big eyes, reduced armor and long bodies, the ptyctodontids bore a superficial resemblance to modern day chimaeras (Holocephali). Their armor was reduced to a pattern of small plates around the head and neck. Like the extinct and related acanthothoracids, and the living and unrelated holocephalians, most of the ptyctodontids are thought to have lived near the sea bottom and preyed on shellfish.

Brindabellaspis stensioi is a placoderm with a flat, platypus-like snout from the Early Devonian of the Taemas-Wee Jasper reef in Australia. When it was first discovered in 1980, it was originally regarded as a Weejasperaspid acanthothoracid due to anatomical similarities with the other species found at the reef.

Jagorina pandora is a rhenanid placoderm of Upper Frasnian Germany. As with other rhenanids, it was a flattened, skate-like fish protected in an armor made up of unfused tubercles, and preyed on other, smaller fish by ambushing them from the sea bottom.

Psarolepis is a genus of extinct bony fish which lived around 397 to 418 million years ago. Fossils of Psarolepis have been found mainly in South China and described by paleontologist Xiaobo Yu in 1998. It is not known certainly in which group Psarolepis belongs, but paleontologists agree that it probably is a basal genus and seems to be close to the common ancestor of lobe-finned and ray-finned fishes. In 2001, paleontologist John A. Long compared Psarolepis with onychodontiform fishes and refer to their relationships.

Lunaspis is an extinct genus of armor-plated petalichthyid placoderm fish that lived in shallow marine environments of the Early Devonian period, from approximately 409.1 to 402.5 million year ago. Fossils have been found in Germany, China and Australia. There are three different identified species of within the genus Lunaspis: L. broilii, L. heroldi, and L. prumiensis.

Homosteus is a genus of flattened arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian. Fossils are found primarily in Eifelian-epoch aged strata of Europe, Canada, Greenland, and Estonia. All of the species had comparatively large, flattened heads with, as suggested by the upward opening orbits, upward-pointing eyes. These adaptations suggest that the various species were benthic predators. A study on Titanichthys, in contrast, suggests that species of Homosteus may have been filter-feeders instead.

Murrindalaspis is an extinct genus of acanthothoracid placoderm found in the McLarty Member of the Murrindal Limestone, of the Early Devonian-aged Buchan Group in eastern Victoria, Australia. Murrindalaspis differs from other acanthothoracids by having a dorsal plate with a large, blade-like flattened, recurved crest emanating from the medial line, and no ventral keel. So far, the genus is known only from dorsal plates and ossified eyeballs. The genus differs from the closely related Weejasperaspis in that the dorsal crest of the latter is shorter, and triangular-shaped.

The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fish lineages belong to the Agnatha, or jawless fish. Early examples include Haikouichthys. During the late Cambrian, eel-like jawless fish called the conodonts, and small mostly armoured fish known as ostracoderms, first appeared. Most jawless fish are now extinct; but the extant lampreys may approximate ancient pre-jawed fish. Lampreys belong to the Cyclostomata, which includes the extant hagfish, and this group may have split early on from other agnathans.

Holonematidae is an extinct family of relatively large arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Almost all fossil specimens are of armor fragments, though, all have distinctive ornamentation, often of unique arrangements and patterns of tubercles, that are diagnostic of the family. The trunkshield is very elongated, giving the armor an overall "barrel" like appearance.

Weejasperaspis is an extinct acanthothoracid placoderm found in the Taemas-Weejasper Reef, of the Early Devonian-aged Buchan Group in eastern Victoria, Australia and the type species is W. gavini. Weejasperaspis differs from other acanthothoracids in that the median dorsal crest is short, and triangular-shaped. Its sister genus, Murrindalaspis, differs from it by having large, blade-like median dorsal crests that are recurved. Like Murrindalaspis, it is only known from a dorsal plate and ossified eyeballs.

Romundina is a small, heavily armored extinct genus of acanthothoracid placoderms which lived in shallow marine environments in the early Devonian (Lochkovian). The name Romundina honors Canadian geologist and paleontologist Dr. Rómundur (Raymond) Thorsteinsson of Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Romundina are believed to have lived on Earth between 400 and 419 million years ago. The closest known relative to Romundina is the acanthothoracid Radotina. The type and only described species is R. stellina.

Qilinyu is a genus of early placoderm from the late Silurian of China. It contains a single species, Qilinyu rostrata, from the Xiaoxiang fauna of the Kuanti Formation. Along with its contemporary Entelognathus, Qilinyu is an unusual placoderm showing some traits more similar to bony fish, such as dermal jaw bones and lobe-like fins. It can be characterized by adaptations for a benthic lifestyle, with the mouth and nostrils on the underside of the head, similar to the unrelated antiarch placoderms. The shape of the skull has been described as "dolphin-like", with a domed cranium and a short projecting rostrum.



















