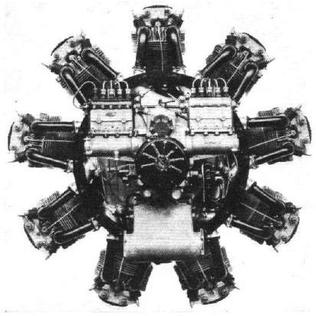
The Phoenix was an experimental version of the Bristol Aeroplane Company's Pegasus engine, adapted to run on the Diesel cycle. Only a few were built between 1928 and 1932, although samples fitted to a Westland Wapiti held the altitude record for diesel-powered aircraft at 27,453 ft from 11 May 1934 until World War II. The primary advantage of the Phoenix was better fuel efficiency at cruise, by up to 35%.

The Bristol Perseus was a British nine-cylinder, single-row, air-cooled radial aircraft engine produced by the Bristol Engine Company starting in 1932. It was the first production sleeve valve aero engine.

The Aquila was a nine-cylinder single-row radial aircraft engine designed by the Bristol Engine Company starting in 1934. A sleeve valve engine, its basic design was developed from the Bristol Perseus. The Aquila was never used in production, but further developments led to the Bristol Hercules, Bristol Taurus, and Bristol Centaurus.

The Armstrong Siddeley Leopard was a British 14-cylinder twin-row air-cooled radial aero engine developed in 1927 by Armstrong Siddeley. It was the most powerful radial engine in the world when introduced.

The Armstrong Siddeley Panther was a 27-litre 14-cylinder twin-row air-cooled radial aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley. It was originally named the Jaguar Major.

The Armstrong Siddeley Lynx is a British seven-cylinder aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley. Testing began in 1920 and 6,000 had been produced by 1939. In Italy Alfa Romeo built a 200 horsepower (150 kW) licensed version of this engine named the Alfa Romeo Lynx.

The Armstrong Siddeley Mongoose is a British five-cylinder radial aero engine produced by Armstrong Siddeley. Developed in the mid-1920s it was used in the Hawker Tomtit trainer and Parnall Peto seaplane amongst others. With a displacement of 540 cubic inches (9 litres) the Mongoose had a maximum power output of 155 horsepower (115 kilowatts).
The Bristol Draco was an air-cooled nine-cylinder radial engine from the British manufacturer Bristol Aeroplane Company. It was essentially a version of their famous Pegasus converted to use a fuel injection system.

The Armstrong Siddeley Serval was a British ten-cylinder aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley in the late 1920s. Following company tradition, the engine was named for the serval.

The Gnome et Rhône 18L was a French-designed twin-row 18-cylinder air-cooled radial engine. The 18L was a large step up in terms of displacement, power and number of cylinders. The majority of Gnome-Rhone engines were either 7, 9 or 14 cylinders. The engine proved not to be a success, and it was dropped in 1939 due to a poor power-to-weight ratio.

The ABC Wasp was an experimental 170 hp (127 kW) seven-cylinder radial engine designed by the noted British engineer Granville Bradshaw, and primarily built by ABC Motors Limited. An order for twelve experimental ABC Wasp engines was placed with Guy Motors on 19 April 1918. Eight ABC Wasp engines were made by Crossley Motors Ltd of Manchester, England.

The Blackburne Thrush was a 1,500 cc three-cylinder radial aero-engine for light aircraft produced by Burney and Blackburne Limited. Burney and Blackburne were based at Bookham, Surrey, England and was a former motorcycle manufacturer.

The Armstrong Siddeley Ounce was a small two-cylinder aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley in 1920. The engine was originally conceived as a test piece but ran very well and was put into production for early ultralight aircraft and use in target drones. The Ounce used two cylinders from the preceding Jaguar I radial engine.

The Alvis Pelides was an unflown British air-cooled radial aero engine first developed in 1936. The Pelides Major was a projected but unbuilt development as were the Alcides, Alcides Major and the Maeonides Major, the Alvis aircraft engine range taking their names from Greek mythology.

The Bristol Neptune was a seven-cylinder air-cooled radial engine developed in 1930. It had the same size cylinders as the earlier Mercury and Titan engines, 5.75 in (146 mm) x 6.5 in (165 mm) which gave a displacement of 1,182 cu in and produced a maximum of 320 horsepower (239 kW). The Neptune was effectively a seven-cylinder version of the Titan.
The ABC Mosquito was a 120 hp (90 kW) six-cylinder radial aero engine designed by the noted British engineer Granville Bradshaw for use in light aircraft. The single Mosquito engine was built by ABC Motors, first running in 1916. It is thought that the design resulted from a bet between Harry Hawker and Bradshaw, Hawker proposing that Bradshaw could not build and fly a six-cylinder radial engine. The Mosquito used copper-plated steel Gnat cylinders. The engine was not a success.

The Wolseley 60 hp or Type C was a British liquid-cooled V-8 aero engine that first ran in 1910, it was designed and built by Wolseley Motors. The engine featured water-cooled exhaust ports and employed a 20 lb (9 kg) flywheel. During an official four-hour test the engine produced an average of 55 horsepower. A larger capacity variant known as the 80 hp or Type B used an internal camshaft and propeller reduction gear.

The Wolseley Aries III or A.R.9 was a British nine-cylinder, air-cooled radial aero engine that first ran in 1933, it was designed and built by Wolseley Motors. Intended for the military trainer aircraft market few were produced as Wolseley withdrew from the aero engine market in 1936.

The Walter Scolar was a Czechoslovakian nine-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that first ran in 1936. With a displacement of 8 litres, it produced 132 kW at 2,500 rpm.

The Walter Bora was a Czechoslovakian nine-cylinder, air-cooled radial engine for powering light aircraft that was developed in the 1930s by Walter Aircraft Engines.














