Related Research Articles

The Boeing 767 is an American wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. The aircraft was launched as the 7X7 program on July 14, 1978, the prototype first flew on September 26, 1981, and it was certified on July 30, 1982. The initial 767-200 variant entered service on September 8, 1982, with United Airlines, and the extended-range 767-200ER in 1984. It was stretched into the 767-300 in October 1986, followed by the extended-range 767-300ER in 1988, the most popular variant. The 767-300F, a production freighter version, debuted in October 1995. It was stretched again into the 767-400ER from September 2000.

The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a 5,710-foot (1,740-meter) peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles.

An airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system is an airborne radar early warning system designed to detect aircraft, ships, vehicles, missiles and other incoming projectiles at long ranges, as well as performing command and control of the battlespace in aerial engagements by informing and directing friendly fighter and attack aircraft. AEW&C units are also used to carry out aerial surveillance over ground and maritime targets, and frequently perform battle management command and control (BMC2). When used at altitude, the radar system on AEW&C aircraft allows the operators to detect, track and prioritize targets and identify friendly aircraft from hostile ones in real-time and from much farther away than ground-based radars. Like ground-based radars, AEW&C systems can be detected and targeted by opposing forces, but due to aircraft mobility and extended sensor range, they are much less vulnerable to counter-attacks than ground systems.
Kalitta Air is an American cargo airline headquartered at Willow Run Airport, Ypsilanti Township, Michigan. The company operates international scheduled and cargo charter services. Its call sign "Connie" is from its founder, Connie Kalitta.

Mahan-class destroyers of the United States Navy were a series of 18 destroyers of which the first 16 were laid down in 1934. The last two of the 18, Dunlap and Fanning, are sometimes considered a separate ship class. All 18 were commissioned in 1936 and 1937. Mahan was the lead ship, named for Rear Admiral Alfred Thayer Mahan, an influential historian and theorist on sea power.

Prometheus or X-303 and later BC-303 is a fictional starship that appears in the military science fiction television series Stargate SG-1. The ship was first introduced during the shows sixth season in the episode titled "Prometheus", and would go on to become a recurring setting over the remainder of the series as well as being depicted in various spin-off media.
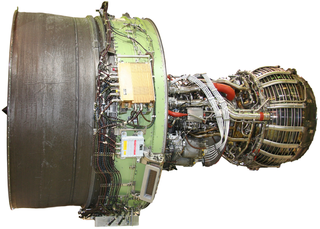
The General Electric GEnx is an advanced dual rotor, axial flow, high-bypass turbofan jet engine in production by GE Aerospace for the Boeing 747-8 and 787. The GEnx succeeded the CF6 in GE's product line.

Boeing Defense, Space & Security (BDS) is a division of The Boeing Company based in Arlington, Virginia, near Washington, D.C. The division builds military airplanes, rotorcraft, and missiles, as well as space systems for both commercial and military customers, including satellites, spacecraft, and rockets.

Birr Castle is a large castle in the town of Birr in County Offaly, Ireland. It is the home of the 7th Earl of Rosse and his family, and as the castle is generally not open to the public, though the grounds and gardens of the demesne are publicly accessible, and include a science museum and a café, a reflecting telescope which was the largest in the world for decades and a modern radio telescope.

Manhattan Regional Airport in Riley County, Kansas, United States, is the second-busiest commercial airport in Kansas. Owned by the city of Manhattan, Kansas, the airport is located about five miles southwest of downtown Manhattan. American Airlines serves the airport with five daily flights to Chicago O'Hare International Airport and Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport.The airport also accommodates general aviation and charter planes for the military and college sports teams, being conveniently located four miles east of Fort Riley and eight miles southwest of Kansas State University's athletic complex).
"A Flight to Remember" is the tenth episode in the first season of the American animated television series Futurama. It originally aired on the Fox network in the United States on September 26, 1999. The title is a reference to Walter Lord's non-fiction book about the Titanic disaster A Night to Remember. This episode was written by Eric Horsted and directed by Peter Avanzino. Dawnn Lewis guest-stars in this episode as LaBarbara Conrad. The episode is a direct parody of the 1997 film Titanic.

A solar telescope or a solar observatory is a special-purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph.

The Algonquin Radio Observatory (ARO) is a radio observatory located in Algonquin Provincial Park in Ontario, Canada. It opened in 1959 in order to host a number of the National Research Council of Canada's (NRC) ongoing experiments in a more radio-quiet location than Ottawa.

A heavy hauler is a very large transporter for moving oversize loads too large for road travel without an escort and special permit.

Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP) is a German research institute. It is the successor of the Berlin Observatory founded in 1700 and of the Astrophysical Observatory Potsdam (AOP) founded in 1874. The latter was the world's first observatory to emphasize explicitly the research area of astrophysics. The AIP was founded in 1992, in a re-structuring following the German reunification.

America's Toughest Jobs is a reality television show that lasted one season and aired on NBC. It pitted contestants against each other as they attempted a series of difficult and dangerous jobs. The prize was the sum of the salaries that would be earned by people doing these jobs in their first year.

The Chinese Deep Space Network (CDSN) is a network of large antennas and communication facilities that are used for radio astronomy, radar observations, and spacecraft missions of China. The CDSN is managed by the China Satellite Launch and Tracking Control Center General (CLTC) of the People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force Space Systems Department.

The first season of the American science-fiction television series Star Trek, originally created by Gene Roddenberry, premiered on NBC on September 8, 1966, and concluded on April 13, 1967. The season debuted in Canada on CTV two days before the US premiere, on September 6, 1966. It consisted of 29 episodes, which is the highest number of episodes in a season for the original series of Star Trek. It features William Shatner as Captain James T. Kirk, Leonard Nimoy as Spock, and DeForest Kelley as Leonard McCoy.
Horizons-1, also known as Galaxy 13, is a geostationary communications satellite operated by Intelsat and SKY Perfect JSAT (JSAT) which was designed and manufactured by Boeing on the BSS-601 platform. It has Ku-band and C-band payload and was used to replace Galaxy 9 at the 127.0° West longitude. It covers North America, Puerto Rico, Alaska, Hawaii and Mexico.
Building Giants is a British television series covering the design and construction of large structures, including stadiums, tunnels, bridges, cruise ships, and other giant engineering feats that premiered in early 2018.
References
- ↑ "World's Toughest Fixes on NGC". TheFutonCritic. Retrieved 2010-08-24.