
The Wright brothers, Orville Wright and Wilbur Wright, were American aviation pioneers generally credited with inventing, building, and flying the world's first successful airplane. They made the first controlled, sustained flight of an engine-powered, heavier-than-air aircraft with the Wright Flyer on December 17, 1903, four miles (6 km) south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, at what is now known as Kill Devil Hills. In 1904 the Wright brothers developed the Wright Flyer II, which made longer-duration flights including the first circle, followed in 1905 by the first truly practical fixed-wing aircraft, the Wright Flyer III.

Airplane inventors Wilbur and Orville Wright are famed for making the first controlled, powered, heavier-than-air flights on 17 December 1903 at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Lesser-known are other flights of theirs which played an important role at the dawn of aviation history. In 1909 Wilbur was invited by the Hudson-Fulton Celebration Committee to make paid exhibition flights to help mark 300 years of New York history, including Henry Hudson discovering Manhattan and Robert Fulton starting a successful commercial steamboat service on the Hudson River. The committee wanted the Wrights to demonstrate flights over the water around New York City. Orville was making flights for customers in Germany, so Wilbur, who had just finished training U.S. Army pilots, accepted the job.

Charles Edward Taylor was an American inventor, mechanic and machinist. He built the first aircraft engine used by the Wright brothers in the Wright Flyer, and was a vital contributor of mechanical skills in the building and maintaining of early Wright engines and airplanes.

Thomas Etholen Selfridge was a first lieutenant in the U.S. Army and the first person to die in an airplane crash. He was also the first active-duty member of the U.S. military to die in a crash while on duty. He was killed while seated as a passenger in a Wright Flyer, on a demonstration flight piloted by Orville Wright.
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1908:
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1905:

The Wright Flyer made the first sustained flight by a manned heavier-than-air powered and controlled aircraft—an airplane—on December 17, 1903. Invented and flown by brothers Orville and Wilbur Wright, it marked the beginning of the pioneer era of aviation.
The Wright Flyer III is the third powered aircraft by the Wright Brothers, built during the winter of 1904–05. Orville Wright made the first flight with it on June 23, 1905. The Wright Flyer III had an airframe of spruce construction with a wing camber of 1-in-20 as used in 1903, rather than the less effective 1-in-25 used in 1904. The new machine was equipped with the engine and other hardware from the scrapped Flyer II and, after major modifications, achieved much greater performance than Flyers I and II.
Wing warping was an early system for lateral (roll) control of a fixed-wing aircraft or kite. The technique, used and patented by the Wright brothers, consisted of a system of pulleys and cables to twist the trailing edges of the wings in opposite directions. In many respects, this approach is similar to that used to trim the performance of a paper airplane by curling the paper at the back of its wings.

The Wright Flyer II was the second powered aircraft built by Wilbur and Orville Wright. During 1904 they used it to make a total of 105 flights, ultimately achieving flights lasting five minutes and also making full circles, which was accomplished by Wilbur for the first time on September 20.

The Wright Model A is an early aircraft produced by the Wright Brothers in the United States beginning in 1906. It was a development of their Flyer III airplane of 1905. The Wrights built about seven Model A's in their bicycle shop during the period 1906–1907, in which they did no flying. One of these was shipped to Le Havre in 1907 in order to demonstrate it to the French. The Model A had a 35-horsepower (26 kW) engine and seating for two with a new control arrangement. Otherwise, it was identical to the 1905 airplane. The Model A was the first aircraft that they offered for sale, and the first aircraft design to enter serial production anywhere in the world. Apart from the seven machines the Wrights built themselves in 1906–1907, they sold licences for production in Europe with the largest number of Model A's actually being produced in Germany by Flugmaschine Wright GmbH, which built about 60 examples.

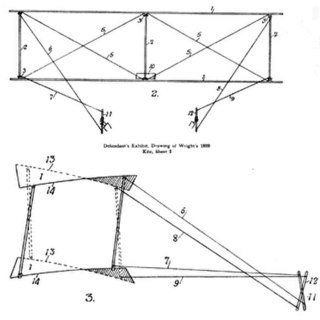
The Wright brothers designed, built and flew a series of three manned gliders in 1900–1902 as they worked towards achieving powered flight. They also made preliminary tests with a kite in 1899. In 1911 Orville conducted tests with a much more sophisticated glider. Neither the kite nor any of the gliders were preserved, but replicas of all have been built.

Louis Ferdinand Ferber was a French Army officer who played an important role in the development of aviation during the early 1900s. Although his aircraft experiments were belatedly successful, his early recognition and publicizing of the work of the Wright Brothers was a major influence on the development of aviation in Europe.

The Farman III, also known as the Henry Farman 1909 biplane, was an early French aircraft designed and built by Henry Farman in 1909. Its design was widely imitated, so much so that aircraft of similar layout were generally referred to as being of the "Farman" type.
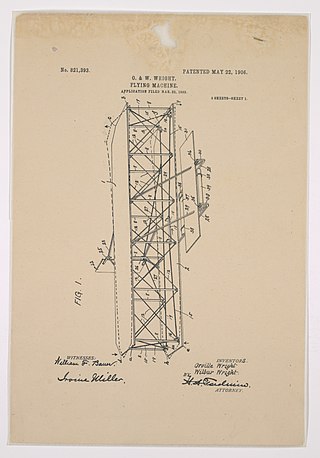
The Wright brothers patent war centers on the patent that the Wright brothers received for their method of airplane flight control. They were two Americans who are widely credited with inventing and building the world's first flyable airplane and making the first controlled, powered, and sustained heavier-than-air human flight on December 17, 1903.

With the purchase of its first airplane, built and successfully flown by Orville and Wilbur Wright, in 1909 the United States Army began the training of flight personnel. This article describes the training provided in those early years, though World War I, and the immediate years after the war until the establishment of the United States Army Air Corps Flight Training Center in San Antonio, Texas during 1926.

The Sommer 1910 Biplane was an early French aircraft designed by Roger Sommer. It was a pusher configuration biplane resembling the successful Farman III, and was built in large numbers for the time. One was owned by Charles Rolls.

The pioneer era of aviation was the period of aviation history between the first successful powered flight, generally accepted to have been made by the Wright Brothers on 17 December 1903, and the outbreak of the First World War in August 1914.

Hart Ostheimer Berg (1865–1941) was an American-born engineer and businessman. Celebrated for his transatlantic promotion of innovative industrial products in the early twentieth century, he is best known for having represented the Wright Brothers’ aviation interests in Europe.
















