
The Catskill Park is in the Catskill Mountains in the U.S. state of New York. It consists of 700,000 acres of land inside a Blue Line in four counties: Delaware, Greene, Sullivan, and Ulster. As of 2005, 287,500 acres (116,300 ha) or 41 percent of the land within, is owned by the state as part of the Forest Preserve; it is managed by the Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC). Another 5% is owned by New York City to protect four of the city's reservoirs in the region that lie partially within the park and their respective watersheds.

The Cherokee National Forest is a United States National Forest located in the U.S. states of Tennessee and North Carolina that was created on June 14, 1920. The forest is maintained and managed by the United States Forest Service. It encompasses an estimated area of 655,598 acres (2,653.11 km2).

The Monongahela National Forest is a national forest located in the Allegheny Mountains of eastern West Virginia, USA. It protects over 921,000 acres of federally managed land within a 1,700,000 acres proclamation boundary that includes much of the Potomac Highlands Region and portions of 10 counties.

The Dolly Sods Wilderness is a U.S. Wilderness Area in the Allegheny Mountains of eastern West Virginia and is part of the Monongahela National Forest of the U.S. Forest Service.

The White Mountain National Forest (WMNF) is a federally managed forest contained within the White Mountains in the northeastern United States. It was established in 1918 as a result of the Weeks Act of 1911; federal acquisition of land had already begun in 1914. It has a total area of 750,852 acres (303,859 ha). Most of the WMNF is in New Hampshire; a small part is in the neighboring state of Maine. Conservationist and community activist Katherine Sleeper Walden was instrumental in securing at-risk land for the forest, including thousands of acres in the region surrounding the locally famous Bowl near Wonalancet.

Sawtooth National Forest is a National Forest that covers 2,110,408 acres in the U.S. states of Idaho and Utah. Managed by the U.S. Forest Service in the U.S. Department of Agriculture, it was originally named the Sawtooth Forest Reserve in a proclamation issued by President Theodore Roosevelt on May 29, 1905. On August 22, 1972, a portion of the forest was designated as the Sawtooth National Recreation Area (SNRA), which includes the Sawtooth, Cecil D. Andrus–White Clouds, and Hemingway–Boulders wilderness areas. The forest is managed as four units: the SNRA and the Fairfield, Ketchum, and Minidoka Ranger Districts.
The Slide Mountain Wilderness Area is, at 47,500 acres (19,200 ha), the largest tract of state-owned Forest Preserve in New York's Catskill Park, and the largest area under any kind of wilderness area protection between the Adirondacks and the southern Appalachians. It is located in the towns of Shandaken, Denning and Olive in Ulster County.

The Linville Gorge Wilderness is the third largest wilderness area in North Carolina and one of only two wilderness gorges in the Southern United States. Maintained by the United States Forest Service, it comprises 11,786 acres (47.70 km2) around the Linville River, and is situated inside the Pisgah National Forest. The river is approximately 1,400 feet (430 m) below the ridge, thus hiking in and out of the Gorge is challenging and enjoyable for those who like serious hiking. The plant and animal community is extremely diverse, with a dense hardwood/pine forest and a wide variety of smaller trees and other plants as well as bear, fox, raccoon, trout, grouse, wild turkey, vultures, owls, hawks, copperheads, and timber rattlesnakes.

The Wild River is a 17.2-mile-long (27.7 km) river in the White Mountains of New Hampshire and Maine in the United States. It is a tributary of the Androscoggin River, which flows east and south to the Kennebec River near the Atlantic Ocean.

The Salmon River is a 33.5-mile (53.9 km) river in the Cascade Range in the U.S. state of Oregon that drains part of southwestern Mount Hood. The entire length of the river is a protected National Wild and Scenic River. Several portions are in protected wilderness. It is affluent to the Sandy River, a tributary of the Columbia River.

Ellicott Rock Wilderness is a wild area lying at and around the tripoint of Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina, spanning 8,274 acres. It is managed by the United States Forest Service and is part of the National Wilderness Preservation System.
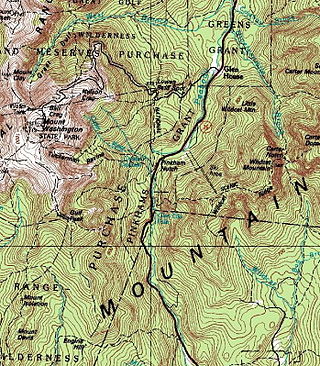
Pinkham Notch is a mountain pass in the White Mountains of north-central New Hampshire, United States. The notch is a result of extensive erosion by the Laurentide Ice Sheet during the Wisconsinian ice age. Pinkham Notch was eroded into a glacial U-shaped valley whose walls are formed by the Presidential, Wildcat, and Carter-Moriah ranges. Due to the volatility of the area's climate and rugged character of the terrain, a number of rare or endemic ecosystems have developed throughout the notch.
The Appalachian National Scenic Trail spans 14 U.S. states over its roughly 2,200 miles (3,500 km): Georgia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine. The southern end is at Springer Mountain, Georgia, and it follows the ridgeline of the Appalachian Mountains, crossing many of its highest peaks and running almost continuously through wilderness before reaching the northern end at Mount Katahdin, Maine.

Mount Willey is a mountain located in Grafton County, New Hampshire. The mountain is named after Samuel Willey, Jr. (1766–1826) and his family, who in 1825 moved into a house in Crawford Notch. The family was killed a year later in August 1826 during a landslide.

The Pemigewasset Wilderness is a 45,000-acre (182 km2) federally designated Wilderness Area in the heart of New Hampshire's White Mountains. It is a part of the White Mountain National Forest. It is New Hampshire's largest wilderness area.

The Domeland Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located 55 miles (89 km) northeast of Bakersfield, California USA. It encompasses 130,081 acres (526.42 km2), is jointly managed by the U.S. Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and is mostly within the Sequoia National Forest.
The South Sierra Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area in the Southern Sierra Nevada, in eastern California. It is located 65 miles (105 km) northeast of Bakersfield, and is southwest of Owens Lake and Olancha.

The Golden Trout Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area in the Sierra Nevada, in Tulare County and Inyo County, California. It is located 40 miles (64 km) east of Porterville within Inyo National Forest and Sequoia National Forest.

The Caribou Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area created by the Wilderness Act of 1964 and is part of the National Wilderness Preservation System. It is located 60 miles (97 km) east of Redding in the state of California, United States. The Caribou Wilderness comprises 20,546 acres (83.15 km2) and is adjacent to the east side of Lassen Volcanic National Park. Although the park is surrounded by Lassen National Forest, it is managed separately by the National Park Service, whereas the U.S. Forest Service manages the wilderness.
Ramsey's Draft Wilderness is a designated wilderness area in the North River Ranger District of the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of Virginia in the United States. The wilderness area was established in 1984 and comprises 6,518 acres (26.38 km2). It is administered by the US Forest Service.

















