
Geldanamycin is a 1,4-benzoquinone ansamycin antitumor antibiotic that inhibits the function of Hsp90 by binding to the unusual ADP/ATP-binding pocket of the protein. HSP90 client proteins play important roles in the regulation of the cell cycle, cell growth, cell survival, apoptosis, angiogenesis and oncogenesis.

Hitachimycin, also known as stubomycin, is a cyclic polypeptide produced by Streptomyces that acts as an antibiotic. It exhibits cytotoxic activity against mammalian cells, Gram-positive bacteria, yeast, and fungi, as well as hemolytic activity; this is mediated by changes at the cell membrane and subsequent lysis. Owing to its cytotoxic activity against mammalian cells and tumors, it was first proposed as an antitumor antibiotic.

The calicheamicins are a class of enediyne antitumor antibiotics derived from the bacterium Micromonospora echinospora, with calicheamicin γ1 being the most notable. It was isolated originally in the mid-1980s from the chalky soil, or "caliche pits", located in Kerrville, Texas. The sample was collected by a scientist working for Lederle Labs. It is extremely toxic to all cells and, in 2000, a CD33 antigen-targeted immunoconjugate N-acetyl dimethyl hydrazide calicheamicin was developed and marketed as targeted therapy against the non-solid tumor cancer acute myeloid leukemia (AML). A second calicheamicin-linked monoclonal antibody, inotuzumab ozogamicin, an anti-CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 17, 2017, for use in the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Calicheamicin γ1 and the related enediyne esperamicin are two of the most potent antitumor agents known.

Rhizoxin is an antimitotic agent with anti-tumor activity. It is isolated from the fungus Rhizopus microsporus which causes rice seedling blight.

Rebeccamycin (NSC 655649) is a weak topoisomerase I inhibitor isolated from Nocardia bacteria. It is structurally similar to staurosporine, but does not show any inhibitory activity against protein kinases. It shows significant antitumor properties in vitro (IC50=480nM against mouse B16 melanoma cells and IC50=500nM against P388 leukemia cells). It is an antineoplastic antibiotic and an intercalating agent.

Ascofuranone is an antibiotic produced by various ascomycete fungi including Acremonium sclerotigenum that inhibits the Trypanosoma brucei alternative oxidase and is a lead compound in efforts to produce other drugs targeting this enzyme for the treatment of sleeping sickness. The compound is effective both in vitro cell culture and in infections in mice.

Macbecins are a pair of chemical compounds in the ansamycin family of antibiotics. They are designated macbecin I and macbecin II and they were first isolated from actinomycete bacteria. Macbecin possesses antitumor properties. In vitro studies have shown that macbecins are effective in the eradication of Gram-positive bacteria, fungi, and protozoa including Tetrahymena pyriformis.

The esperamicins are chromoprotein enediyne antitumor antibiotics of bacterial origin. Esperamicin A1 is the most well studied compound in this class. Esperamcin A1 and the related enediyne calicheamicin are the two most potent antitumor agents known. The esperamicins are extremely toxic DNA splicing compounds.

Enediynes are organic compounds containing two triple bonds and one double bond.

Romidepsin, sold under the brand name Istodax, is an anticancer agent used in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) and other peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs). Romidepsin is a natural product obtained from the bacterium Chromobacterium violaceum, and works by blocking enzymes known as histone deacetylases, thus inducing apoptosis. It is sometimes referred to as depsipeptide, after the class of molecules to which it belongs. Romidepsin is branded and owned by Gloucester Pharmaceuticals, a part of Celgene.

Kinamycins are a group of bacterial polyketide secondary metabolites containing a diazo group. Kinamycins are known for their cytotoxicity and are considered of interest for potential use in anti-cancer therapies.
Bohemic acid is a mixture of chemical compounds which is obtained through fermentation by actinobacteria species in the genus Actinosporangium (Actinoplanaceae). The name honors the Puccini opera La Bohème and many individual components of the acid carry the names of characters from La Bohème. Most of those components are antitumor agents and anthracycline antibiotics active against Gram-positive bacteria.
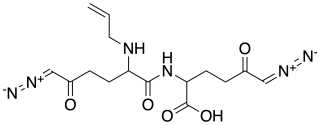
Alazopeptin is an antibiotic, with moderate anti-trypanosomal and antitumor activity. It was originally isolated from Streptacidiphilus griseoplanus, sourced from soil near Williamsburg, Iowa. It is also isolated from Kitasatospora azatica It is still largely produced via fermentation broths of that organism. Structurally, alazopeptin is a tripeptide and contains 2 molecules of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine and one molecule of L-alanine. In 2021 the biosynthetic pathway of alazopeptin was elucidated.

Streptonigrin is an aminoquinone antitumor and antibacterial antibiotic produced by Streptomyces flocculus. Streptonigrin was a successful target of Total synthesis in 2011.

Macromomycin B is an antibiotic with anticancer activity.

Maduropeptin consists of a 1:1 complex of a carrier protein (MdpA) and a chromophore isolated from Actinomadura madurae. The chromophore has an enediyne structure and is an antibiotic with anticancer activity.
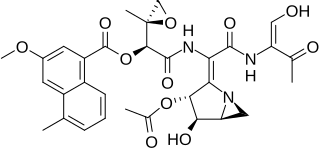
Azinomycin B is a natural product that contains densely assembled functionalities with potent antitumor activity. It is isolated from Streptomyces sahachiroi which is reisolated from S. griseofuscus along with its analog azinomycin A. Azinomycin B can bind within the major groove of DNA and forms covalent interstrand crosslinks (ISCs) with the purine bases. The DNA alkylation and crosslinking by azinomycin B suggests its potent antitumor activity.

Thiocoraline is a microbial natural product of the depsipeptide class. Thiocoraline was isolated from the mycelium cake of a marine actinomycete strain L-13-ACM2-092. In vitro, thiocoraline causes an arrest in G1 phase of the cell cycle and decreases the rate of S phase progression towards G2/M phase. Thiocoraline is likely to be a DNA replication inhibitor. Thiocoraline is produced on a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) assembly line.

C-1027 or lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks.
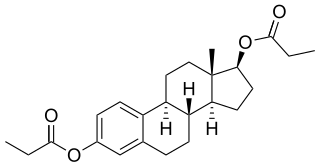
Estradiol dipropionate/hydroxyprogesterone caproate (EDP/OHPC), sold under the brand name EP Hormone Depot, is a combined estrogen–progestogen medication which is used in Japan. It is manufactured by Teikoku Zoki Pharmaceutical Co., Tokyo and contains 1 mg/mL estradiol dipropionate and 50 mg/mL hydroxyprogesterone caproate.



















