
Fort McMurray is an urban service area in the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo in Alberta, Canada. It is located in northeast Alberta, in the middle of the Athabasca oil sands, surrounded by boreal forest. It has played a significant role in the development of the national petroleum industry. The 2016 Fort McMurray wildfire led to the evacuation of its residents and caused widespread damage.

Aerial firefighting, also known as waterbombing, is the use of aircraft and other aerial resources to combat wildfires. The types of aircraft used include fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters. Smokejumpers and rappellers are also classified as aerial firefighters, delivered to the fire by parachute from a variety of fixed-wing aircraft, or rappelling from helicopters. Chemicals used to fight fires may include water, water enhancers such as foams and gels, and specially formulated fire retardants such as Phos-Chek.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 63, commonly referred to as Highway 63, is a 434-kilometre (270 mi) highway in northern Alberta, Canada that connects the Athabasca oil sands and Fort McMurray to Edmonton via Highway 28. It begins as a two-lane road near the hamlet of Radway where it splits from Highway 28, running north through aspen parkland and farmland of north central Alberta. North of Boyle, it curves east to pass through the hamlet of Grassland and becomes divided west of Atmore where it again turns north, this time through heavy boreal forest and muskeg, particularly beyond Wandering River. Traffic levels significantly increase as Highway 63 bends through Fort McMurray, crossing the Athabasca River before connecting the city to the Syncrude and Suncor Energy plants further north. It ends approximately 16 km (10 mi) beyond a second crossing of the Athabasca River northeast of Fort McKay.

The cumulonimbus flammagenitus cloud (CbFg), also known as the pyrocumulonimbus cloud, is a type of cumulonimbus cloud that forms above a source of heat, such as a wildfire or volcanic eruption, and may sometimes even extinguish the fire that formed it. It is the most extreme manifestation of a flammagenitus cloud. According to the American Meteorological Society’s Glossary of Meteorology, a flammagenitus is "a cumulus cloud formed by a rising thermal from a fire, or enhanced by buoyant plume emissions from an industrial combustion process."

Bushfires in Australia are a widespread and regular occurrence that have contributed significantly to shaping the nature of the continent over millions of years. Eastern Australia is one of the most fire-prone regions of the world, and its predominant eucalyptus forests have evolved to thrive on the phenomenon of bushfire. However, the fires can cause significant property damage and loss of both human and animal life. Bushfires have killed approximately 800 people in Australia since 1851, and billions of animals.

On May 1, 2016, a wildfire began southwest of Fort McMurray, Alberta, Canada. On May 3, it swept through the community, forcing the largest wildfire evacuation in Alberta's history, with upwards of 88,000 people forced from their homes. Firefighters were assisted by personnel from both the Canadian Armed Forces and Royal Canadian Mounted Police, as well as other Canadian provincial agencies, to fight the wildfire. Aid for evacuees was provided by various governments and via donations through the Canadian Red Cross and other local and national charitable organizations.

The 2016 Uttarakhand forest fires were a series of widespread, damaging wildfires that took place in Uttarakhand, India between April and May. The fires were caused by a heatwave that spread across Uttarakhand and were the worst recorded in the region with a reported 4,538 hectares of forest burnt down and seven people dead.

In 2016, a total of 7,349 fires had burned an area 669,534 acres (2,709.51 km2) in California, according to the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection.

The 2017 wildfire season involved wildfires on multiple continents. On Greenland, which is mostly covered by ice and permafrost, multiple fires occurred in melted peat bogs, described as "unusual, and possibly unprecedented". Popular media asked whether the wildfires were related to global warming. Research published by NASA states "climate change has increased fire risk in many regions", but caused "greater severity in the colder latitudes" where boreal and temperate forests exist, and scholars have described "a warm weather fluctuation that has become more frequent in recent decades" related to wildfires, without naming any particular event as being directly caused by global warming.
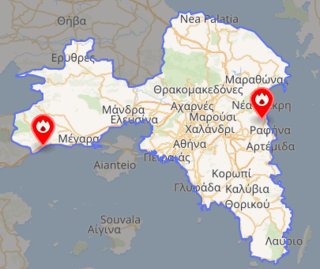
A series of wildfires in Greece, during the 2018 European heat wave, began in the coastal areas of Attica in July 2018. 104 people were confirmed dead from the Mati fires. The fires were the second-deadliest wildfire event in the 21st century, after the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires in Australia that killed 173.

The 2019 Alberta wildfires have been described by NASA as part of an extreme fire season in the province. In 2019 there were a total of 803,393.32 hectares, which is over 3.5 times more land area burned than in the five-year average burned. The five year average is 747 fires destroying 146,360.08 hectares. There were 644 wildfires recorded in Alberta. By May 31, 10,000 people had been evacuated, 16 homes, and the Steen River CN railway bridge, had been destroyed.

The 2019–20 Australian bushfire season or Black Summer was a period of bushfires in many parts of Australia, which, due to its unusual intensity, size, duration, and uncontrollable dimension, was considered a megafire. Exceptionally dry conditions, a lack of soil moisture, and early fires in Central Queensland led to an early start to the bushfire season, beginning in June 2019. Hundreds of fires burnt, mainly in the southeast of the country, until May 2020. The most severe fires peaked from December 2019 to January 2020.
The 2020 wildfire season involves wildfires on multiple continents.

A megafire is an exceptional fire that devastates a large area. They are characterised by their intensity, size, duration and uncontrollable scale. There is no precise scientific definition.
The Royal Commission into National Natural Disaster Arrangements, also referred to as the Bushfires Royal Commission, was a royal commission established in 2020 by the Australian government to inquire into and report upon natural disaster management coordination as it related to the 2019–20 Australian bushfire season. The Commission was charged with the responsibility of examining the coordination, preparedness for, response to and recovery from disasters, as well as improving resilience and adapting to changing climatic conditions and mitigating the impact of natural disasters.
The 2021 wildfire season involves wildfires on multiple continents. Even at halfway through the calendar year, wildfire seasons were larger than in previous history, with increased extreme weather caused by climate change strengthening the intensity and scale of fires.















