The Annals of Mathematics is a mathematical journal published every two months by Princeton University and the Institute for Advanced Study.

Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier was the seventh prime minister of Canada, in office from 11 July 1896 to 6 October 1911.

Witness for the Prosecution is a 1957 American film depicting an English courtroom drama with film noir elements. It was co-adapted and directed by Billy Wilder and starred Tyrone Power, Marlene Dietrich, and Charles Laughton, with Elsa Lanchester in a supporting role. Set in the Old Bailey in London, the picture is based on the play of the same name by Agatha Christie and deals with the trial of a man accused of murder. This was the first film adaptation of Christie's story, and was adapted for the screen by Larry Marcus, Harry Kurnitz and Wilder.

Wilfrid was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Gaul, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and became the abbot of a newly founded monastery at Ripon. In 664 Wilfrid acted as spokesman for the Roman position at the Synod of Whitby, and became famous for his speech advocating that the Roman method for calculating the date of Easter should be adopted. His success prompted the king's son, Alhfrith, to appoint him Bishop of Northumbria. Wilfrid chose to be consecrated in Gaul because of the lack of what he considered to be validly consecrated bishops in England at that time. During Wilfrid's absence Alhfrith seems to have led an unsuccessful revolt against his father, Oswiu, leaving a question mark over Wilfrid's appointment as bishop. Before Wilfrid's return Oswiu had appointed Ceadda in his place, resulting in Wilfrid's retirement to Ripon for a few years following his arrival back in Northumbria.

David Harold Bailey is a mathematician and computer scientist. He received his B.S. in mathematics from Brigham Young University in 1972 and his Ph.D. in mathematics from Stanford University in 1976. He worked for 14 years as a computer scientist at NASA Ames Research Center, and then from 1998 to 2013 as a Senior Scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. He is now retired from the Berkeley Lab, but continues as a Research Associate at the University of California, Davis, Department of Computer Science.
Experimental mathematics is an approach to mathematics in which computation is used to investigate mathematical objects and identify properties and patterns. It has been defined as "that branch of mathematics that concerns itself ultimately with the codification and transmission of insights within the mathematical community through the use of experimental exploration of conjectures and more informal beliefs and a careful analysis of the data acquired in this pursuit."

A motte-and-bailey castle is a fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised earthwork called a motte, accompanied by an enclosed courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to build with unskilled, often forced, labour, but still militarily formidable, these castles were built across northern Europe from the 10th century onwards, spreading from Normandy and Anjou in France, into the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century. The Normans introduced the design into England and Wales following their invasion in 1066. Motte-and-bailey castles were adopted in Scotland, Ireland, the Low Countries and Denmark in the 12th and 13th centuries. By the end of the 13th century, the design was largely superseded by alternative forms of fortification, but the earthworks remain a prominent feature in many countries.
Peter Benjamin Borwein is a Canadian mathematician and a professor at Simon Fraser University. He is known as a co-author of the paper which presented the Bailey–Borwein–Plouffe algorithm for computing π.

Wilfrid Augustine Hodges, FBA is a British mathematician, known for his work in model theory.

Melling-with-Wrayton is a civil parish in the City of Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. It includes the village of Melling and the hamlet of Wrayton, to the northeast. The parish had a population of 290 recorded in the 2001 census, increasing slightly to 299 at the 2011 census.
Berhtwald was the ninth Archbishop of Canterbury in England. Documentary evidence names Berhtwald as abbot at Reculver before his election as archbishop. Berhtwald begins the first continuous series of native-born Archbishops of Canterbury, although there had been previous Anglo-Saxon archbishops, they had not succeeded each other until Berhtwald's reign.
Norman Leslie Robert Franks is an English militaria writer who specialises in aviation topics. He focuses on the pilots and squadrons of World Wars I and II.

Curiosities Volume I is an album by English musician Brian Eno, released in 2003 by record label Opal Ltd. It is the first in a series of albums compiling Eno's previously unreleased recordings.

St Wilfrid's Church is in Church Lane, Grappenhall, a village in Warrington, Cheshire, England. It is designated by Historic England as a Grade I listed building. It is an active Anglican parish church in the diocese of Chester, the archdeaconry of Chester and the deanery of Great Budworth.

St Wilfrid's Church is in Main Street, Melling, Lancashire, England. It is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building, and is an active Anglican church in the united benefice of East Lonsdale, the deanery of Tunstall, the archdeaconry of Lancaster and the diocese of Blackburn. Its benefice is combined with those of St Peter, Leck, St John the Baptist, Tunstall, St James the Less, Tatham, the Good Shepherd, Lowgill, and Holy Trinity, Wray.
In mathematics, a Bailey pair is a pair of sequences satisfying certain relations, and a Bailey chain is a sequence of Bailey pairs. Bailey pairs were introduced by W. N. Bailey while studying the second proof Rogers (1917) of the Rogers–Ramanujan identities, and Bailey chains were introduced by Andrews (1984).
St Wilfrid's RC College is a mixed Roman Catholic secondary school and sixth form located in South Shields, Tyne and Wear, England.
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 37, commonly abbreviated to Jasta 37, was a "hunting group" of the Luftstreitkräfte, the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. The unit would score over 70 aerial victories during the war, including 13 observation balloons downed. The squadron's victories came at the expense of seven killed in action, two killed in flying accidents, three wounded in action, and three taken prisoner of war.
Secondary Highway 504, commonly referred to as Highway 504, was a provincially maintained secondary highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The highway was 26.1 kilometres (16.2 mi) long, connecting Highway 28 south of Apsley with Highway 620 in Glen Alda. The only other community served by Highway 504 was Lasswade.
Lucy Joan Slater was a mathematician who worked on hypergeometric functions, and who found many generalizations of the Rogers–Ramanujan identities. Her advisor was Wilfrid Norman Bailey. In the early 1950s she played a leading role at Cambridge University in devising a precursor of modern computer operating systems, and subsequently she helped to develop computer programs for econometrics, working for much of the time with UK government officials.

In computing, a Digital Object Identifier or DOI is a persistent identifier or handle used to identify objects uniquely, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). An implementation of the Handle System, DOIs are in wide use mainly to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports and data sets, and official publications though they also have been used to identify other types of information resources, such as commercial videos.
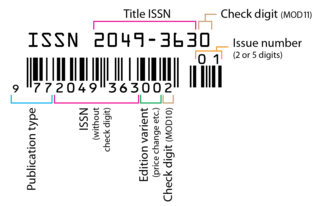
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication, such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSN are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature.













